|
In this section: |
The Define and Compute functionality in InfoAssist, which is used to create virtual fields, supports the use of functions. These functions can be used to create expressions and calculations for use in your reports and charts.
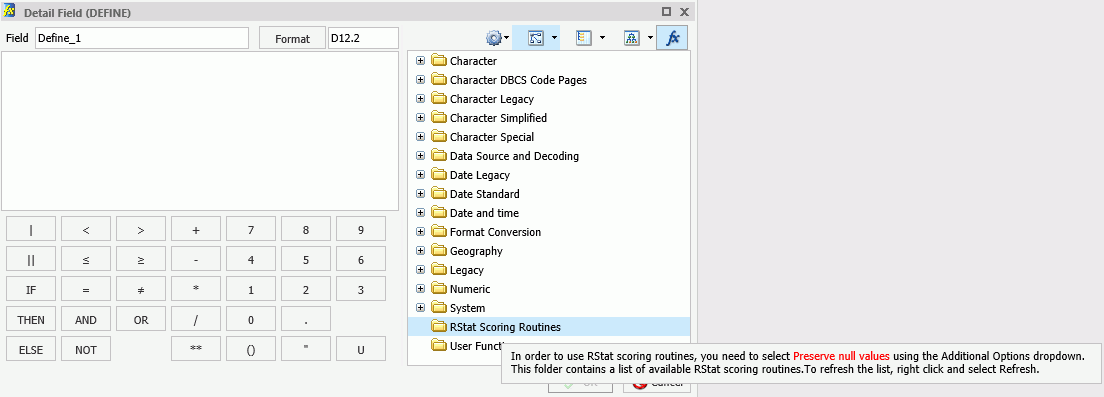
Predictive models or scoring routines, built with the separately licensed WebFOCUS RStat for Predictive Analytics, allow you to add predictive analytics to your reports and charts in InfoAssist. In order to access a scoring routine, an administrator or other designated individual must first deploy the scoring routine using TIBCO WebFOCUS® App Studio. Once the scoring routine is deployed, it will appear in the RStat Scoring Routines folder and can be used when creating a virtual field.
For more information on scoring routine deployment and creating scoring routines, see the TIBCO WebFOCUS® App Studio User’s Manual and the Using WebFOCUS RStat for Predictive Analytics manual.
To access functions in InfoAssist, open the Define or Compute dialog box and click the Functions button, as shown in the following image.
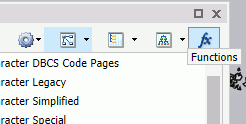
The list of available functions is displayed, including the RStat Scoring Routines folder. If one or more scoring routines have been deployed, the RStat Scoring Routines folder will have a plus sign (+) next to it, indicating that the scoring routines are available and ready for use.