An asynchronous method is specified using the
@Asynchronous annotation. The @Asynchronous
annotation is inherited by overridden methods in child types. The
isolation level of the transaction in which the asynchronous method is
executed can be specified in the @Asynchronous
annotation.
Asynchronous methods have these restrictions:
asynchronous methods are only supported on managed objects.
an asynchronous method must be declared as
void.an asynchronous method cannot be declared
static.asynchronous method parameters have the same restrictions as distributed method parameters. See the section called “Distributed method signature restrictions”.
Adding the @Asynchronous annotation to a method
that does not meet the above restrictions will fail at class load time
with a java.lang.NoclassDefFoundError exception.
Class com/kabira/snippets/managedobjects/AsynchronousMethod$MyObject failed class audit:
[Asynchronous method queueWork must return void]
Java main class com.kabira.snippets.managedobjects.AsynchronousMethod.main exited with an exception.
java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: com/kabira/snippets/managedobjects/AsynchronousMethod$MyObject
at com.kabira.snippets.managedobjects.AsynchronousMethod$1.run(AsynchronousMethod.java:50)
at com.kabira.platform.Transaction.execute(Transaction.java:303)
at com.kabira.snippets.managedobjects.AsynchronousMethod.main(AsynchronousMethod.java:41)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:39)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at com.kabira.platform.MainWrapper.invokeMain(MainWrapper.java:49)
Example 5.28, “Asynchronous method” shows a snippet of declaring and using an asynchronous method.
Example 5.28. Asynchronous method
// $Revision: 1.1.2.1 $
package com.kabira.snippets.managedobjects;
import com.kabira.platform.Transaction;
import com.kabira.platform.annotation.Managed;
import com.kabira.platform.annotation.Asynchronous;
/**
* Asynchronous methods
* <p>
* <h2> Target Nodes</h2>
* <ul>
* <li> <b>domainnode</b> = A
* </ul>
*/
public class AsynchronousMethod
{
/**
* A managed object
*/
@Managed
public static class MyObject
{
@Asynchronous
void queueWork()
{
System.out.println(
"Executed in transaction: "
+ Transaction.getIdentifier().toString());
}
};
/**
* Main entry point
* @param args Not used
*/
public static void main(String [] args)
{
new Transaction("Asynchronous Method")
{
@Override
protected void run() throws Rollback
{
System.out.println(
"Calling transaction: "
+ Transaction.getIdentifier().toString());
MyObject e = new MyObject();
e.queueWork();
}
}.execute();
}
}
When this snippet is run it outputs the following:
[A] Calling transaction: 872:1 [A] Executed in transaction: 850:1
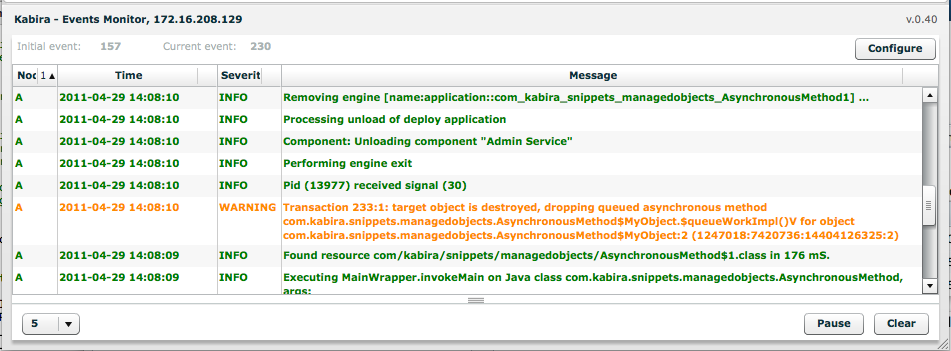
Queued asynchronous methods are discarded with a log message if the target object was destroyed before the method could be executed. Object lifecycle must be carefully managed to ensure that all queued asynchronous methods are executed before destroying objects.