Contents
This tutorial page describes how to use StreamBase Studio to build a runnable archive of a StreamBase Application, and automatically package that archive into a Docker container.
On this tutorial page, you will:
-
Configure a simple StreamBase Application.
-
Use StreamBase Studio to build a Docker-ready Image for that application.
-
Package this image into a Docker container managed locally in Docker Desktop.
To configure a StreamBase application for Docker, you must have:
-
StreamBase Studio.
-
A no-cost login on Docker Hub.
-
Docker Desktop for Mac or Windows installed, running, and logged into Docker Hub.
Note
When you obtain third-party software or services, it is your responsibility to ensure you understand the license terms associated with such third-party software or services and comply with such terms.
When configuring Docker Desktop, there is no need to enable the Kubernetes option at this point, but you can if you prefer.
Notes
The steps on this and the next few pages were tested in May, 2020 with release 2.3.0.2 of Docker Desktop for Windows and Docker Desktop for Mac, in both cases from the Stable release channel. Earlier releases of Docker Desktop and other Docker client solutions may work, but are explicitly not supported — including Docker Toolbox. Later releases of Docker Desktop are expected to work.
Docker Desktop for Windows requires 64-bit Windows 10 Pro or Enterprise with Microsoft Hyper-V available and enabled. Note that installing Hyper-V conflicts with VMware Workstation or Oracle VirtualBox on the same Windows computer, and the Docker Desktop installer disables those products if encountered. This is because Windows 10 allows only one virtualization hypervisor to run at the same time. See Docker's site for any further requirements of Docker Desktop for Windows.
Docker Desktop for Mac requires macOS 10.13 (High Sierra), 10.14 (Mojave), or 10.15 (Catalina). The Mac hardware must be a 2010 model or later. See Docker's site for any further requirements of Docker Desktop for Mac.
-
From StreamBase Studio, select >
In the search field for the StreamBase Sample Importer dialog, type
firstto narrow the list of options. Select theGetting Started Guide tutorialsearch result, then click .
-
It may take some time for Studio to build the loaded project the first time, as it resolves and copies Maven dependencies. The project is ready when there are no red marks on any folder or file of the
sample_firstapproject in the Project Explorer view.
You must invoke > to build and install the fragment project before packaging the StreamBase Application project.
Note
This step is not required before packaging application projects for regular use without Docker. In that case, the packaging wizard, described in the next section, installs all dependent fragments as part of the packaging.
Follow these steps:
-
In the Project Explorer view, select and right-click the
sample_firstappfolder. Select >(Be sure to select the option with the three dots. If you inadvertently run the other Maven build option and it fails, come back to this point and start over.)
-
In the Edit Configuration and launch dialog:
-
In the Goals field, enter
clean install
-
Select the Skip Tests and Resolve Workspace artifacts check boxes.

-
Click , then click .

-
-
Keep an eye on the Console view as messages scroll by. Look for the BUILD SUCCESS message.
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] BUILD SUCCESS [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] Total time: 4.980 s [INFO] Finished at: 2020-05-16T08:12:18-04:00 [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
The steps in this section create a StreamBase Application project with its Docker option enabled.
-
Optional. Open the
firstappproject's/src/main/eventflowfolder to make a note of the Group ID used by the EventFlow fragment project, which iscom.tibco.sb.sample. -
Select >>.
-
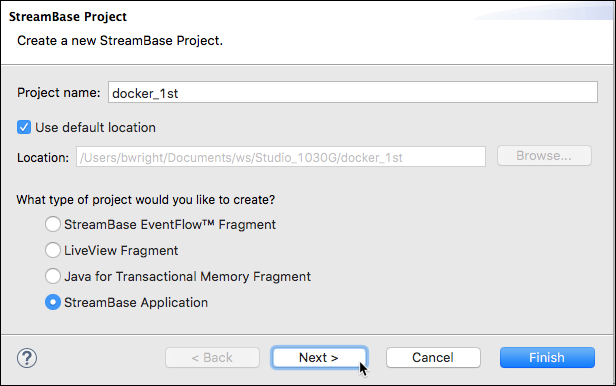
In the StreamBase Project dialog, enter a project name. This tutorial uses
docker_1stthroughout. -
Select the StreamBase Application option and click Next. (If you click in error, start over.)
-
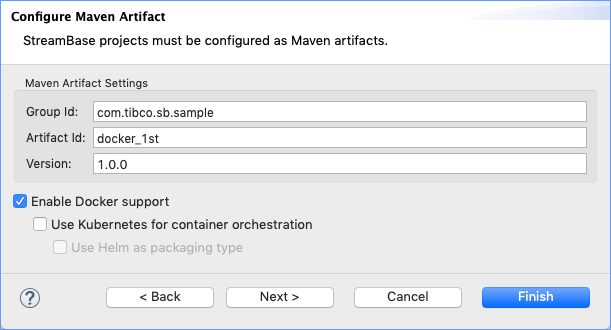
In the Configure Maven Artifact panel, change the value of the Group ID to
com.tibco.sb.sampleto match the Group ID of the fragment sample as determined in step 1. (You are not required to use the same Group ID for an Application project as for its dependent fragment projects, but doing this brings clarity to the process.)Select the Enable Docker support check box. This is the entire difference between building an application that runs locally and one that runs in a Docker container.
Optional. This tutorial suggests changing the Version number to
1.0.0to save some typing with upcoming Docker commands, but that is not required.Click .
-
Optional. Make changes In the Archetype Properties panel as needed, following the guidelines in the table below.

Property Default Description description My ApplicationEnter any text to characterize this application and distinguish it from other applications in your network. This string ends up in the <description>element of your application project'spom.xmlfile.testnodes A,B,CSpecify one or more node names for test nodes that are started when you run Maven Test or another Maven goal that requires Test. You can reduce project build time at the expense of test coverage by replacing the default three nodes, A,B,Cwith justA.dockerDomain example.comSpecify a domain name that will allow your Docker containers to communicate with each other. The domain name you specify here is configured into a TrustedHostsconfiguration file for this application. This allows all StreamBase Runtime nodes to participate in the same domain as the Docker containers, which allows node-to-node communication to occur without user authentication for nodes in the same Docker network. Members of this domain will be trusted hosts for each other.To take advantage of this feature, use the
--networkand--hostnameoptions in yourdocker runcommand, as described in Configuring Multiple Docker Containers. -
Click . (Also click if prompted with a follow-up dialog.)
This creates a new project named
docker_1stin the Project Explorer view.
The next step is to configure docker_1st application
project to be aware of its Maven dependency on the firstapp EventFlow fragment project.
-
Select the
docker_1stproject name in the Project Explorer view. Right-click and select >. -
Studio shows a message dialog like the following.

When you click , Studio performs the following actions:
-
Opens the POM Editor for the application project's
pom.xmlfile. -
Switches to the Dependencies tab of the POM Editor.
-
Opens the Add Dependency dialog,
-
-
In the Add Dependency Dialog, type
firstappin the Enter groupId filter field. -
Select com.tibco.sb.sample firstapp in the Search Results field and open the arrowhead on its left.
If there is more than one
ep-eventflow-fragmententry (perhaps because your local Maven repository has artifacts from previous StreamBase releases), select the entry whose version number matches the current StreamBase release.Click .

-
Confirm that the
pom.xmlfile for thedocker_1stproject is saved.
Build the Docker image as follows:
-
Make sure your development machine is connected to the Internet. This procedure runs best with no
settings.xmlfile in your local~/.m2directory, or with a minimal one. -
Important! Make sure your Docker for Windows or Docker for Mac installation is currently running, and that you are logged into Docker Hub.
-
In the Project Explorer view, select and right-click the
docker_1stfolder. Select >. -
This opens the Package an Application dialog.

-
There is nothing to configure on this dialog (unless something went wrong in a previous run), so click .
-
Keep an eye on the Output of packaging steps (which has the same content as the Console view) as messages scroll by. Look for one BUILD SUCCESS message for the fragment included in the application, plus a final BUILD SUCCESS message.

-
To confirm success, open a StreamBase Command Prompt (Windows) or a StreamBase-configured Terminal window (macOS). Get a list of your currently installed Docker images using the
docker imagescommand:REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE deploy_1st 1.0.0 5dbddbadc3e1 23 minutes ago 1.02GB sbrt-base 10.6.0 c39719f31fba 2 hours ago 1.02GB centos 8 470671670cac 3 months ago 237MB
Your
imageslist may include other Docker images from running the Docker Getting Started tutorial, or from Kubernetes setup. The three images listed above are the ones generated by the Package Application dialog.
This concludes the work in StreamBase Studio to generate the StreamBase Application archive and package it into a Docker image in your local Docker environment.
The tutorial continues on the next page to demonstrate using Docker commands to run this image, and communicate with the containerized StreamBase application. Use the Next link on the bottom right below, or click Tutorial: Run and Manage with Docker Commands.
