Cluster Federation
Cluster Federation helps user to create virtual cluster that span across multiple real cluster.
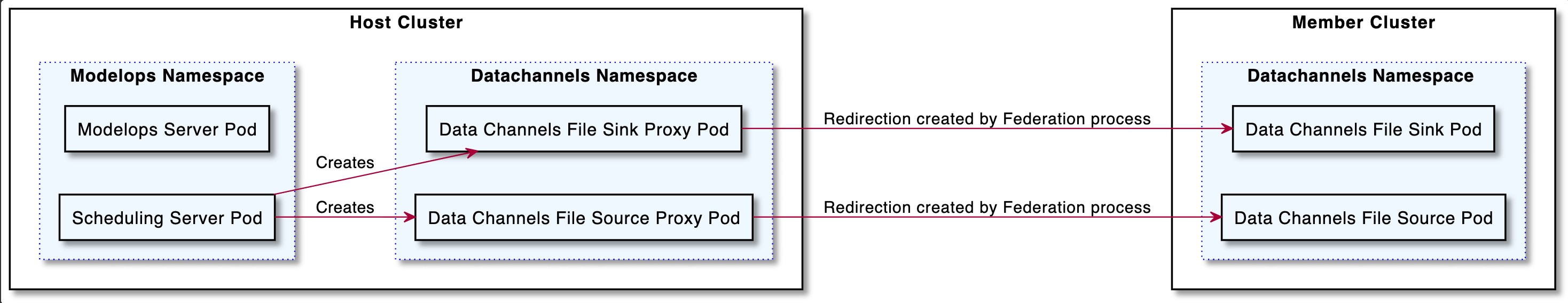
Overview
This design will allow to deploy data channels and pipelines across K8s clusters.
Pre-requisites
- Install licoctl CLI tool on host machine
- Host K8 cluster (i.e AKS, Openshift etc) with Tibco Modelops installed, with kubernetes version >= 1.19.0
- Member K8 cluster (i.e AKS, Openshift etc), with kubernetes version >= 1.19.0
Note : If AKS is used as a Host or Member cluster than network-plugin should be set to kubenet while creating a K8 cluster
Configuration
Install liqo on Host cluster and member cluster
AKS Cluster:
-
Configuration:
az login -
Export few variables about your cluster:
export AKS_RESOURCE_GROUP=myResourceGroup # the resourceGroup where the cluster is created export AKS_RESOURCE_NAME=myCluster # the name of AKS cluster resource on Azure export AKS_SUBSCRIPTION_ID=subscriptionId # the subscription id associated to the AKS cluster's resource group -
Now, you can perform the proper Liqo installation on your cluster.
liqoctl install aks --resource-group-name "${AKS_RESOURCE_GROUP}" \ --resource-name "${AKS_RESOURCE_NAME}" \ --subscription-id "${AKS_SUBSCRIPTION_ID}"
Other Platform:
To install Liqo on other platforms please refer this link
Cluster Registration
To establish a connection between Host cluster and Member cluster.
-
Execute below command at Member cluster which will print the unique output per Member cluster.
liqoctl generate peer-command -
Now, execute the command received as output above at Host Cluster.
-
Verify the connection between Host Cluster and Member cluster, by executing the below command to Host cluster.
kubectl get foreignclusters
There should be ForeignCluster resources in that state:
NAME OUTGOING PEERING PHASE INCOMING PEERING PHASE NETWORKING STATUS AUTHENTICATION STATUS
membercluster Established None Established Established
NamespaceOffloading
Liqo provides a NamespaceOffloading resource. The policies defined inside the NamespaceOffloading object specify how the local namespace can be replicated on Member clusters.
cat << "EOF" | kubectl apply -f - -n mynamespace
apiVersion: offloading.liqo.io/v1alpha1
kind: NamespaceOffloading
metadata:
name: offloading
namespace: mynamespace
spec:
clusterSelector:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: liqo.io/type
operator: In
values:
- virtual-node
namespaceMappingStrategy: EnforceSameName
podOffloadingStrategy: Remote
EOF
-
NamespaceOffloadingobject defines “per-namespace boundaries", limiting the scope where pods can be remotely offloaded. -
namespaceMappingStrategy: This defines the naming strategy used to create the remote/member cluster namespaces. The accepted values are:-
DefaultName(Default) : The remote namespaces have the name of the local namespace followed by the local cluster-id to guarantee the absence of conflicts. -
EnforceSameName: The remote namespaces have the same name as the namespace in the local cluster (this approach can lead to conflicts if a namespace with the same name already exists inside the selected remote clusters).
-
-
podOffloadingStrategy: The podOffloadingStrategy defines constraints about pod scheduling. The accepted values are:-
LocalAndRemote: The pods deployed in the local namespace can be scheduled both locally and remotely. Also, the LocalAndRemote strategy does not impose any constraints, and it leaves the scheduler the choice to select both local and remote nodes. The Remote and Local strategies force the pods to be scheduled respectively only remotely and only locally. -
Local: The pods deployed in the local namespace are always scheduled inside the local cluster, never remotely. -
Remote: The pods deployed in the local namespace are always scheduled inside the remote clusters, never locally.
-
Limitations
- Liqo doesn't support AWS with STS configurations. Reference ticket.
- Liqo installation fails on openshift environment. Here is a workaround required to proceed. We need to change the protocol for liqo-gateway from “UDP” to “TCP”
- Liqo doesn't work with Windows node, to install Liqo on AKS the network-plugin should be set to kubenet, and windows node doesn't work with network-plugin as kubenet
