Contents
This topic describes the various ways to aggregate data into and out of LiveView tables.
TIBCO LiveView supports the aggregation of data in three ways:
- Dynamic Aggregation
-
Dynamic aggregation uses ad hoc aggregate functions expressed in a query sent to a LiveView Server instance over a client connection. Client connections include those made by LiveView Desktop, lv-client, and any custom querying utility or function you have made using the LiveView Client API.
Use dynamic aggregation in cases like the following:
-
You are using LiveView Desktop, and you want to collate the results of certain columns into groups.
-
You are pursuing data mining on a new set of data streams and you need to figure out which aggregate functions provide the most valuable insights.
-
You want to use special LiveView query structures, such as time windows, to limit a query's scope.
-
- Author-Time Aggregation
-
Author-time aggregation is configured in a LiveView configuration file that defines a LiveView data table with an aggregation data source. Author-time aggregations run on the LiveView Server and cannot be changed once the server has started. Use author-time aggregation in cases like the following:
-
You have a large team viewing and analyzing the same data using the same aggregate querys. In this case, having several users issuing similar aggregate queries simultaneously against the same LiveView Server instance may have adverse effects on server performance.
-
You want to use additional LiveView table-based features, such as alerting, on your aggregated data. In this case, configure an aggregate table and then configure an alert against that table.
-
- Static Aggregation (Deprecated)
-
Static aggregation was provided in LiveView releases before 2.0 as another version of aggegation defined in lvconf files for running on LiveView Server. Static aggregation is still supported by LiveView 2.x servers, but this feature is now deprecated and will be removed in a future release.
For both dynamic and author-time aggregation, the projection portion of the query must include one or more expressions that start with one of the aggregation functions listed in the Aggregation Function Reference. The body of each expression can in turn contain any expression construction that is valid in the StreamBase expression language. Notice that both dynamic, ad-hoc aggregation and server-based, author-time aggregation use the same set of initiating aggregation functions.
In contrast to the simple functions of the StreamBase expression language, which do not maintain state, the LiveView aggregation functions do maintain state, and allow you to return a single value from a group of input rows. Continuously updated aggregate values are emitted as a data stream.
The deprecated static aggregation feature supports a small set of specialized aggregate functions listed in Legacy Static Aggregation (Deprecated). See the comparison of the two sets of functions below.
Dynamic aggregation is the name for ad hoc queries that aggregate data in some way. You use dynamic aggregation in a query sent over a client connection to a LiveView Server instance, by specifying a query projection that contains one of the supported aggregate functions.
An aggregate expression uses the following basic syntax:
aggregate-function(expression) ASalias
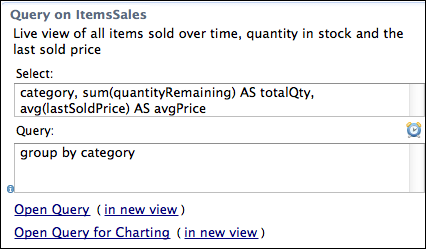
You can use the Select and Query fields in the Tables view of LiveView Desktop to create aggregate queries. The Select field in LiveView Desktop is analogous to the SELECT clause in a SQL statement; the Query field is analogous to the WHERE or WHEN clauses.
|
The examples in this section are based on a LiveView Desktop connection to a LiveView Server instance running the Hello LiveView sample.
-
To return the total number of items in the
ItemsSalestable and the average price of all these items, enter nothing in the Query window and the following text in the Select window:sum(quantityRemaining) AS totalQty, avg(lastSoldPrice) AS avgPrice
Accompany this text with an empty Query field.
This returns a single row containing the fields totalQty and avgPrice.
-
The Query field contains the query predicate. For example, to break down the previous aggregate query by category and item, use the following text in the Select window:
category, sum(quantityRemaining) AS totalQty, avg(lastSoldPrice) AS avgPrice
Then use the following text in the Query field:
GROUP BY category
-
A GROUP BY entry is required for any simple field name by itself in the Select window — that is, a field name that is not part of an aggregate function. To include a field from the table without grouping on it, you can use
lastval(. For example:field-name)lastval(Item) AS Item, category, sum(quantityRemaining) AS totalQty, avg(lastSoldPrice) AS avgPriceUse the following text in the Query field:
GROUP BY category
-
An aggregate query can incorporate any simple function and all features of the StreamBase expression language. For example, a query can use an
ifstatement to create conditions for inclusion in the aggregation. The following expression in the Select field counts the number of copies sold of a specific book in the ItemsSales table:count(if (Item=='Tom Sawyer' AND category=='book') then true else bool()) as TomSawyerSoldAccompany this text with an empty Query field.
-
You can also use aliases for individual field names that are not part of an expression, which changes the field name in the result table. For example:
category AS Department, avg(lastSoldPrice) AS AverageSalePrice
Use the following text in the Query field:
GROUP BY category
LiveView data tables can have as a data source the aggregated results of data published to another LiveView table. This is sometimes called author-time aggregation, because the query's aggregate and predicate expressions are written in the lvconf file that defines an aggregation table, and cannot be changed once the LiveView Server is running. The LiveView table with the aggregate results is called the aggregate table, while the LiveView table used as a source is called the base table.
An aggregate expression is the projection portion of a query, where the expression contains one of the supported aggregate functions. The projections used in author-time aggregation are identical to those used by LiveView clients when they send ad hoc, dynamic aggregate queries to LiveView.
Just like ad hoc client aggregate queries, author-time aggregation predicates can use
any simple function and any feature of the standard StreamBase expression language.
The predicate can include simple expressions such as Price > 10.0 and can also contain a time
windowed component such as when transactionTime
between now()-minutes(1) and now().
The primary key of the aggregate table defines the projection's GROUP BY field or fields. Aggregate table primary key fields are automatically populated from the base table; do not include them in the projection.
Each aggregate function in the projection must use the AS keyword to assign a target
field name in the aggregate table where the aggregate result is written. For example,
in the expression sum (lastSoldPrice) as
MySum, MySum is a non-primary key field
in the aggregate table, and lastSoldPrice is a field in the base table.
The fact that dynamic and author-time aggregation both use the same set of aggregation functons means you can develop and refine the projection and predicate that will be used in an author-time aggregate table by making ad hoc queries with a LiveView client such as LiveView Desktop. Once you have narrowed down the exact result desired, you can copy the projection and predicate portions of the the ad hoc query into the projection and predicate sections of the aggregate table's data source specifications.
The Hello LiveView sample provides an example of author-time aggregation. It has a
base table named ItemsSales where each new item
purchased inserts a new row. It also has an author-time aggregation table named
ItemsInventory which has an aggregate data source
specified in its lvconf file that references the ItemsSales table.
To specify an aggregation table using the Lvconf Visual Editor, use → → to create a Data Table type configuration.
Specify a schema for this table using the fields you want to aggregate over, using the same field names you will specify with the AS keyword.
In the Data Sources tab of the Lvconf Visual Editor, select the Aggregation check box, which opens a three-field section on the right. Fill in these three fields as follows:
-
Table Reference: use the drop-down list to select the basename of lvconf file in the current project that defines the base table you want to use.
-
Projection: enter the tested, known working projection portion of the aggregate query you will use to select data from the base table and apply an aggregation function on. The projection also defines with the AS keyword the names of the columns in this aggregation table that will receive the aggregated data.
-
Predicate: enter an optional predicate portion of the aggregate query.
Since author-time aggregation tables have the same features as ad hoc queries, why use them?
Aggregate queries use more CPU and memory resources than simple queries. Resource consumption increases as the number of aggregate functions in a projection increase. Using aggregate functions that can underflow can be especially expensive. If there are a number of users that all desire to have the same aggregate data, it is generally much more efficient to aggregate the data once in an author-time aggregation table and have all the users issue a simple query to the aggregation table.
Another reason to use aggregation tables is to maintain central control over what data is aggregated and how it is done. Administrators might also wish to limit access to base tables by means of LiveView authentication and entitlements, while allowing access to aggregated data.
LiveView releases before 2.0 provide a different implementation of aggregate tables which was called static aggregation. This legacy implementation is deprecated starting with LiveView 2.0 and is not supported by the LVconf Visual Editor. While deprecated, the static aggregation table implementation remains unchanged in 2.0, so existing static aggregation tables will continue to work as before against a LiveView 2.0 server.
Static aggregation uses a LiveView-specific set of aggregate function implementations as listed in Legacy Static Aggregation (Deprecated). These functions are a subset of the functions supported by dynamic and author-time aggregation. Static aggregation does not support a predicate that allows filtered aggregation.
New aggregation tables in new or newly maintained projects should use author-time aggregation going forward.
Static aggregation tables were configured using <field-map> elements that contained individual <field> elements in the defining lvconf file. This feature
provided a map that converted a base table's schema into the aggregation table's
schema; see an example of such a configuration in the description of the static
Avg function.
It is not difficult to migrate static aggregation table configurations to the author-time aggregation table projection strings. TIBCO encourages but does not require such migration starting with LiveView 2.0.
The following table compares the aggretation functions provided for dynamic and author-time aggregation, and compares them with the functions provided for the legacy static, table-based aggregation.
In the first column, each function is linked to its reference manual description. In the second column, all legacy static aggregation functions are documented on the same page.
Notice that all legacy static aggregation function names begin with an uppercase
letter, while all dynamic and author-time aggregation function names begin with a
lowercase letter. All function names are case-sensitive, which helps keep the two
sets of functions separate, especially where the names are the same in the two lists
except for the initial uppercase letter. In addition, in the four legacy functions
whose names end with If, the I is uppercase.
| Aggregate Functions for Dynamic and Author-Time Aggregation | Aggregate Functions for Legacy Static Aggregation |
|---|---|
| avg() | Avg() |
| correlation_coefficient() | ― |
| correlation_coefficientp() | ― |
| count() | Count() |
Use count(if
|
CountIf() |
| covariance() | ― |
| covariancep() | ― |
| firsval() | ― |
| intercept() | ― |
| joinlist() | ― |
| lastval() | ― |
| max() | Max() |
| min() | Min() |
| product() | ― |
| slope() | ― |
| stdev() | Stdev() |
Use stdev(if
|
StdevIf() |
| stdevp() | Stdevp() |
Use stdevp(if
|
StdevpIf() |
| sum() | Sum() |
Use sum(if
|
SumIf() |
| unique() | ― |
| variance() | ― |
| variancep() | ― |
| vwap() | ― |
