Python Execute (HD)
Runs a Jupyter notebook stored in your current workspace from a workflow in Team Studio.
Information at a Glance
- At least one input or output is specified in the notebook with argument use_input_substitution = True or use_output_substitution = True.
- Notebook input(s) argument execution_label are distinct and exclusively one of the following strings: 1, 2 or 3.
- For example, your Notebook code might look something like this:
df_account=cc.read_input_table(table_name='account', schema_name='demo', database_name='miner_demo',use_input_substitution=True, execution_label="1")
- Inputs/output defined with use_input_substitution = True must all be Hadoop inputs (in this case, the notebook is usable with the Python Execute (HD) operator).
Input
From zero to three inputs to use as substitute inputs for the notebook selected, depending on the number of inputs for substitution the notebook configuration allows.
You can substitute up to three inputs, or use the inputs defined in the notebook if you prefer not to specify substitutions. To run Python Execute, each substituted input must contain a superset of columns in the corresponding notebook input with compatible data types. One data set can be output, or zero outputs if this is a terminal operator in your workflow.
Depending on the notebook configuration for inputs and output, the operator can be a source operator (if no inputs are selected for substitution in the notebook), or a terminal operator (if no output is specified in the notebook). If a single output is specified, the operator transmits this output to subsequent operators.
Restrictions
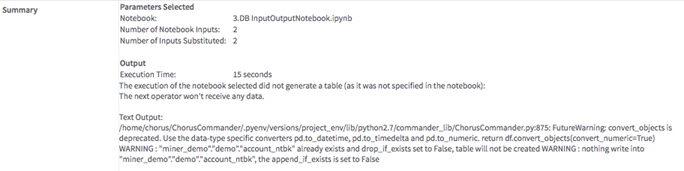
If the notebook selected has no tabular output defined with argument use_output_substitution = True, the Python Execute operator transmits no data to subsequent operators and is considered a terminal operator. Although following operators cannot run, the user can still draw a connection with subsequent operators.
Parquet and Avro inputs are supported only with PySpark notebooks (that is, the cc.read_input_file method in the notebook should have the sqlContext argument specified).
If the notebook selected is set up to transmit an output that contains variables with datetime format, the Python Execute operator transmits those as string variables to the next operator. (The user can then convert those to the correct format in a Variables operator.)
Configuration
Output
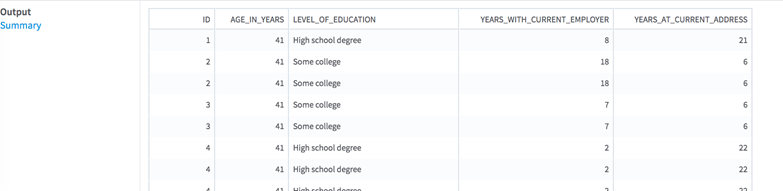
- Visual Output
- The operator result panel displays one or two tabs, depending on whether it is terminal.
- Data Output
- If the notebook contains an output with argument
use_output_substitution = True, the operator transmits a tabular data set to subsequent operators.
If no output is defined in the notebook, this operator is terminal.