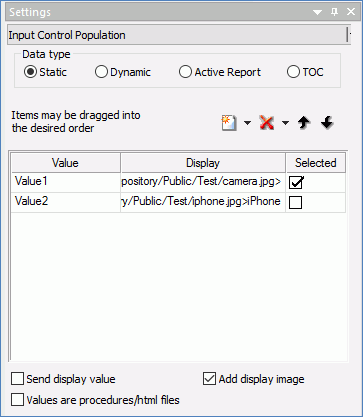
Inserting Components in an HTML Page Using the Components Tab
|
In this section: |
You can add a variety of components to an HTML page found in the command groups in the Components tab. For example, suppose you want to add a button to your page that a user can click to refresh the data. The button is a component. You select it from the Generic Elements command group in the Components tab, then add it to your page as desired.
The Components tab contains the Reports, Generic Elements, Containers, and Objects groups, as shown in the following image.

When you click a command from a ribbon, your mouse pointer turns into a cross-hair to let you draw the object in the HTML canvas. If you click a command in error, press the Escape key to return your mouse to a pointer.
Inserting a Report or Chart in an HTML Page Using the Reports Group
|
How to: |
From the Reports group, you can add a report or chart to your HTML page. The Reports group is shown in the following image.
The commands in the Reports group are:
- Report
-
Inserts a report object. You can add reports to the HTML canvas that will display when you run the layout. You can either embed or reference reports. Double-clicking a blank report object opens the Report canvas where you can create and style a report to be used in the HTML page.
You can also include parameters in a report whose values can be assigned with controls that are added with the HTML canvas.
- Chart
-
Inserts a chart object. You can add charts to the HTML canvas that will display when you run the layout. You can either embed or reference charts. Double-clicking on a blank chart object will open the Chart canvas where you can create and style a chart to be used in the HTML canvas.
Procedure: How to Add a New Report or Chart to an HTML Page
- Insert a report or chart object by doing
one of the following:
- On the Components tab, in the Reports group, click the Report or Chart.
- Right-click in the layout and select New Report or New Chart from the shortcut menu.
The pointer changes into a crosshair.
- Drag the crosshair to create a report or chart object
and adjust it to the size that you want.
A report or chart object is created in the layout and assigned the name report(n) or chart(n), where n is a number. The object will appear in gray and white to indicate that the placeholder does not have a report or chart associated with it. Once a report or chart is associated with the object, the object displays the contents of the report or chart if live or simulated data is active (live data is the default) or a colored placeholder if preview is off in the HTML Page tab, located in the App Studio Options dialog box.
- Create a report or chart by doing one of the following:
- Double-click the placeholder.
or
- Right-click the placeholder and select New Report for a report, or New Chart for a chart.
The Open File dialog box appears.
- Double-click the placeholder.
- Select the Master File you want to use and click OK.
The Report canvas opens for reports and the Chart canvas opens for charts.
- Optionally, after creating the report or chart, you can change its properties by adjusting the properties displayed in the Properties panel.
Procedure: How to Add an Existing Report or Chart to a Layout
- Insert a report or chart object by doing
one of the following:
- On the Components tab, in the Reports group, click Report or Chart.
- Right-click in the layout and select New Report or New Chart from the shortcut menu.
The pointer changes into a crosshair. Drag the crosshair to create a report or chart object and adjust it to the size you want.
A report or chart object is created in the layout and assigned the name report(n) or chart(n), where n is a number. The object will appear in gray and white to indicate that the placeholder does not have a report or chart associated with it. Once a report or chart is associated with the object, the object displays the contents of the report or chart if live or simulated data is active (live data is the default) or a colored placeholder if preview is off in the HTML Page tab, located in the App Studio Options dialog box.
- Right-click the report or chart.
- Select Reference existing procedure.
- For a report, right-click the report object and select Import existing report.
- For a chart, right-click the chart object and select Import existing chart.
The Open File dialog box appears.
- Enter the name of the procedure you want to add to the layout.
- Click OK.
The report or chart object appears in the Design view of the HTML canvas.
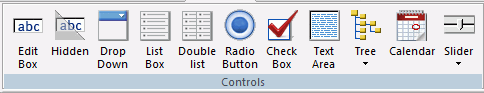
Adding Basic Elements to an HTML Page Using the Generic Elements Group
|
How to: |
You can add a variety of basic elements. The Generic Elements group is shown in the following image.
The commands in the Generic Elements group are:
- Image
-
Inserts an image. You can add an image to the layout. This is useful for including graphics, such as a company logo.
You can insert an image into your report layout and add a hyperlink. After you run your report and click the image, you can launch a URL or run a report the same way by clicking a hyperlink or push button.
Note: When inserting images, images must be referenced from a specific directory location.
- Hyperlink
-
Inserts a hyperlink.
- Button
-
Inserts a button. A push button enables you to execute a report or link to a URL or HTML file. This behavior is similar to a hyperlink.
Note: You can either double click to change the text or can use the Text property in the Properties panel.
- Reset
-
Inserts a reset button. A reset button enables you to revert the entire page back to its initial settings.
- Save Selection
-
Inserts a Save Selection button. At run time, the user can select given parameters and save them in a snapshot by clicking the Save Selection button. This creates a static HTML file that is saved in the same folder as the source file, by default.
To make the default save location for the parameterized HTML page your nearest My Content folder instead, select the Save Selection button on the canvas and, in the Properties panel, select My Content for the File default folder property. You can still navigate to another folder in your environment to save it there. The new save location becomes the default for saved parameter pages for the remainder of the session.
The static Save Selection files are not editable in the HTML canvas or in the text editor. To verify that a file is a Save Selection file:
- Right-click the file in the Configured Environments tree and
select Properties from the shortcut menu.
The File/Folder Properties panel opens.
- The value for the Properties attribute is tool=saveparam. This indicates that the file is not editable in the HTML canvas or in the text editor.
- Right-click the file in the Configured Environments tree and
select Properties from the shortcut menu.
- Hamburger
-
Inserts a hamburger control, which can be used to hide or display a form or control panel. A control panel is a panel component that has the Control panel property enabled.
To use a hamburger control, add it to the page, select it, and open the Properties panel. In the Hamburger specific section, select a form or control panel on the page from the Navigation and controls panel drop-down menu. You can also use the Properties panel to set the animation used when the hamburger control is clicked, and automatically hide the form or control panel when a request is executed on the page.
When you run the HTML page, the selected form or control panel does not appear until you click the hamburger control. You can hide it by clicking the hamburger control again.
- Label
-
Inserts a label. The label component lets you create and name a label, and link it to a control. To link a label to a control, you can select a value from the Htmlform property drop-down list in the Properties panel, or you can select the Bind label to option from the shortcut menu, when the label and control are both selected.
- Text
-
Inserts a text box. You can add text to the layout. This is useful for including headings for your webpage, or adding directions or explanations for your report or chart.
- Line
-
Inserts a line. You can add a horizontal or vertical line to the layout. This is useful for distinguishing between sections of your launch or display page.
- Menu
-
Inserts a menu. You can add a horizontal or vertical menu to the layout. This component can be used with Maintain code.
- Table
-
Inserts a table. This component can be used with Maintain code.
- Grid
-
Inserts a grid.
Procedure: How to Toggle the Display of a Form Using a Hamburger Control
A hamburger control allows you to show and hide a form, saving space on an HTML page.
- Create an HTML page.
- Add a chart or report component to the page, and reference a procedure that includes at least one parameter.
The New Parameters dialog box opens.
- Click OK to create a form on the page using the default options.
- On the Components tab, in the Generic Elements group, click Hamburger and draw a hamburger control onto the page.
Note: Forms appear below and to the right of the hamburger control when it is clicked. Make sure to leave enough space between the hamburger control and the right side of the page to display the entire form.
- Select the hamburger control and open the Properties panel.
- Link the hamburger control to a form. In the Hamburger specific section of the Properties panel, click the drop-down menu
for the Navigation and controls panel property, and select the form that you want to access using the hamburger control.
You can also link a hamburger control to a control panel. To create a control panel, on the Components tab, in the Containers group, click Panel, and draw a panel onto the page. Select it and, in the Properties panel, set the Control panel property to Yes.
- Optionally, set the Animation and Auto-hide panel properties.
The Animation property allows you to set the animation that occurs when the form appears.
When the Auto-hide panel property is enabled, clicking the submit button in the form hides the panel. If Auto-hide panel is not enabled, you can hide the form again by clicking the hamburger control.
- Run the HTML page. The form is hidden, by default, and it appears when you click the hamburger control.
Procedure: How to Format Text in an HTML Page
You may apply various formatting and style options to words and individual text characters within the text object.
Note: Any formatting and styling that you have applied to individual text strings within the text object will remain unchanged. Changes made to the entire text object are only applied to part of the text string that has not been formatted.
- On the
Components tab, in the Generic Elements group, click Text.
The pointer changes to a crosshair.
- Drag your pointer across the canvas to create a text
object.
A text object with the default text, Enter text, is created.
- Select
the text that you wish to format:
- To format the entire text object, single-click the text object in the layout.
- To format an individual word or text character, highlight part of the text within the text object.
- Right-click the text, point to Style,
and then click Font.
The Style Composer dialog box opens with Font selected automatically.
Note: You can also access font formatting options in the Properties panel.
- Select from the formatting options available. You can
change the type, style, color, size, and effect of the font.
Note: When you enter a Specific font size, the unit defaults to px (pixels).
- Click OK to close the Style Composer dialog box.
The formatting options that you selected are applied to the text.
Procedure: How to Insert a Bulleted List or Numbered List Into a Text Element
To insert a bulleted list or numbered list into a text object:
- On the Components tab, in the Generic
Elements group, click Text.
The pointer changes to a crosshair.
- Drag your pointer across the canvas to create a text
object.
A text object with the default text, Enter text, is created.
- Add multiple lines of text to the text object.
- Highlight and right-click the text that you want to include in the list.
- In the shortcut menu, select one of the following list
options:
- Bullets
- Disc
- Circle
- Square
- None
- Numbering
- Numbers
- Lowercase Letters
- Uppercase Letters
- Small Roman numerals
- Large Roman numerals
- None
- Note: Alternatively, you can select a bullet type before typing text to begin the list. Pressing enter will begin the next item in the list on a separate line.
- To change the bullet or number list type of an existing list, place your pointer on the list level you want to change and reselect a bullet or number list type. Selecting None will remove the bullets or numbers for that level and move any nested lists up one level. In order to switch between bullets and numbers, you must first remove the current list option by selecting None and then applying the list option you want.
- Bullets
Procedure: How to Insert Nested Lists Into a Text Element
To insert a nested list into the text object:
- On the Components tab, in the Generic
Elements group, click Text.
The pointer changes to a crosshair.
- Drag your pointer across the canvas to create a text
object.
A text object with the default text, Enter text, is created.
- Add a list to the text object. For more information, see How to Insert a Bulleted List or Numbered List Into a Text Element.
- Place your pointer after a list item.
- Right-click, point to Nested List and
then select a bulleted or numbered list option.
A list is started within the current list, allowing you to enter text on that list level.
Note: Pressing Tab while your pointer is on the same line as a list item will move that item one level down, resulting in a nested list. The bullet or number type selected is the next list type in the right-click shortcut menu. For example, if you have a bulleted list that uses the disc bullet type, pressing Tab to move an item down one level will cause that nested list to have the circle bullet type.
You can continue to nest lists within other lists by using the same steps shown above.
Note: You cannot skip a list level. For example, in order to insert a nested bulleted list or nested numbered list on a lower level, there must be a list one level up from it.
Adding Containers to an HTML Page Using the Containers Group
|
In this section: |
|
How to: |
You can add specific containers that group objects together on an HTML page. The Containers group is shown in the following image.
The commands in the Containers group are:
- Form
-
Inserts either a multi-layer form or single-layer form.
- Tab
-
Inserts a tab control. Tab controls enable you to create multiple pages in one HTML form and present a better display for viewing secondary information. You can select Top, Bottom, Left, or Right. This means you can choose to add a tab control that displays tabs at the top, bottom, left, or right on the control.
You can drag and resize this object, at run time, if the Enable dragging and Enable resizing properties, in the Properties panel, are set to Yes.
To change the header text, you can either double click and change the header text or enter a value in the Selected Page: Title property.
When a tab control object is added to the layout, each tab control consists of:
- A tab item.
A tab item is the tab label. You may edit the name of the tab item, style the tab item, and add multiple tab items. Each tab item is associated with a tab body.
- A tab body.
A tab body is the tab page where you associate your components, such as report and graph objects, images, and lines.
The Tab control can be displayed as a full screen or part of an HTML page.
- A tab item.
- Accordion
-
Inserts an Accordion styled box. You can drag and resize this object, at run time, if the Enable dragging and Enable resizing properties, in the Properties panel, are set to Yes.
To change the header text, you can either double click and change the header text or enter a value in the Selected Page: Title property.
- Window
-
Inserts a window. You can drag and resize this object, at run time, if the Enable dragging and Enable resizing properties, in the Properties panel, are set to Yes.
To change the header text, you can either double click and change the header text or enter a value in the Selected Page: Title property.
- Output Widget
-
Inserts an output widget. The output widget container includes buttons in the widget title bar that let you display or hide filter controls and that let you maximize to display full-screen, and minimize to return it to its original size.
- Mobile Container
-
Inserts a mobile container containing an output widget. You can right-click the mobile container to add multiple pages, and then create tasks using the Go to page action to navigate between them. If you right-click a page in a mobile container and click Selected page as prototype, any subsequently added pages are created as clones of the prototype page.
The output widgets on mobile container pages include hamburger controls, allowing you to access collapsible forms and control panels to interact with the page at run time.
You can enable responsive design on an HTML page that includes a mobile container so that the mobile container and the output widgets in it can resize to comfortably fit on mobile devices.
- Maintain Data App
-
Inserts a Maintain Data app window. You can drag and resize this object, at run time, if the Enable dragging and Enable resizing properties, in the Properties panel, are set to Yes.
- Group Box
-
Inserts a group box. A group box can be used to create a border around a group of objects, for example, forms or reports and charts.
- Panel
-
Inserts a panel to group objects together. The panel is invisible at run time.
Procedure: How to Use a Form Object to Create a Pop-Up Dialog Box
You can use a form object to create a pop-up dialog box.
- Create a form object.
- Create a button.
- Select the form.
- In the Properties panel, change the Display container as property to As popup dialog.
- Create a new task in the Tasks section of the Tasks & Animations panel.
- Use the button you create as the trigger.
- Make the button object toggle the visibility of the form you created.
- Run the page and click the button to display the form as a dialog box.
Procedure: How to Create a Pop-Up Dialog Box or Pop-Up Window From a Form Control
- Add a button object to your HTML page.
- Add a form control to your HTML page.
- Delete the run and back buttons created with the form control.
- While the form control is selected, in the Properties
panel, change the Display container as property to either As
popup dialog or As popup window.
As popup dialog causes the form to display as a pop-up dialog box. When the dialog box is displayed, you must click Close to return to your HTML page.
As popup window causes the form to display as a pop-up window. When the window is displayed, you can resize and move the window around your screen.
- Create a new task in the Tasks section of the Tasks and Animations panel that uses the button object to toggle the visibility of the form you created.
- Run your HTML page.When you click the button you added to the HTML page, the form will be displayed as either a pop-up dialog box or a pop-up window, depending on what option you selected.
Reordering Tabs, Accordions, and Windows
You can reorder tabs, accordions, and windows by dragging the page that you want to appear first onto the page that you want it to display before. For example, if you have 3 tabs, Tab1, Tab2, and Tab3, and you drag Tab3 onto Tab1, Tab3 will now display ahead of Tab1. The order of the tabs will then be Tab3, Tab1, Tab2. You can reorder windows when they are in tile view.
Procedure: How to Navigate Between Pages in a Mobile Container
You can add multiple pages to a mobile container on an HTML page to provide different sets of content with expandable forms and control panels. You can add a task using the Go to page action to allow users to move between pages.
- Create a new HTML page.
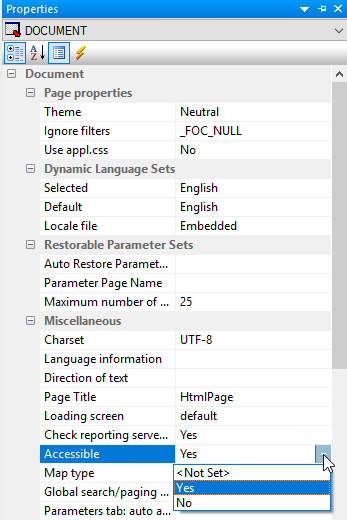
- Open the Properties panel and, with the DOCUMENT object selected, set the Enable responsive property, in the Responsive design section, to Yes.
Using responsive design will make the content on the page easier to use on mobile devices.
- On the Components tab, in the Containers group, click Mobile Container and draw a mobile container on the page.
The mobile container contains one page by default.
- Click on the output widget in the first page of the mobile container, and open the Properties panel. Enter a new title for
the page using the Widget Title property.
Since the Go to page action differentiates between pages by the widget title, using different titles for each one helps to ensure you select the correct page to navigate to.
- Add content to the first page inside the output widget.
- Create a control panel that will include a button to navigate to the second page. The control panel can also include filter
controls to interact with the content on the page.
- On the Components tab, in the Containers group, click Panel, and create a panel on the page.
- On the Components tab, in the Generic Elements group, click Button and draw a button inside the panel.
Optionally, double-click the button to change the text in it.
- Select the panel containing the button and open the Properties panel. Set the Control panel property to Yes.
This turns the panel into a control panel that can be accessed using the hamburger control in the mobile container output widget.
- Select the mobile container output widget and open the Properties panel. Select the control panel that you created previously from the menu next to the Navigation and controls property.
- Right-click the mobile container, outside of the output widget, and click Add Page.
A second page with an output widget is created in the mobile container.
- Repeat steps 4 through 7 to create the second page. Follow these steps again for any additional pages that you want to add.
- Create two new tasks using the Go to page action to navigate between the first and second page.
- Open the Tasks & Animations panel.
- Click the New button to create a new task.
- Leave the Trigger Type as Click.
- For the Trigger Identifier, select the first button that you created, which is in the collapsible panel on the first page of the mobile container.
- Click the arrow next to the Requests selections button, point to Go to page, point to the name of the mobile container, and select the name of the second page in the mobile container.
This will allow you to access the second page from a button accessible from the first page.
- Click New to create a second task.
- Leave the Trigger Type as Click.
- For the Trigger Identifier in the second task, select the button that will be accessible from the second page of the mobile container.
- Click the arrow next to the Requests selections button, point to Go to page, point to the name of the mobile container, and select the name of the first page in the mobile container.
This will allow you to return to the first page using a button accessible on the second page.
- Save the HTML page and access it from a mobile device.
When you tap the hamburger control, a panel with a button opens. Tap the button to access the other page created using the mobile container.
Adding Objects to an HTML Page Using the Objects Group
You can add objects other than reports, charts, elements, or containers to customize your HTML page. The Objects group is shown in the following image.
The commands in the Objects group are:
- Frame
-
Inserts a frame object. You can use a frame to embed additional web sources or run reports. You can also use a frame as the output location or target for a drill-down report. You can also use a frame to run a table of contents report, an OLAP report, a PDF report, or an Excel® report.
- Flash
-
Inserts a Flash component. You can add SWF files that are Adobe® Flash Player compatible to accompany reports or graphs on an HTML page.
Note: When inserting Flash animations, only files that are 1 MB or smaller can be run using the HTML canvas.
- Map
-
Inserts a map object. You can add a Google™ or ESRI map to your HTML page. Maps are services offering powerful, user-friendly mapping technology that can be customized to show points on a map with drill-down capabilities. You can customize the map properties and bind them to a report or chart.
- HTML
-
Inserts an HTML object. Developers can use the Settings panel to type a valid snippet of HTML code for the HTML object, such as HTML code to browse for a file.
- ESRI Map
-
Inserts an ESRI map object. You can use the Settings panel to configure the properties and components.