TIBCO BusinessEvents® Extreme supports online versioning of configuration data. This allows a configuration to change without having to restart a running application. Configuration data is stored as managed objects in shared memory. Applications can define their own configuration data by defining a Java class. Application defined configuration data is operationally managed the same way as predefined TIBCO BusinessEvents® Extreme configuration data.
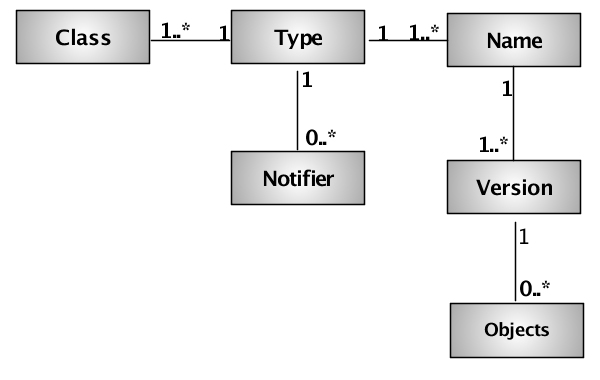
Figure 9.1, “Configuration model” shows the configuration concepts.
These concepts are defined as:
Type - a specific category of configuration data that is loaded in a single configuration file. A configuration type consists of one or more configuration classes.
Class - a Java configuration class. This Java class defines a new configuration object. All configuration classes are associated with a configuration type.
Name - a unique name per configuration type. Multiple unique names can be associated with a configuration type. The configuration name is the unit of versioning.
Version - a unique configuration version per configuration name. Multiple versions can be associated with a configuration name, but only one can be active.
Objects - zero or more configuration objects associated with a configuration version. All of the configuration objects are associated with one of the configuration classes associated with the related configuration type.
Notifier - a configuration notifier that handles configuration state changes (see the section called “Configuration notifiers”).
Configuration data is loaded into TIBCO BusinessEvents® Extreme using configuration files. The detailed syntax of these configuration files is described in the TIBCO BusinessEvents® Extreme Administration. In addition to the configuration data for the configuration objects, the configuration files also contain:
Type -- type of configuration data
Name -- configuration name
Version -- version number of configuration file
The type, name, and version information in the configuration files maps directly to the configuration concepts described above.
The type information in a configuration file is used to locate any configuration notifiers associated with the configuration data. The name and version are used to create or replace a configuration when the configuration is activated. See the section called “Configuration life cycle” for more details.
For example, this configuration file is associated with a
configuration type of distribution,
it has a name of myconfiguration,
and it is version 1.0.
//
// This file defines version 1.0 of a distribution configuration named myconfiguration
//
configuration "myconfiguration" version "1.0" type "distribution"
{
...
};