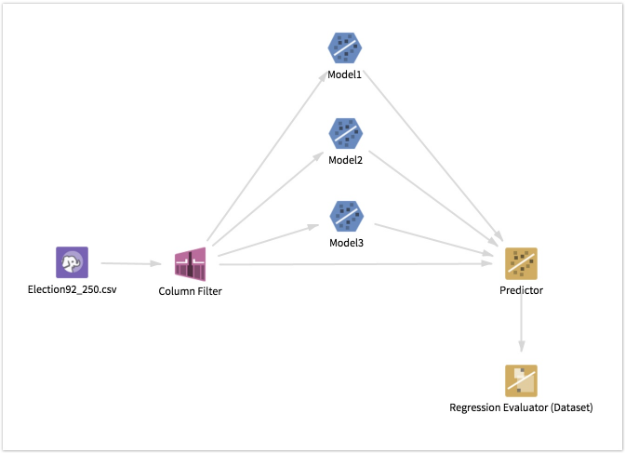
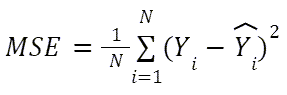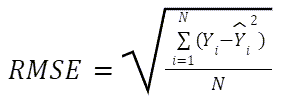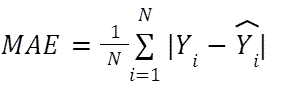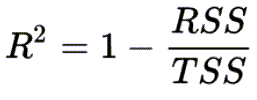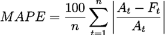Computed Metrics and Use Case for the Regression Evaluator
For model validation, the Regression Evaluator operator uses the MLlib regression evaluator. You can use it with.
| Accuracy | Description | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Mean Squared Error (MSE) |
The sum of the squared difference between actual and predicted columns, divided by the number of observations in the dataset. A value of 0 indicates that the predicted and actual values are the same for each observation. A very high value indicates that on average, the difference between actual and predicted values is very large. |
|
| Mean Squared Error (MSE) | The square root of the MSE metric. |
|
| Mean Absolute Error (MAE) | The average of the absolute difference between the predicted and actual columns for each observation. A value of 0 indicates that the predicted and actual values are the same for each observation. A very high value indicates that on average, the difference between actual and predicted values is very large in both directions. |
|
| Coefficient of Determination R2 ) | The proportion of the variance in the dependent variable that is predictable from the independent variables. See
Coefficient of Determination for more details.
An R2of 1 indicates that the regression line perfectly fits the data, while a value of 0 indicates that it doesn't fit the data at all. When a value is negative, it indicates that the regression model is worse than the horizontal line, and does not capture the trend of the data. |
RSS = sum of squares of residuals TSS = total sum of squares |
| Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) | A measure of prediction accuracy. It expresses accuracy as a percentage. However, it cannot be used if there are zero values, because there would be a division by zero. If a row contains a zero value, the row is skipped.
See Mean Absolute Percentage Error for more details. |
|
See the MLlib information at the Spark site for more information.
The Regression Evaluator operator (for either Regression Evaluator (DB) or Regression Evaluator (HD)) handles null values by eliminating them from the input calculation. If you want a different behavior, use the Null Value Replacement operator (for either Null Value Replacement (DB) or Null Value Replacement (HD)) on the initial training data to replace bad or missing values. All of the TIBCO Data Science – Team Studio MapReduce operators replace bad data with null values in a format suitable for the Regression Evaluator, so this operation does not fail on output of a MapReduce operator such as a Column Filter.