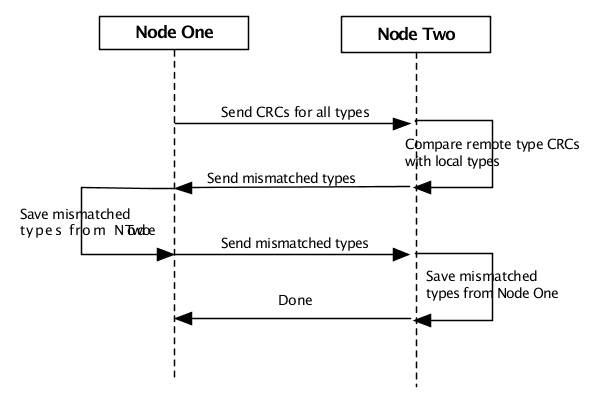
Version changes are detected automatically during initialization and as classes are loaded into JVMs running on a node. As nodes connect to each other, and as new types are loaded into a JVM, a type exchange occurs between the two nodes. A type exchange is performed for both application classes and product runtime structures. The type exchange protocol is shown in Figure 8.1, “Type exchange”.
The steps in Figure 8.1, “Type exchange” are:
Node one sends CRC values for all types defined on node one.
Node two compares the CRC values for all types sent from node one found on node two.
If the CRC values are different for a type, node two sends node one its definition of the type.
Node one saves the definition of the types received from node two in a type mismatch table for node two.
Node one sends node two its definition of the mismatched types received from node two.
Node two saves the type definitions received from node one in a type mismatch table for node one.
The CRC defined above, is a computed numeric value that is used to determine whether a type definition has changed. The CRC value is identical on nodes that have the same type definition. The type information sent if the CRC values differ is a complete type definition that includes:
field definitions
inheritance hierarchy
version information
The use of a CRC to determine type changes mimizes network bandwidth in the case where type information is identical.
Type mismatch tables exist for each node for which mismatched type information was detected. Type mismatch tables contain this information;
Complete type definition, including the type name.
Version number
Whenever objects are marshaled for a type (reading and writing), the type mismatch table is checked to see if the type matches for the two nodes communicating. If a type is found in the type mismatch table - the object is upgraded as described in the section called “Object upgrades”.