The Linear Regression option calculates the p-value under the assumption that there are no empty values in the data table.
Note: If there are empty values in the data table, the data table will first be reduced to the rows containing values for both the first and the second column.
Let n be the total number of values and denote by (xi, yi), i = 1, ..., n the set of data points to fit a straight line
![]() .
.
The least square estimates of ![]() and
and ![]() are:
are:
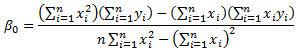
![]()
The p-value is then calculated from the F-distribution where the F-statistic is calculated with the sum of squares between the estimated line and the total mean of the yi's having one degree of freedom as numerator and the residual sum of squares divided by the number of degrees of freedom (n-2) as denominator.
References:
Arnold, Steven F., The Theory of Linear Models and Multivariate Analysis.
Rice, John A., Mathematical Statistics and Data Analysis, 2nd ed. pp 509.
Back to Overview of Data Relationships theory