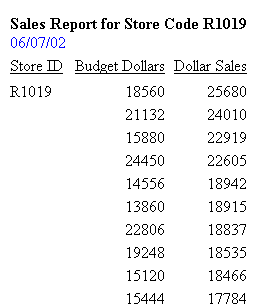
Including a Field Value in a Heading or Footing
|
How to: |
You can include a field name in heading or footing text. When the request is run, the output includes the field value. The result is a customized heading or footing with specific data identification for the user.
While you can use this technique in any report, it is essential if you are creating a free-form report. For details, see Creating a Free-Form Report.
For requests with multiple display and sort field sets, fields in a report heading or footing, or page heading or footing, are evaluated as if they were objects of the first display command. Fields in a sort heading or footing are evaluated as part of the first display command in which they are referenced. If a field is not referenced, it is evaluated as part of the last display command.
You can use a prefix operator to derive a field value in a heading or footing. However, the DST., MDE., and MDN. prefix operators are not supported in headings or footings in requests that have an ACROSS phrase or multiple display commands. For a list of operations you can perform with prefix operators, see Displaying Report Data.
Two operators are specifically designed for use with a sort footing:
- ST. produces a subtotal value of a numeric field at a sort break in a report.
- CT. produces a cumulative total of a numeric field.
Syntax: How to Include a Field Value in a Heading or Footing
<[prefix_operator]fieldname<fieldname[>]
or
<fieldname[>]
where:
- <fieldname
- Places the field value in the heading or footing, and suppresses trailing blanks in an alphanumeric field for all values of SET STYLEMODE.
- <fieldname>
- Places the field value in the heading or footing, and retains trailing blanks in an alphanumeric field if SET STYLEMODE = FIXED. Suppresses trailing blanks for all other values of SET STYLEMODE. PDF output retains trailing blanks regardless of the STYLEMODE setting.
- prefix_operator
- Performs a calculation directly on the value of a field. A prefix operator is applied to a single field, and affects only that field.
Note: To display the caret character (<) as text in a heading or footing, use two consecutive caret symbols (<<).
Example: Including the Department Name in a Page Heading and Footing
This request includes the field name DEPARTMENT in both the page heading and footing text. The command HEADING is not required in the request because the page heading text appears before the command PRINT.
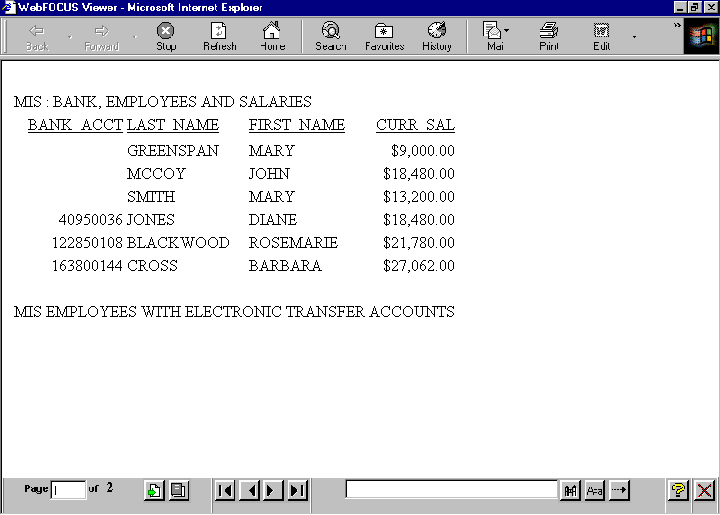
TABLE FILE EMPLOYEE "<DEPARTMENT : BANK, EMPLOYEES AND SALARIES" PRINT CURR_SAL BY DEPARTMENT NOPRINT BY BANK_ACCT BY LAST_NAME BY FIRST_NAME ON DEPARTMENT PAGE-BREAK FOOTING "<DEPARTMENT EMPLOYEES WITH ELECTRONIC TRANSFER ACCOUNTS" ON TABLE SET ONLINE-FMT HTML ON TABLE SET WEBVIEWER ON ON TABLE SET PAGE-NUM OFF ON TABLE SET STYLESHEET * TYPE=REPORT, GRID=OFF, $ ENDSTYLE END
The output displays the output for a multi-page HTML report. On the first page of output, the value of DEPARTMENT in the page heading and footing is MIS.
On the second page of output, the value of DEPARTMENT is PRODUCTION.
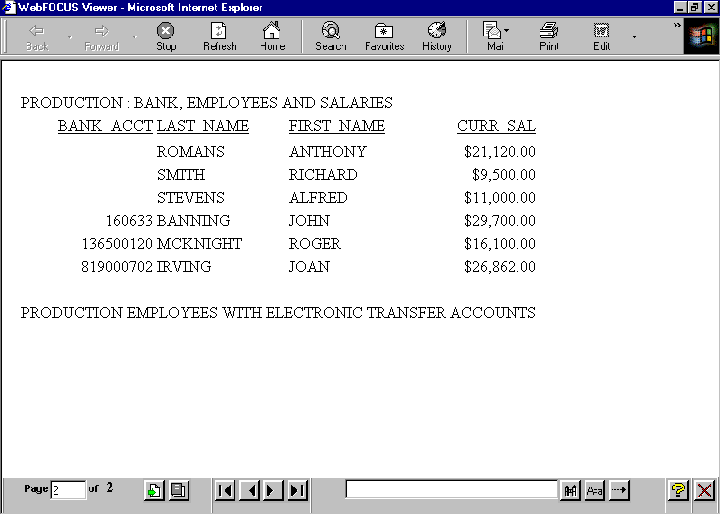
Note: If you do not see the navigation arrows, click the maximize button.
Example: Displaying a Less Than Symbol in a Heading
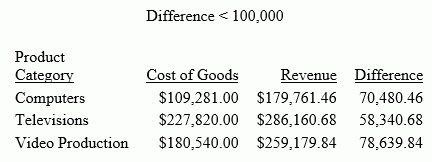
The following request computes the difference between REVENUE_US and COGS_US and displays those rows in which the difference is less than 100,000.
TABLE FILE WF_RETAIL_LITE HEADING CENTER " Difference << 100,000" " " SUM COGS_US REVENUE_US COMPUTE Difference/D20.2 = REVENUE_US - COGS_US; BY PRODUCT_CATEGORY WHERE TOTAL Difference LT 100000 ON TABLE SET PAGE NOLEAD ON TABLE SET STYLE * GRID=OFF,$ ENDSTYLE END
The heading displays the text Difference < 100,000, as shown in the following image.
Example: Retaining Trailing Blanks in an Alphanumeric Field
Trailing blanks are not retained in standard HTML output. When the output type is HTML, STYLEMODE is set to FULL by default. To retain trailing blanks in the alphanumeric field DEPARTMENT, the STYLEMODE setting has been changed to FIXED in this request and the delimiters < and > have been included around the field name in the sort footing text.
SET STYLEMODE = FIXED TABLE FILE EMPLOYEE SUM SALARY BY DEPARTMENT SUBFOOT "<DEPARTMENT> DEPARTMENT TOTAL SALARY IS <SALARY" ON TABLE SET PAGE-NUM OFF ON TABLE SET ONLINE-FMT HTML ON TABLE SET STYLESHEET * TYPE=REPORT, GRID=OFF, $ ENDSTYLE END
Values for DEPARTMENT appear in the sort footing as MIS and PRODUCTION.
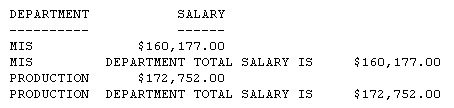
Note: SET STYLEMODE=FIXED turns off the HTML formatting of your browser for that report. The resulting report displays in a fixed font without colors and other web capabilities.
Example: Using the Prefix Operator TOT in a Page Heading
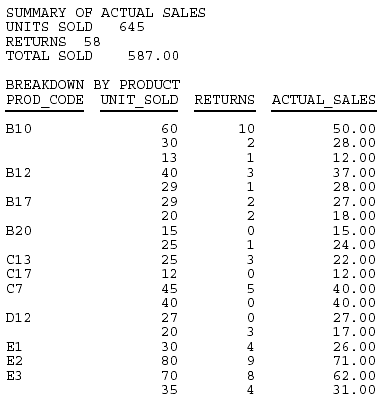
This request uses the prefix operator TOT to generate grand totals for three fields.
DEFINE FILE SALES ACTUAL_SALES/D8.2 = UNIT_SOLD - RETURNS; SALES/F5.1 = 100 * ACTUAL_SALES / UNIT_SOLD; END TABLE FILE SALES "SUMMARY OF ACTUAL SALES" "UNITS SOLD <TOT.UNIT_SOLD" "RETURNS <TOT.RETURNS" "TOTAL SOLD <TOT.ACTUAL_SALES" " " "BREAKDOWN BY PRODUCT" PRINT UNIT_SOLD AND RETURNS AND ACTUAL_SALES BY PROD_CODE ON TABLE SET PAGE-NUM OFF ON TABLE SET ONLINE-FMT PDF ON TABLE SET STYLESHEET * TYPE=REPORT, GRID=OFF, $ ENDSTYLE END
The totals appear in the page heading.
Example: Using Multiple Prefix Operators in a Page Heading
This request uses the prefix operators MAX, MIN, AVE, and TOT. It does not require a display command because the page heading text contains data fields.
TABLE FILE SALES "MOST UNITS SOLD WERE <MAX.UNIT_SOLD" "LEAST UNITS SOLD WERE <MIN.UNIT_SOLD" "AVERAGE UNITS SOLD WERE <AVE.UNIT_SOLD" "TOTAL UNITS SOLD WERE <TOT.UNIT_SOLD" ON TABLE SET PAGE-NUM OFF ON TABLE SET ONLINE-FMT HTML ON TABLE SET STYLESHEET * TYPE=REPORT, GRID=OFF, $ ENDSTYLE END
The prefix operators generate summary data in the page heading.
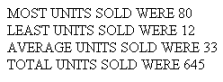
Example: Using Multiple Prefix Operators in a Sort Footing
This request uses the prefix operators CNT and AVE in a sort footing. The output does not contain columns of data. All data is included in the sort footing itself.
TABLE FILE EMPLOYEE BY DEPARTMENT NOPRINT SUBFOOT "NUMBER OF EMPLOYEES IN DEPARTMENT <DEPARTMENT = <CNT.LAST_NAME" "WITH AVERAGE SALARY OF <AVE.CURR_SAL" ON TABLE SET ONLINE-FMT HTML ON TABLE SET PAGE-NUM OFF ON TABLE SET STYLESHEET * TYPE=REPORT, GRID=OFF, $ ENDSTYLE END
The sort footing is a summary report on the number of employees in a department and their average salary.
The prefix operators generate summary data in the page heading.
NUMBER OF EMPLOYEES IN DEPARTMENT MIS = 6 WITH AVERAGE SALARY OF $18,000.33 NUMBER OF EMPLOYEES IN DEPARTMENT PRODUCTION = 6 WITH AVERAGE SALARY OF $19,047.00