RedHat OpenShift Installation
Table of Contents
Introduction
This guide’s intention is to help a user deploy TIBCO ModelOps on RedHat OpenShift Platform, regardless of which platform OpenShift is installed on.
Prerequisites
- Create a RedHat account
- Ensure OpenShift is installed
- Optional, In case of windows node is required, install opensift with hybrid network
- Download and install Tools Kubectl and OC (OpenShift CLI)
- Download and Install HELM Cli
- Download and Install Tekton CLI (Optional)
- Download and Install Lens (Optional)
Supported OpenShift Environments
ModelOps is supported on OpenShift running in these environments:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Azure
- vSphere (Datacenter)
ModelOps supports both installer-provisioned infrastructure (IPI) as well as user-provisioned infrastructure (UPI). Installer-provisioned infrastructure is recommended for a ModelOps installation.
To install an OpenShift cluster please use the official RedHat installation documents:
Installation
-
Log in into OpenShift cluster, using any of the two ways below:
-
Using the kubeconfig file:
export KUBECONFIG = $path/kubeconfig
-
Using OC for login:
oc login \ https://api.${clustername}.${domain}:6443 \ -u ${cluster_username} \ -p ${cluster_password}
-
-
Create a namespace
kubectl create namespace ${namespace} -
Add the secrets
kubectl create secret generic elasticsearch-es-elastic-user \ --from-literal=${elastic_username}=${elastic_password} \ --namespace ${namespace} --dry-run=client --output=yaml 2>/dev/null > secret.yaml kubectl apply --filename secret.yaml kubectl create secret generic git-server \ --from-literal=${git_username}=${git_password} \ --namespace ${namespace} kubectl create secret generic nexus-server \ --from-literal=${nexus_username}=${nexus_password} \ --namespace ${namespace} kubectl create secret generic modelops-server \ --from-literal=${modelops_username}=${modelops_password} \ --namespace ${namespace} kubectl create secret generic grafana-server \ --from-literal=${grafana_username}=${grafana_password} \ --namespace ${namespace} kubectl create secret generic scoring-admin \ --from-literal=${scoring_username}=${scoring_password} \ --namespace ${namespace} -
Install Helm charts
helm upgrade \ --install modelops ${home}/helm-charts/kubernetes-installer-1.0.0.tgz \ --set global.cloud=openshift \ --namespace ${namespace} -
Copy the shipped Maven artifacts to the Maven repository Pod
kubectl cp \ ${path}/kubernetes-installer-1.0.0-mavenrepo.zip mavenrepo-0:mavenrepo.zip \ --namespace ${namespace}This command takes some time to run, and gives no output.
-
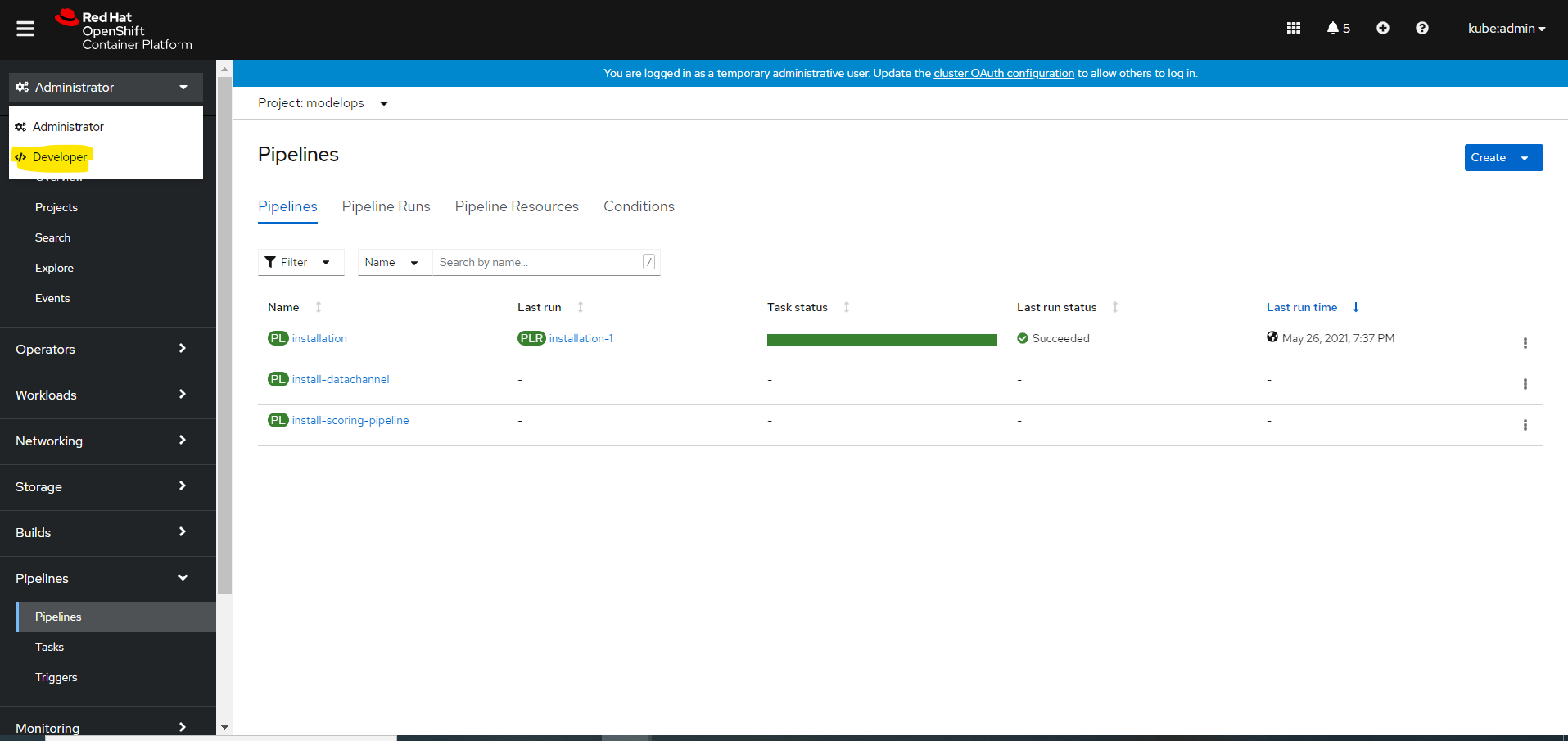
To monitor installation logs, use:
tkn pipelinerun logs installation-1 --follow --namespace ${namespace} -
The installation is completed when all tasks display
Succeeded$ tkn taskrun list --namespace ${namespace} -
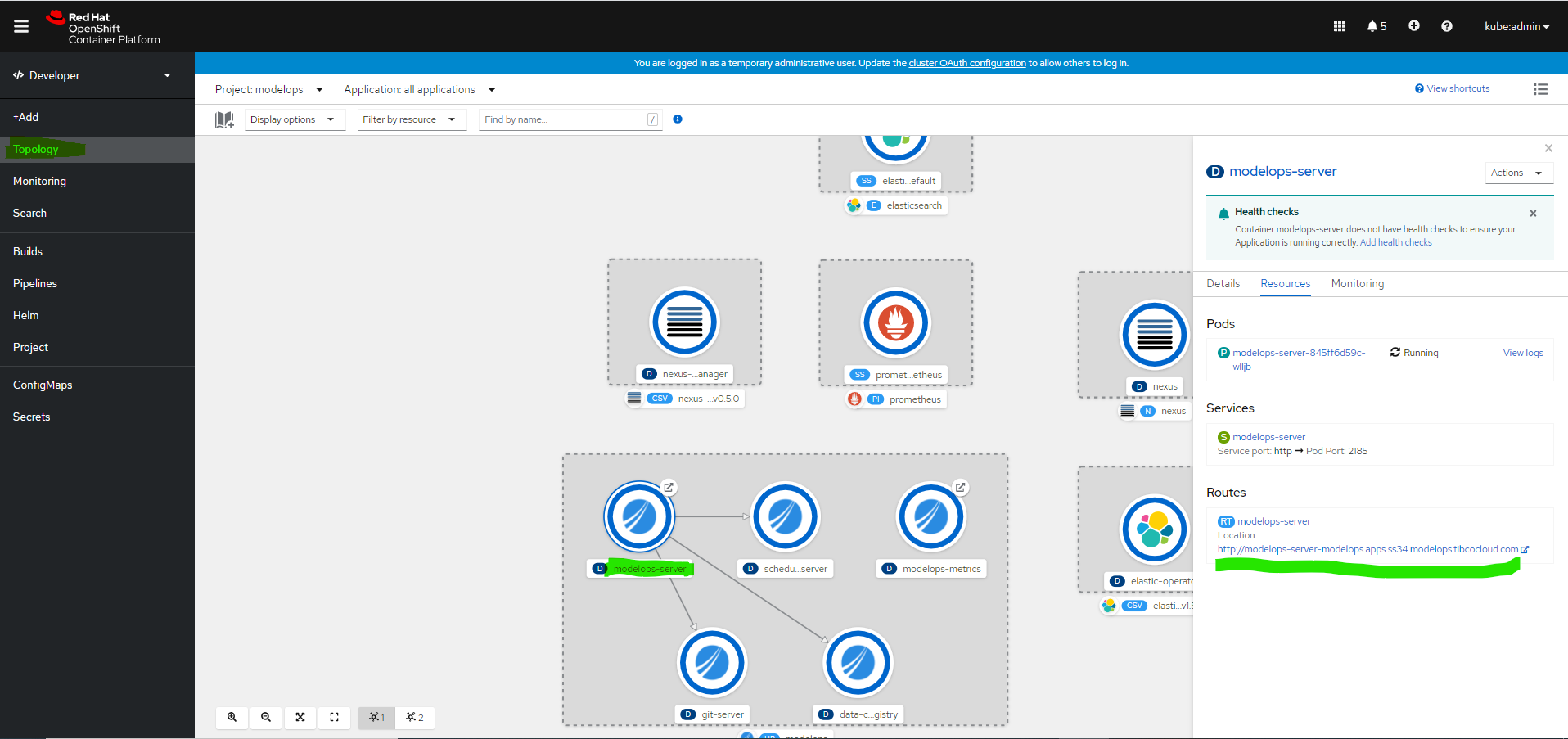
Capturing ModelOps UI url