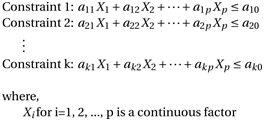Experimental Design Builder - Design Options Tab
Select the Design Options tab in the Experimental Design Builder to access the options described here.
Optimization Criterion. Specify what design criterion to be optimized during design creation.
- D-Optimal (useful for screening factors)
- D-optimal designs are important for inference with respect to the parameter estimates of the specified linear model. The design criterion maximizes the determinant of the information matrix, XTX (or for split plot designs XTV-1X, where V is the covariance matrix of the responses). This criterion is equivalent to minimizing the volume of the joint confidence region of the regression coefficients.
- I-Optimal (minimizes average prediction variance)
- I or IV-optimal designs minimize the average prediction variance of the design. These designs are useful when the emphasis is not specifically on inference of the regression parameters but rather in the precision of the predicted response, e.g., finding the settings of the factors that maximize yield.
Design generation options. Use these options to specify how Statistica should generate the optimal design.
- Random seed
- Specify the random seed, which is used to specify the random starting designs in the cyclic coordinate exchange algorithm.
- Number of random starts
- Specify the number of random starting designs for Statistica to try when searching for the optimal design. The more random starts that are tried, the more likely it is for Statistica to find a global optimum design.
- Number of exchanges per iteration
- Specify the number of design points, k, that are considered for exchange during each iteration of the algorithm. Statistica will find the k worst points in the current design, and for each point in turn, the value of each factor is changed to determine if this new value improves the quality of the design. If it does, the new value is used and the process continues as the algorithm searches across all factors.
- Number of grid points for each continuous factor
- Statistica uses a grid to search for new values of each continuous factor. Use this option to specify the number of grid points for Statistica to consider.
Advanced design options.
- Ratio of whole plot variance to error variance
- If there are hard-to-change factors in the design, Statistica will automatically add a random whole plot term to the design. The introduction of the random whole plot term introduces another source of error into the design, namely the whole plot error variance. In order to generate an optimal design, the ratio of the whole plot to error variance must be specified.
More specifically, the covariance matrix of the response in a split-plot design has a block diagonal structure where each block is a square matrix of dimension equal to the number of runs within the specific whole plot. The variance ratio, η, must be specified in order to generate this type of design. See below for an example of such a block. The variance ratio can be thought of as a measure of how correlated runs are within a given block.
- Number of whole plots
- If there are hard-to-change factors in the design, Statistica will automatically add a random whole plot term to the design. Specify the number of whole plots (random blocks) to place in this type of design. The number of whole plots is equal to the number of resettings of the hard-to-change factor(s). The minimum number of whole plots is equal to the number of coefficients in the model associated with only hard-to-change effects plus one additional whole plot for the intercept.
- Mixture sum
- If there are mixture factors in the design, you can specify the sum that the mixtures must total for each observation. The default values is 1.
- Place old and new runs into separate blocks
- If you are augmenting an existing design, select this check box to place old and new runs into separate blocks. Designs that consist only of Covariate (Categorical) and/or Covariate (Continuous) factors can be augmented.
Specify aliased effect(s). Click this button to display the Specify Effects dialog box, where you can specify the effects of interest. If 1 or more aliased effects are selected, Statistica will compute the alias matrix as well as the correlation matrix between the effects in the model and the selected aliased effects.
Constraints on design space.
- Add constraints to design
- Select this check box to specify linear constraints of continuous factors, that is, constraints of the form:
- Number of constraints
- Specify the number of constraints in the design.
- Define list of restricted factor combinations
- Select this check box to define a list of restricted factor combinations. Statistica will ignore the specified list of factor combinations when generating the optimal design.
- Add restrictions
- Click this button to display the Add restricted combinations of factor levels dialog box.
Specify constraints. Click this button to display a user-defined input spreadsheet where you can enter the coefficients of the linear constraints.
- Specify aliased effect(s)
- Click this button to investigate the aliasing structure between effects in the current design and those effects that are not present. A typical example of when you might want to do this is in the case of a screening design, which contains only main effects. In this case, if a main effect is significant in the subsequent analysis of the data, it may not actually be the main effect, which is significant, but rather a higher order term that was left out of the model and which is aliased with the main effect.
In general, it can be shown that the expected value of the least squares estimate,
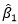 , corresponding to the coefficients of those effects in the current design,
, corresponding to the coefficients of those effects in the current design,
 , is equal to
, is equal to
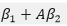 where A is the alias matrix and is equal to
where A is the alias matrix and is equal to
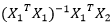 , where
, where
 is the set of columns corresponding to those effects that were not included in the design, and
is the set of columns corresponding to those effects that were not included in the design, and
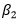 is the coefficient vector associated with those terms not included in the design. In general, the least squares estimate of the coefficient vector is biased, unless A is the zero matrix and/or
is the coefficient vector associated with those terms not included in the design. In general, the least squares estimate of the coefficient vector is biased, unless A is the zero matrix and/or
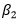 is the zero vector.
is the zero vector.
In order to gain better insight into the possible aliasing and confounding of the set of effects in the current design you can specify a set of aliased effects. After creation of the design, you can review the alias matrix and correlations between the current and aliased effects by clicking on the Alias matrix button on the Design Summary tab on the Results dialog.