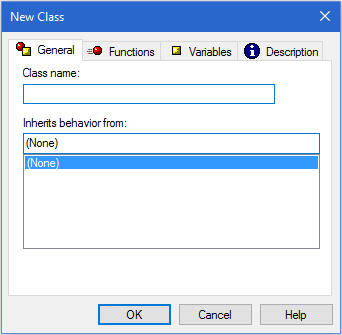
Procedure: How to Define a Class Using the Class Editor
This procedure describes how to define a new class. If you wish to define a new subclass, that is, a class that inherits properties from another class, see How to Define a Subclass Using the Class Editor.
- In the Requests & Data Sources panel, right-click the import module or procedure and select New class in the shortcut menu.
- In the New Class dialog box, type a name for your class.
- Click the Variables tab to specify the member variables of a class. The member variables of a class express its properties.
- To add
a variable, click the New button
 .
.The Member Variable dialog box opens.
The name of each member variable must be unique within the class to which it belongs. It can be identical, however, to the names of member variables of other classes.
- Repeat step 4 to create any additional variables.
- Click the Functions tab to specify the member functions of a class. The member functions of a class define the actions that can be performed on the objects of a class.
- To add
a function, click the New button
 .
.The Member Function dialog box opens.
The name of each member function must be unique within the class to which it belongs. It can be identical, however, to the names of member functions of other classes.
- Repeat step 7 to create any additional functions.
- Optionally, click the Description tab and add a description to your class.
- Click OK to confirm the class definition.