Adding an image layer
With an image layer, you can configure your map chart to use images in combination with both geographical and non-geographical data. For example, you can add a background image and position markers on top of the image.
Procedure
Image layer examples
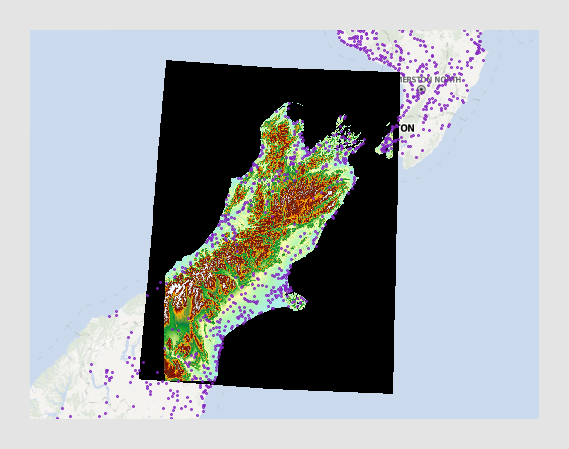
Using a background image works similarly to the map with markers, but with the difference that you do not need to have map data in a data table in order to set it up. If you use a GeoTIFF image, where geographical information is included as metadata in the image file, then the image will automatically be positioned correctly. The example below shows a GeoTIFF image that is projected onto a map layer, and the markers are placed on top of the image layer.
Note that for the GeoTIFF image to be placed correctly on the map, the image must include projection metadata, and that some projections are not supported.
With other types of image files, the data table must contain X and Y coordinates for the markers to be placed correctly in geographical positions.
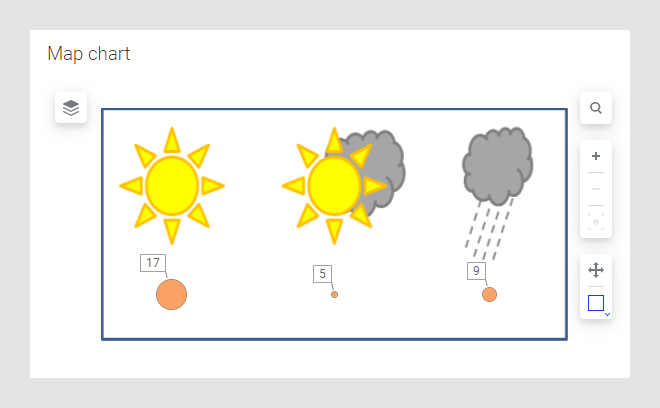
A map chart can also be used to show non-geographical data. The example below shows a map chart where the background is an image illustrating the three weather types sunny, partly cloudy, and rainy. The markers placed on top of the image show how many days in the month of August that were sunny, partly cloudy, and rainy respectively.
See Positioning markers on an image background to learn more about this example.