Contents
The TIBCO StreamBase® HA Heartbeat Adapter is an embedded adapter with a specialized purpose: it monitors the state of each server in a cluster of two or more StreamBase Servers, where the cluster is configured for high availability of a core application.
Instances of the adapter can act as servers, clients, and as broadcasters of information in a multicast group.
You can specify the time intervals for monitoring, as well as other properties of the adapter.
HA design patterns that use the adapter support the availability of the core application by means of two components: an application that monitors leadership status, and an application that controls the behavior of the core application according to the leadership status. The monitoring logic runs in containers that are separate from the application's control logic.
In these design patterns the HA Heartbeat adapter is part of the monitoring application: it monitors the availability and leadership status of one or more other servers. Each heartbeat event is represented as a tuple.
HA Heartbeat adapters are often used in a pair of StreamBase Servers. The following diagram illustrates this design pattern.
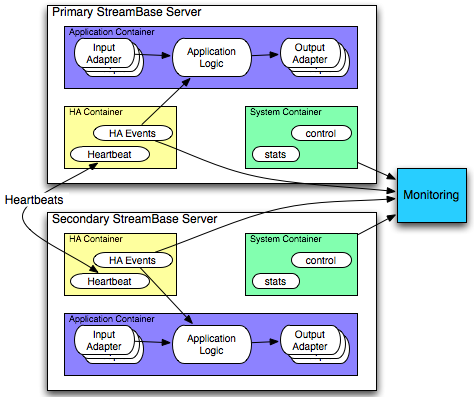
As shown, Application Container holds the core application, while the HA Container holds the Heartbeat adapters as part of
the HA monitoring application. The HA Events module controls the behavior of the core application, for example, in the event of a change in leadership status for the
StreamBase Server on which it is running. See haleadershipcontrol.sbapp and hbtester.sbapp in the HA sample for examples of this design.
In this configuration, instances of the adapter are specified as Client and Server types on the Adapter Properties page.
You can also use HA Heartbeat adapters in a cluster of three or more StreamBase Servers. In this case, one HA Heartbeat adapter functions as a heartbeat server (not a StreamBase Server), while two or more HA Heartbeat adapters function as heartbeat clients of that heartbeat server. Each heartbeat client monitors the status of a single heartbeat server.
In this configuration, instances of the adapter are specified as Server and Client types on the Adapter Properties page.
You can use the HA Heartbeat adapter to broadcast monitoring information to other adapters in a multicast group. In this case you must specify an Endpoint Id, which is an abstract name that indicates where each node in the group connects to the network.
The Multicast type is designed to work in loosely coupled clusters where there are an indefinite number of nodes in the cluster. Each node broadcasts its status to the others at specified intervals. If no status is received from any particular node in the group it is assumed that it is no longer available, and, if it is the leader, another node in the group must become leader.
In this design pattern, instances of the adapter are all specified to be of type Multicast (rather than Client or Server type). Adapters that are Multicast instances do not interact in any way with Server or Client instances.
By default, an instance of the HA Heartbeat adapter has one input port and one output port.
The input port is typically connected to an input stream from the system container's control stream. You can start the HA Heartbeat adapter monitoring on startup using the start container message off the control stream.
The first field in each input tuple specifies a command, such as an instruction to start or stop. The set of accepted command strings are listed in the following table.
| Command String | Description |
|---|---|
| start | Start the adapter, using the value of the Type property to determine whether to start the adapter as heartbeat server, heartbeat client, or multicast. |
| startClient | Start the adapter as an HA Heartbeat client. |
| startServer | Start the adapter as an HA Heartbeat server. |
| startMulticast | Start the adapter as an HA Heartbeat multicast node. |
| stop | Stop the adapter. |
To change the type of an adapter instance or to restart a disconnected adapter, you must first send the stop command.
See Input Schemas for the other schemas for the input port of the adapter.
The adapter sends event tuples in a fixed schema to the output port. See Output Schemas for the schemas.
You can add an optional Error Output Port, which sends as output a StreamBase error tuple for any adapter error.
To specify the properties for the adapter, open its Properties View in StreamBase Studio and select one of the Properties tabs; the tabs are described in the following sections.
Note
When using the HA Heartbeat adapter in a StreamSQL program with the APPLY JAVA statement, you must convert the StreamBase Studio property names to parameter names using the formula described in APPLY Statement.
Name: Use this field to specify or change the component's name, which must be unique in the application. The name must contain only alphabetic characters, numbers, and underscores, and no hyphens or other special characters. The first character must be alphabetic or an underscore.
Adapter: A read-only field that shows the formal name of the adapter.
Class: A field that shows the fully qualified class name that implements the functionality of this adapter. Use this class name when loading the adapter in StreamSQL programs with the APPLY JAVA statement. You can right-click this field and select Copy from the context menu to place the full class name in the system clipboard.
Start with application: If this field is set to Yes or to a module parameter that evaluates to true, an instance of this adapter starts as part of the containing StreamBase Server. If this field is set to No or to a module parameter that evaluates to false, the adapter is loaded with the server, but does not start until you send an sbadmin resume command, or until you start the component with StreamBase Manager. With this option set to No or false, the adapter does not start even if the application as a whole is suspended and later resumed. The recommended setting is selected by default.
Enable Error Output Port: Select this check box to add an Error Port to this component. In the EventFlow canvas, the Error Port shows as a red output port, always the last port for the component. See Using Error Ports and Error Streams to learn about Error Ports.
Description: Optionally enter text to briefly describe the component's purpose and function. In the EventFlow canvas, you can see the description by pressing Ctrl while the component's tooltip is displayed.
The following properties are on the Adapter Properties tab. The required specifications vary according to the type of instance. For example, only a Client instance of the adapter specifies the hostname of a Server.
| Property | Data Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | string | Server | Specifies the type for this instance of the HA Heartbeat adapter. Possible values are:
When When |
| Port | string | –1 |
The TCP port to use for heartbeat connections. The default of –1 is deliberately invalid to force you to specify a valid, unblocked port for your site-specific server and network architecture. Ask your network administrator for advice. For a |
| Hostname/Address | string | localhost | For Server instances: not used.
For Client instances: hostname of the Server instance. For Multicast instance: multicast address to which to send multicast heartbeats. |
| Network Interface | string | The network interface to use when in multicast mode, this value can be the INet address or name of the interface.
Leave blank for default . |
|
| Heartbeat Interval (ms) | integer | 1000 | Number of milliseconds between heartbeats. |
| Heartbeat Timeout (ms) | integer | 2000 | Number of milliseconds in excess of the Heartbeat Interval that are permitted before declaring an instance of the adapter to be non-responsive. |
| Reconnection Attempts | integer | 0 | For Server instances: not used.
For Client and Multicast instances: number of times to attempt to reconnect to an unresponsive Server or Multicast instance. |
| Reconnection Sleep (ms) | integer | 5000 | For Server instances: not used.
For Client and Multicast instances: number of milliseconds to pause between reconnection attempts if a Server or Multicast instance is not responding. |
| Endpoint ID | string | none | For Server and Client instances: optional.
For Multicast instances: members of the Multicast group. |
The HA Heartbeat adapter has the standard Concurrency tab in its Properties View in StreamBase Studio.
Use the Concurrency tab to specify parallel regions for this instance of this component, or multiplicity options, or both. The Concurrency tab settings are described in Concurrency Options, and dispatch styles are described in Dispatch Styles.
Caution
Concurrency settings are not suitable for every application, and using these settings requires a thorough analysis of your application. For details, see Execution Order and Concurrency, which includes important guidelines for using the concurrency options.
This section describes the schemas for the input and output ports, and describes transition events emitted on the output port.
The input port of the HA Heartbeat adapter is flexible; it accepts a tuple using some or all of the schemas in the following table. The adapter looks for specific field names in the input tuple, and uses the values of those fields to change the state of the adapter. The fields can be in any order, as long as the exact field names in the table below are used.
Any fields not specified in the input tuple are taken from the default property values specified as a property of the adapter.
For example, you could send a tuple containing a single field named command. In this case, all other values would be taken from the adapter properties. Because of this feature, the schemas for an input
port typically match the values specified on the Adapter Properties tab of the Properties view.
| Field | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | string | A command string that causes the adapter to change state in some way. See Commands for a list of values for this field. |
| serverHost | string | The hostname of the HA Heartbeat adapter instance acting as the heartbeat server. |
| serverPort | int | The TCP port for the heartbeat server instance. |
| heartbeatInterval | long | The interval in milliseconds between each heartbeat. |
| heartbeatTimeout | long | Specifies how long in milliseconds the Client type adapter is to wait for a heartbeat to arrive. |
| reconnectAttempts | int | Specifies the number of times the Client type adapter is to attempt to reconnect to the server adapter. |
| reconnectSleep | long | Specifies how long in milliseconds the Client type adapter is to wait between reconnection attempts. |
The output port of the HA Heartbeat adapter has the following schema:
| Field | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| eventName | string | For each heartbeat, contains one of the status strings described in Output Port Transition Events. |
| hostname | string | Hostname of the adapter sending the output (Server or Multicast address) |
| port | int | The TCP port of the adapter that is sending the output. |
| receivedTimestamp | timestamp | When the heartbeat was received. |
| seqnum | long | A sequence number for the current heartbeat. |
| endpointId | string | Abstract name specifying source of heartbeat. |
| environment/leadershipstatus | string | Leadership status of the node where the heartbeat came from. |
The eventName field of tuples sent on the HA Heartbeat adapter's output port contains a string representing a state transition on that
adapter instance.
The following table shows the state transitions for a Server type adapter, and the corresponding eventName strings. In cases where there are two values (timeout and disconnected), the timeout event occurs first, and the disconnect occurs after the specified number of reconnect attempts (specified on the input port) has been completed.
| Server Adapter Transition Event | Corresponding eventName string sent |
|---|---|
| Adapter startup | (none) |
| A client HA Heartbeat adapter connects | connected |
| Heartbeat interval | heartbeat |
| A client HA Heartbeat adapter disconnects | timeout
disconnected |
| A client HA Heartbeat adapter hangs | timeout
disconnected |
| A client HA Heartbeat adapter unhangs | connected |
| A stop command was sent to the server adapter | disconnected
timeout |
The following table shows the state transitions for a Client type adapter and the corresponding eventName strings:
| Client Adapter Transition Event | Corresponding eventName string sent |
|---|---|
| Adapter startup | (none) |
| This client adapter connects to a server adapter | connected |
| Heartbeat interval | heartbeat |
| A stop command was sent to this client adapter | disconnected
timeout |
| The server adapter hangs | timeout |
| The server adapter unhangs before the client's reconnection interval or reconnection attempts have expired | reconnect |
| The server adapter unhangs after the client's reconnection interval or reconnection attempts have expired | disconnected |
| The server adapter stops or exits | timeout
disconnected (after the reconnection interval or reconnection attempts have expired) |
Typechecking fails if the adapter does not have streams connected to its input and output ports.
When suspended, a Client adapter stops sending heartbeats to its Server adapter. When suspended, the Server adapter stops responding to heartbeats from its Client adapters. On resume, both Client and Server HA Heartbeat adapters continue sending and responding to heartbeat tuples, respectively.
When suspended, a Multicast adapter leaves the multicast group, and when it is resumed it rejoins the multicast group.
