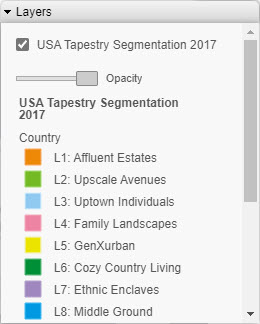
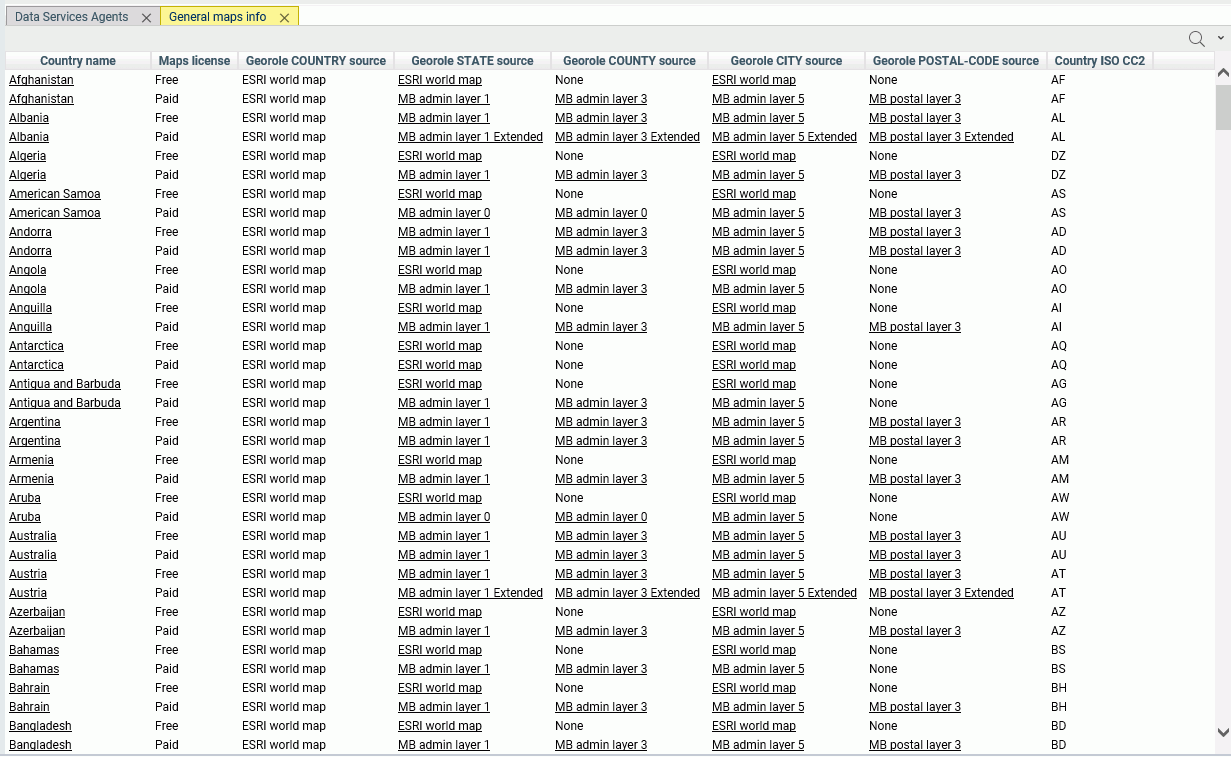
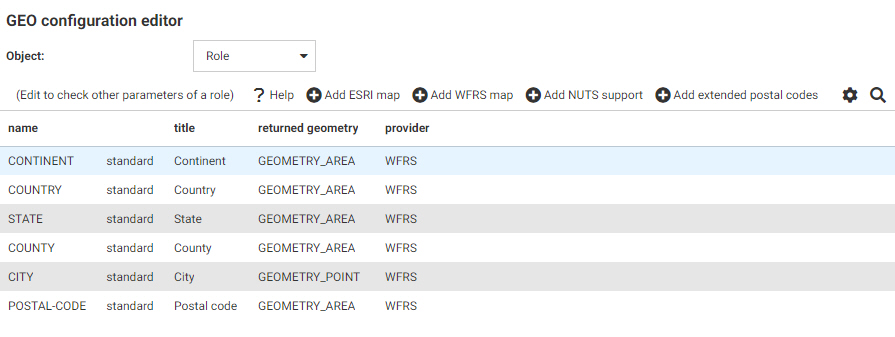
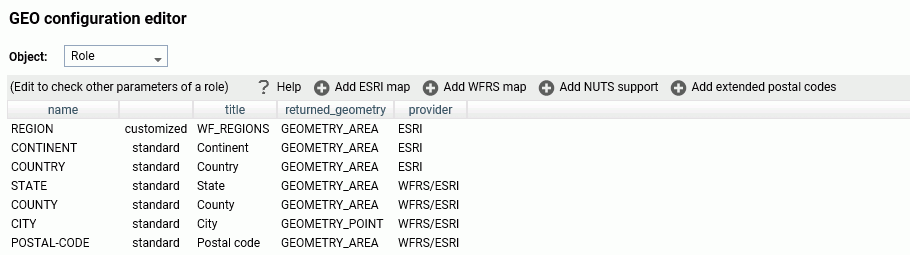
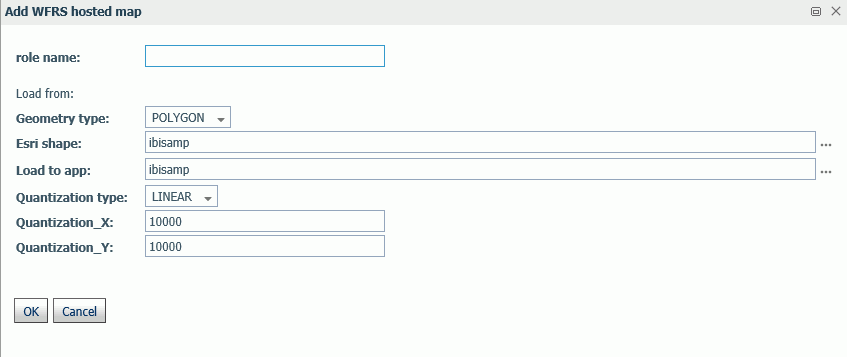
The WebFOCUS Server Console provides a list of first and second level map administrative regions. To open the list, select Server Workspaces from the Management Center on the Hub, click the Settings menu on the Workspace page ribbon, point
to
Geo
Services, and select
General maps info. This opens the list of
administrative regions and postal levels, as shown in the following image.
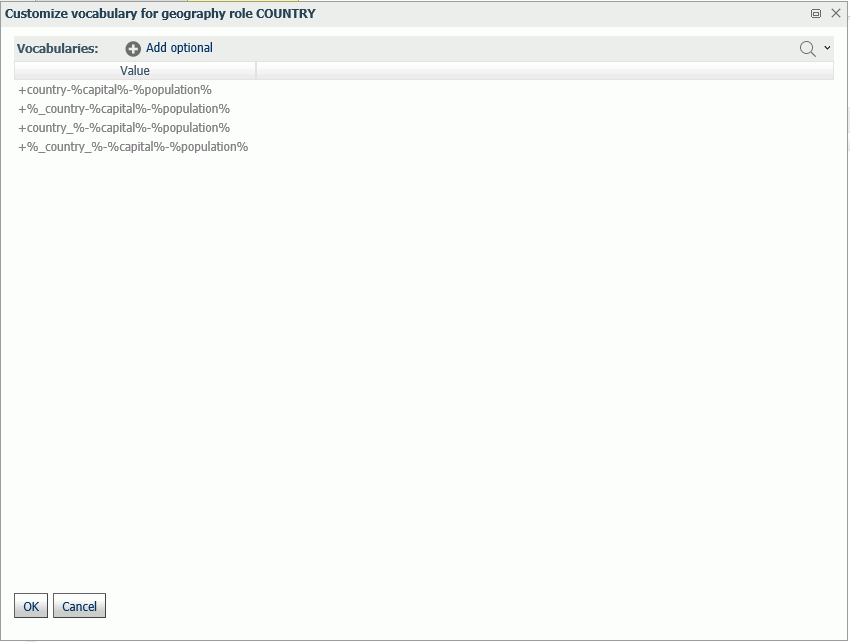
The regions that say
Paid in
the Maps license column are the additional regions you can access with a second
level license.
- The source for the
country administrative level is provided by the Esri World map. Country is
administrative level 0.
- The source for the State
georole can be provided by the Esri World map or by shape files. When there is
a second level license, the state administrative level can be level 1 or level
2.
- The source for the County
georole can be provided by the Esri World map or by shape files. When there is
a second level license, the county administrative level can be level 3 or level
4.
- The source for the City
georole can be provided by the Esri World map or by shape files. When there is
a second level license, the city administrative level is level 5.
- The source for the Postal
Code georole can be provided by the Esri World map or by shape files. When
there is a second level license, the postal code administrative level can be 3,
4, or 5.
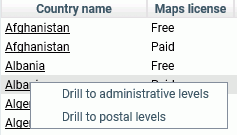
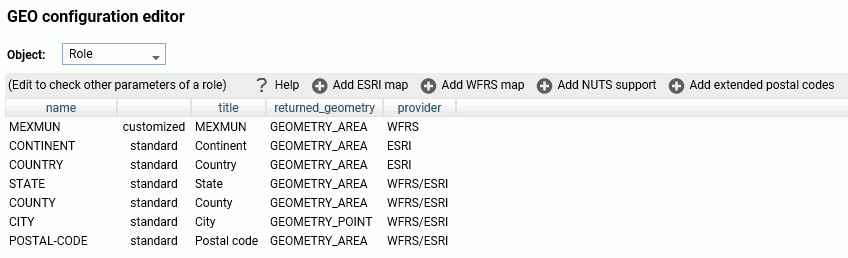
Some georoles may not be applicable to specific countries. You
can see the details of each country and its administrative levels by
right-clicking the country name and clicking
Drill to administrative levels or
Drill to postal levels, as shown in the following
image.
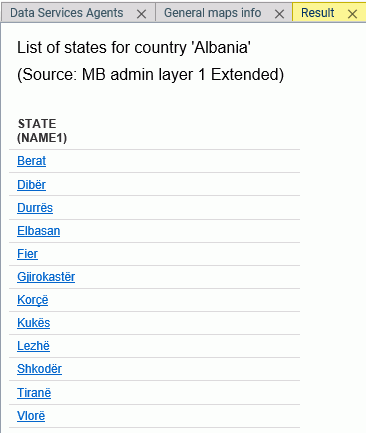
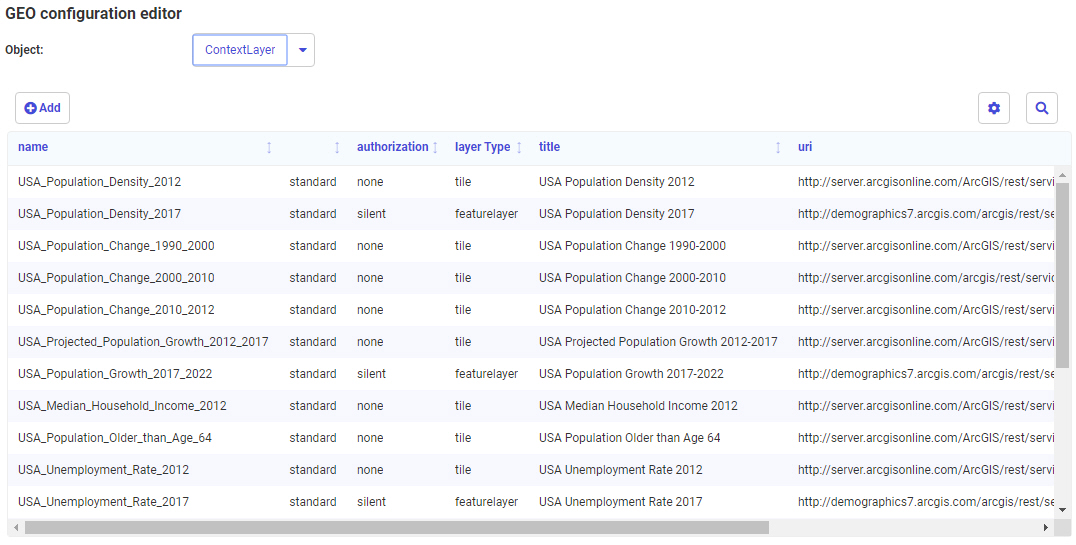
Clicking
Drill to administrative levels opens the list of
States for the country, as shown in the following image.
Clicking any
link opens information about the next level georole.
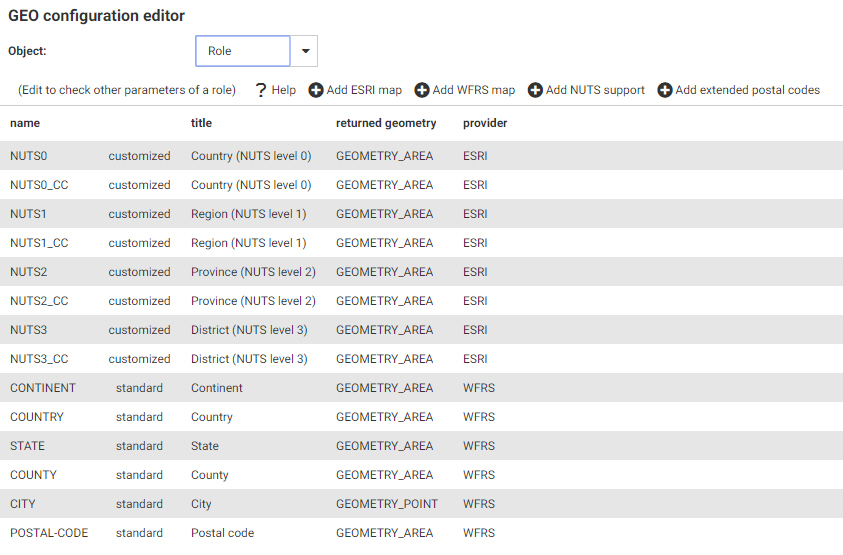
Clicking Drill to postal levels opens the list of postal levels
for the country, as shown in the following image.
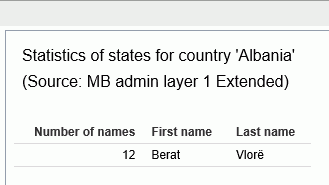
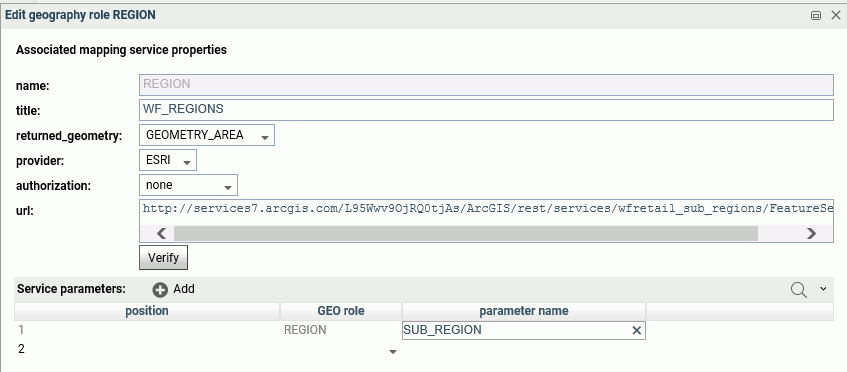
Right-clicking a link in any georole column other than the
Country column opens a summary of the values for that georole, as shown in the
following image.
Example: Using a
Second Level License to Map French Postal Codes
The request used in this example references data about French
state names, city names, and postal codes. This data is readily available
online. The data in this example was downloaded from
https://www.aggdata.com/free/france-postal-codes which is available for free
using a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license detailed at
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. Once you download the data,
you can upload it to the server to create the data file and synonym for use in
requests. This example assumes that the data and synonym are in the ibisamp
application on the server.
Note: Information
Builders takes no responsibility for the accuracy or continued existence of
this data on this site. It is being used only as an example of the detailed
administrative boundaries available with a second level license.
The Master File for the uploaded data follows. The Master File
generated by the upload procedure was edited to change the first field name to
COUNTRY and to remove the folder declarations.
FILENAME=FR_POSTAL_CODES, SUFFIX=DFIX ,
DATASET=ibisamp/fr_postal_codes.ftm (LRECL 1140 RECFM V, BV_NAMESPACE=OFF, $
SEGMENT=FR_POSTAL_CODES, SEGTYPE=S0, $
FIELDNAME=COUNTRY, ALIAS=E01, USAGE=A50V, ACTUAL=A50V,
TITLE='Country for State',
GEOGRAPHIC_ROLE=COUNTRY, $
FIELDNAME=STATE, ALIAS=E02, USAGE=A21V, ACTUAL=A21V,
MISSING=ON,
TITLE='State',
GEOGRAPHIC_ROLE=STATE, $
FIELDNAME=COUNTY, ALIAS=E03, USAGE=A25V, ACTUAL=A25V,
MISSING=ON,
TITLE='County',
GEOGRAPHIC_ROLE=COUNTY, $
FIELDNAME=CITY, ALIAS=E04, USAGE=A48V, ACTUAL=A48V,
MISSING=ON,
TITLE='City',
GEOGRAPHIC_ROLE=CITY, $
FIELDNAME=POSTAL_CODE, ALIAS=E05, USAGE=A16V, ACTUAL=A16V,
MISSING=ON,
TITLE='Postal Code',
GEOGRAPHIC_ROLE=POSTAL-CODE, $
FIELDNAME=PLACE_NAME, ALIAS=E06, USAGE=A56V, ACTUAL=A56V,
MISSING=ON,
TITLE='Place Name', $
FIELDNAME=GEO_POINT, ALIAS=E07, USAGE=A150, ACTUAL=A150,
TITLE='GIS Point',
GEOGRAPHIC_ROLE=GEOMETRY_POINT, $
The Access File for the uploaded data follows.
SEGNAME=FR_POSTAL_CODES,
DELIMITER=',',
CDN=COMMAS_DOT,
CONNECTION=<local>, $
The following
WebFOCUS Procedure generates a choropleth map that shows the postal codes from
the uploaded data source. The DEFINE field is used to assign different numeric
values to each field. When used in the Color bucket, this DEFINE field makes it
easier to differentiate the different postal code areas.
DEFINE FILE fr_postal_codes
FOURTH_CHAR/I1 ( TITLE = 'Fourth,Character' ) =
SUBSTRING(FR_POSTAL_CODES.FR_POSTAL_CODES.POSTAL_CODE, 4, 1);
END
SET COMPONENT=TableChart_1
SET ARVERSION=2
-DEFAULTH &WF_TITLE='WebFOCUS Report';
GRAPH FILE fr_postal_codes
SUM FOURTH_CHAR
BY FR_POSTAL_CODES.FR_POSTAL_CODES.POSTAL_CODE
ON GRAPH PCHOLD FORMAT JSCHART
ON GRAPH SET VZERO OFF
ON GRAPH SET GRWIDTH 1
ON GRAPH SET HAXIS 1008.0
ON GRAPH SET VAXIS 768.0
ON GRAPH SET LOOKGRAPH CHOROPLETH
ON GRAPH SET EMBEDHEADING ON
ON GRAPH SET AUTOFIT ON
ON GRAPH SET STYLE *
INCLUDE=IBFS:/WFC/Global/Themes/Standard/Default/theme.sty,$
TYPE=REPORT, TITLETEXT='Chart1', ORIENTATION=LANDSCAPE, ARREPORTSIZE=DIMENSION,
ARFILTER_TARGET='*', CHART-LOOK=com.esri.map, ARGRAPHENGINE=JSCHART, $
TYPE=DATA, COLUMN=N2, BUCKET=color, $
*GRAPH_SCRIPT
*GRAPH_JS_FINAL
"extensions": {
"com.esri.map": {
"overlayLayers": [
{
"ibiDataLayer": {
"map-metadata": {
"map_by_field": "FR_POSTAL_CODES.FR_POSTAL_CODES.POSTAL_CODE"
}
}
}
],
"baseMapInfo": {
"customBaseMaps": [
{
"ibiBaseLayer": "dark-gray"
}
]
}
}
}
*END
ENDSTYLE
END
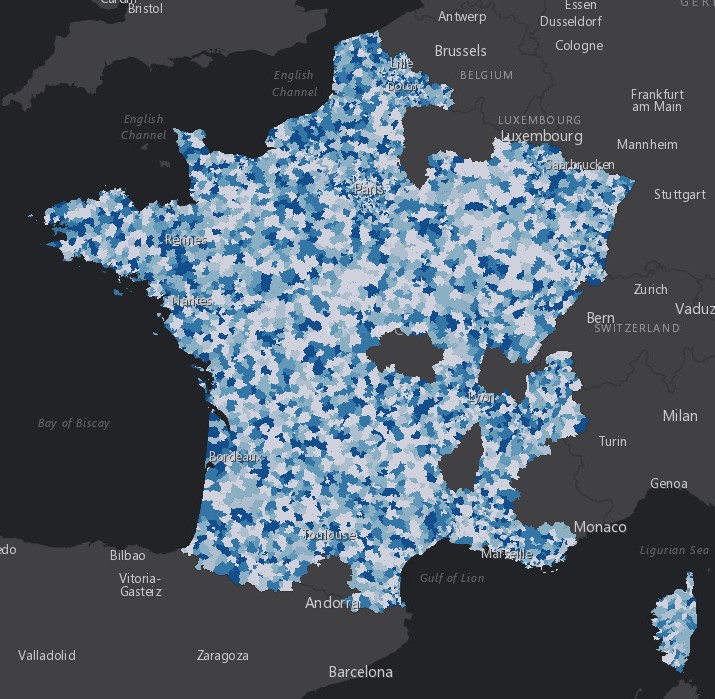
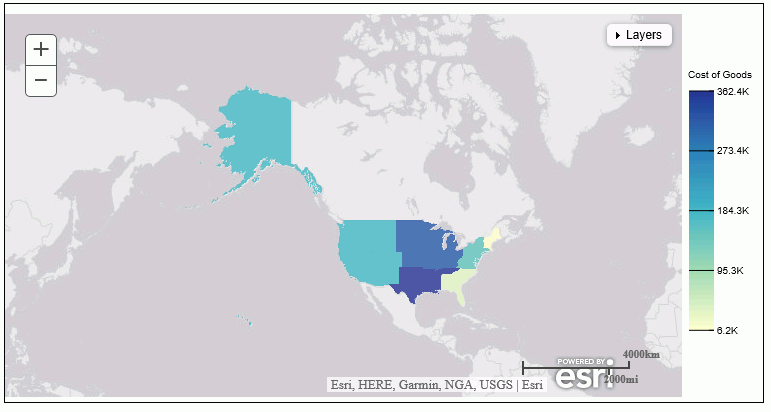
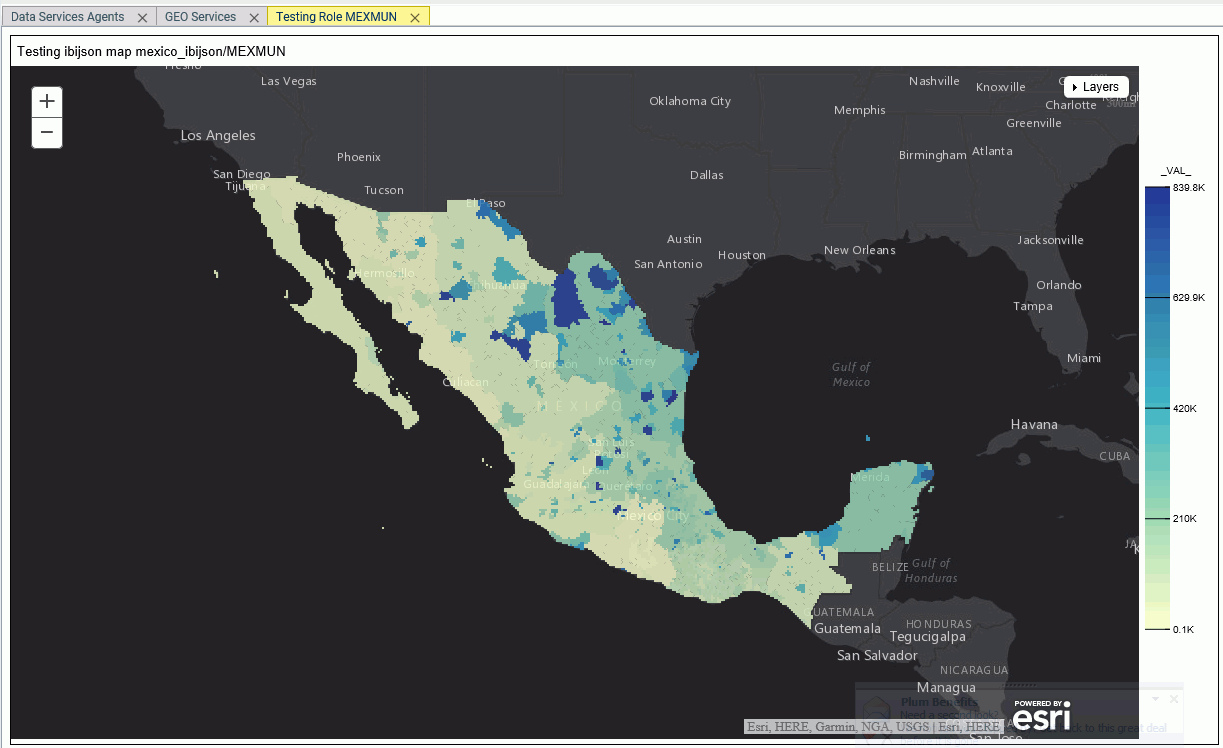
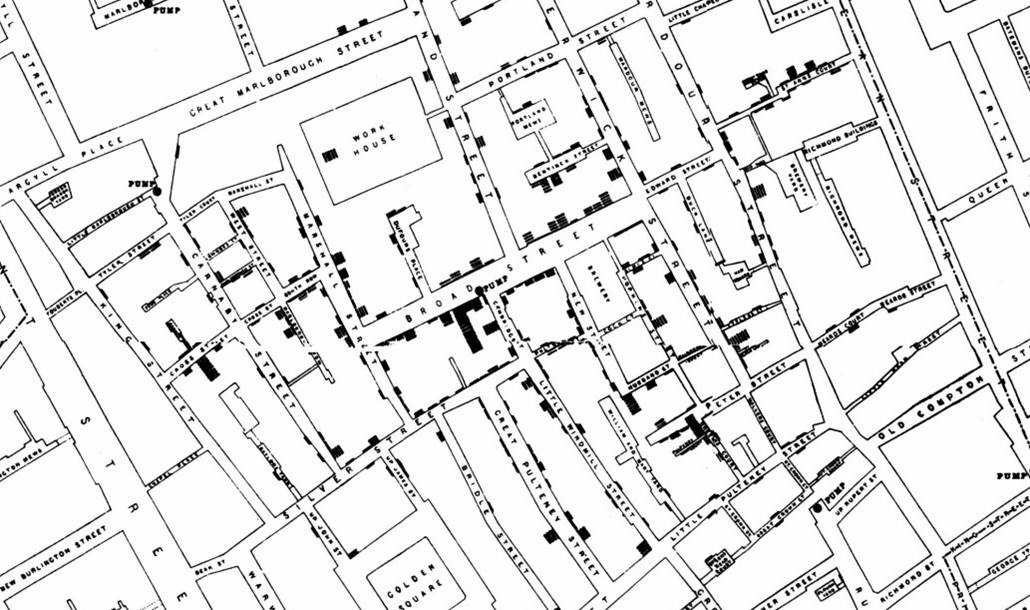
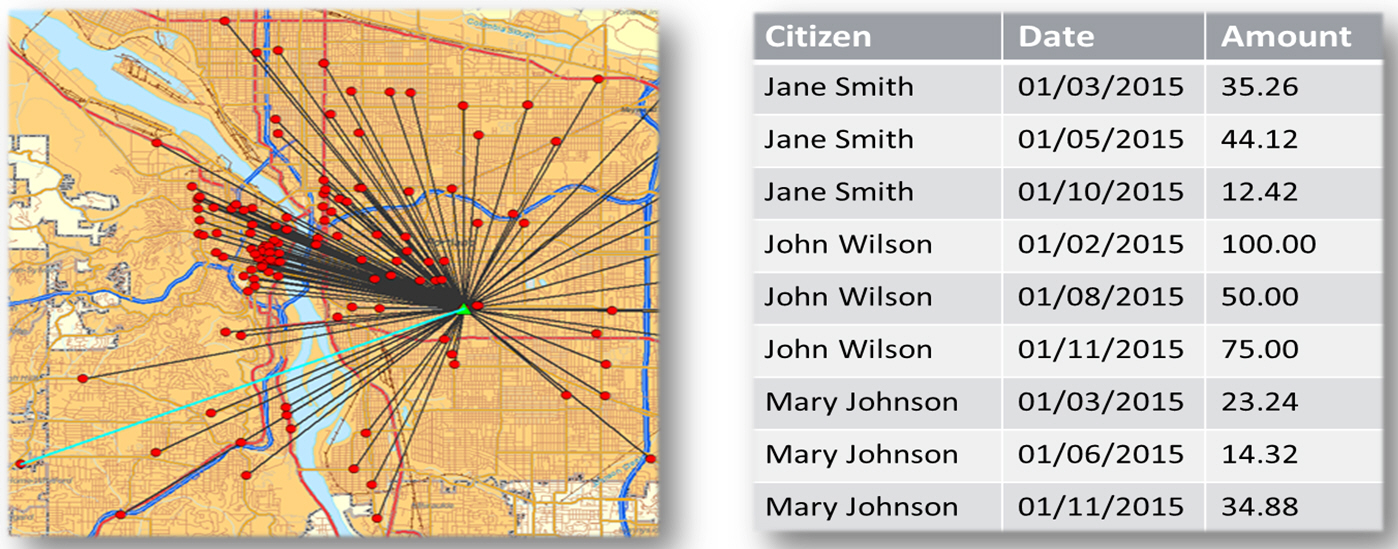
When you run
this procedure, the map displays postal codes in France, as shown in the
following image.
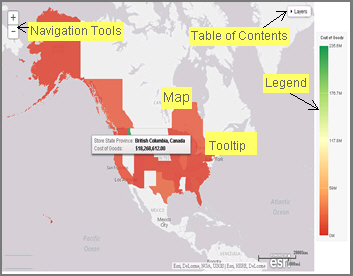
 , within the map to
zoom in and out of different areas of the map. You can also click your left
mouse button to zoom in to a specific location.
, within the map to
zoom in and out of different areas of the map. You can also click your left
mouse button to zoom in to a specific location.