Selecting Columns
The columns you select define the input to your data target. If you are using the Data Management Consoleibi Data Migrator desktop interface to format a new data target, the order of the columns will reflect the order that the columns are specified in the SQL command.
The Server, which ibi Data Migrator uses to process its extraction logic, can have up to approximately 400 columns in a single data flow. If you intend to move more than 400 columns, several data flows may be linked together by creating a process flow. For information on process flows, see Designing a Process Flow.
Automatically Select All Columns
The default settings of the Data Management Consoleibi Data Migrator desktop interface require you to manually select the columns you want to extract. To change your settings so that all columns are selected automatically:
- Procedure
- On the Home tab, in the Tools group, click Options.
- Expand Data Flow and select Data Flow Designer from the tree.
- Select the Automatically select all columns checkbox in the On Add Source section.
- Click OK.
Select Columns
- Procedure
- Right-click
the SQL object in the data flow workspace and click Column
Selection.
The Column Selection dialog opens.
- Double-click
the columns you want to select from the Available Columns grid on
the left.
Or
Select one or more columns and click the right arrow.
Tip: To select all columns, click anywhere in the column list, and press Ctrl + A.The columns appear in the Selected Columns grid on the right.
- You can change the order of the columns by selecting them and clicking the up and down arrows.
- Optionally, you can select the Distinct checkbox to remove duplicate rows from the results of your query.
- You can rename a selected column by entering a name in the Sql Alias field.
- To remove a column from the Selected Columns grid, select it and click the left arrow, or click the Delete button.
- Click OK.
Edit Selected Columns
- Procedure
- Right-click
the SQL object in the data flow workspace and click Column
Selection.
The Column Selection dialog opens.
- Select the column you want to edit.
- Click
the Edit column button, or double-click the
number next to the column in the Selected Columns grid.
The SQL Calculator opens.
- Using the Columns/Variables and Functions tabs and the calculator buttons, edit the expression for the column. For information about using functions, see Using an SQL Function. For information about using variables, see Using Variables in a Flow.
- Click OK.
For information about creating a calculated column in the Selected Columns grid, see Creating an SQL Calculation.
Add or Change Column Descriptions From the Column Selection dialog
If a column in a source synonym has a description, that description will be carried over with the column into any new target synonyms. You can also use the Column Selection dialog to add descriptions for columns that do not have them, or to change the descriptions for columns that do have them. These descriptions will also be carried over into any new target synonyms in the current flow.
- Procedure
- From
the data flow workspace, double-click the SQL object,
or right-click it and click Column Selection.
The Column Selection dialog opens.
- Double-click the Description field for the column in the Selected Columns grid.
- Type the description.
- Click OK.
Column Selection dialog
To access the Column Selection dialog from the data flow workspace, double-click the SQL object, or right-click it and click Column Selection.
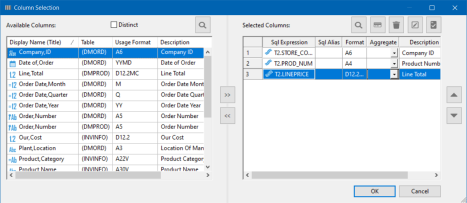
The Column Selection dialog contains the following fields and options by default:
Removes duplicate rows from the results of your query.
Lists the columns in each data source.
Adds columns to the Selected Columns grid.
Deletes columns from the Selected Columns grid.
Lists the columns to be extracted from the data source(s).
Is the column name, or an expression created in the SQL Calculator.
Is an alternate name for referencing the column. If you add an alias and expression, the expression shows up where the column name would normally be.
Is the format of the column.
Is the aggregation applied to the column.
Is the description of the column.
Indicates whether the column can contain NULL values.
Allows you to search for a column.
Opens the SQL Calculator to create a column.
Deletes the selected column.
Opens the SQL Calculator to edit a column.
Tests the SQL statement and displays the result.
Moves the selected column up or down within the Selected Columns grid.
If you right-click anywhere on the header bar, you get the following options:
Allows you to search for a column.
Resizes the column to fit its data.
Allows you to select what information is displayed for each column.
If you right-click any column, you get the following options:
Opens the SQL Calculator where you can edit the properties of a column.
Deletes the selected column.
Aggregating Columns
You can aggregate your columns in the Column Selection dialog.
Aggregate a Column
In the Column Selection dialog:
- Procedure
- Select the column or columns you want to aggregate. To select more than one column, hold the Shift or Ctrl keys while selecting columns.
- Click
the down arrow in the Aggregate field to display the dropdown menu
containing the types of aggregation, and select an aggregation.
Some of your options are:
- Group By. Groups the data by each distinct value in the column.
- Group By Not Selected. Groups the data on (or by) the column that you do not want to appear in the results.
- Sum. Adds the values within the column.
- Min. Returns the minimum value found in the column.
- Max. Returns the maximum value found in the column.
- Count. Returns a count of all non-null column values.
- Avg. Returns the average value for the column.
- Sum Distinct. Adds the distinct values within the column, excluding duplicates.
- Count Distinct. Returns a count of all distinct, non-null column values, excluding duplicates.
- Avg Distinct. Returns the average value for the column, excluding duplicates.
Creating an SQL Calculation
You can create an SQL calculation for your data flow that:
- Renames a column.
- Performs a calculation. For details, see Create a Calculation.
- Designates a constant value for a column.
- Uses a variable to calculate a column. For details, see Create a Column That Uses a Variable.
Create a Calculation
- Procedure
- In the
Column Selection dialog, click the Insert Columns button.
The SQL Calculator opens.
- Enter the calculation you want to perform using the Columns/Variables and Functions tabs, and the calculator buttons. For details, see SQL Calculator. For information about using functions, see Using an SQL Function. For information about using variables, see Using Variables in a Flow.
- In the Alias box, enter an alias for the column.
- Click OK.
The calculation appears in the SQL Expressions field.
Note: When you create expressions, keep in mind their order of evaluation. For details, see Order of Evaluation. - Optionally,
select an aggregation for the column in the Aggregate field.
For details, see Aggregating Columns.
Note:
- You can type a calculation directly into the Selected Columns grid by double-clicking the Sql Expressions field.
- You can type an alias directly into the Selected Columns grid by double-clicking the Sql Alias field.
Create a Column That Uses a Variable
From the Column Selection dialog:
- Procedure
- Click
the Insert Columns button.
The SQL Calculator opens.
- Type an alias for the virtual column.
- Double-click the variable you want assigned to the column from the Columns/Variables tab. You can also type in character-valued or date-valued variables, which must be enclosed in single quotation marks (‘).
- Click OK.
The variable and alias appear in the Selected Columns grid.
For more information about using variables, see Using Variables in a Flow.
SQL Calculator
To access the SQL Calculator from the Column Selection dialog, click the Insert Columns button, or select a column and click the Edit Column button.
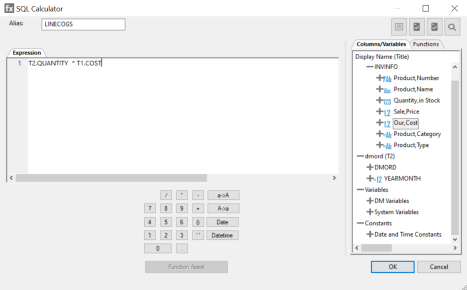
The SQL Calculator contains the following fields and options:
Is an alias for the column.
Displays the expression.
Opens the Filter SQL Optimization Report, which allows you to specify settings for, and run, the report.
Verifies the validity of the expression.
Tests the SQL statement and displays the result.
Allows you to search for a function or variable by name.
Displays available columns and variables in a hierarchical tree or in a grid.
Displays a list of SQL functions that are available for your transformations.
Allows you to specify parameters for the function through a dialog when creating or editing a transformation.
Insert numbers and operators.
Adds parentheses.
Inserts two single quotation marks (‘). Enter alphanumeric test values between these.
Converts selected text to uppercase.
Converts selected text to lowercase.
Opens the Date Editor dialog, which lets you use the current date or specify a date from the calendar.
Opens the Date Editor dialog, which lets you use the current date and time or specify a date and time from the calendar.
SQL Operators
The following table describes the result of an operator on an expression, where expr is an expression.
|
Operator |
Result |
|---|---|
|
expr + expr |
Returns the sum of two expressions. |
|
expr - expr |
Returns the difference of two expressions. |
|
- expr |
Returns the negated value of an expression. |
|
expr * expr |
Returns the product of two expressions. |
|
expr / expr |
Returns the dividend of two expressions. |
|
expr || expr |
Returns the concatenation of two character strings. |
Using an SQL Function
You can use an SQL function in the SQL Calculator to create a complex expression. In addition, most ANSI 92 SQL functions can be used in a SELECT command, depending on the data source type and platform.
Use an SQL Function
- Procedure
- In the SQL Calculator, click the Functions tab.
- Double-click the folder for the type of function you want to use.
- Double-click
the function you want to use.
The Function Assist dialog opens.
- Use the Function Assist dialog to set the parameters for the function and click OK.
- The function appears in the Expressions dialog. Click OK.
- The function is added to the Selected Columns grid of the Column Selection dialog.
For more information about the Function Assist dialog, see Use Function Assist.
SQL Functions
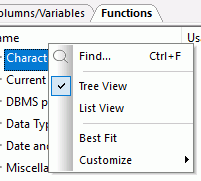
You can view the functions in the SQL Calculator Functions tab by category (Tree View) or alphabetically (List View). Right-click the Name header bar to select between the two views, as shown in the following image. For more information about SQL functions, see the SQL function chapters in the ibi Data Migrator Functions Reference manual.
|
SQL Character Functions |
Description |
|---|---|
CHAR_LENGTH(arg)
|
Returns the length of arg in a character string. |
CONCAT(arg1, arg2) |
Concatenates the values of two arguments. |
EDIT(arg, mask) |
Edits a numeric or character value according to a format specified by a mask. |
GET_TOKEN(string, delimiter_string, occurrence) |
Extracts a token from an input string. |
INITCAP(string)
|
Capitalizes each word in a string, where a word is delimited by white space or characters that are not alphanumeric. |
LCASE(arg)
|
Converts a character string value to lowercase. Identical to LOWER and LOWERCASE. |
string LIKE mask [ESCAPE escape] |
Select records that conform to a pattern. |
LPAD(string, out_length, pad_character) |
Left pads a character string with the pad character to the length specified in out_length. |
LTRIM(arg)
|
Removes leading spaces from a character string. |
PATTERNS(string)
|
Returns a string that represents the pattern of the input string. |
POSITION(substring IN arg) |
Returns the location of substring in arg, or returns a zero if substring is not found. |
REPLACE(string, pattern, [replacement]) |
Replaces the pattern in the pattern in the string with the replacement (if supplied) or removed. |
REVERSE(string)
|
Reverses a character string. |
RIGHT(source_string, substring_limit) |
Returns the right portion of an input string. |
RTRIM(arg)
|
Removes trailing spaces from a character string. |
string RLIKE regular_expression |
Matches a string to a Regular Expression. |
RPAD(string, out_length, pad_character) |
Right pads a character string with the pad character to the length specified in out_length. |
RTRIM(arg)
|
Removes trailing spaces from a character string. |
SPLIT(part, string) |
Returns a part from a string. |
SUBSTR(arg FROM start-pos[FOR length]) |
Returns a string from arg starting at start-pos to the end of the string, or if specified length characters. |
SUBSTR(arg, start_pos[, length]) |
Returns a string from arg starting at start-pos to the end of the string, or if specified length characters. |
TOKEN(string, delimiter, number) |
Extracts a token from a string. |
TRIM(arg)
TRIM(trim_char FROM arg) TRIM(trim_where[trim_char] FROM arg) |
Removes leading and/or trailing spaces and other characters from a character string. The character to be removed may be specified as trim-char. If it is not, the space character is assumed. Whether to remove leading and/or trailing characters may be specified as trim-where. If not, both leading and trailing spaces are removed. |
UCASE(arg)
|
Converts a character string value to uppercase. Identical to UPPER and UPPERCASE. |
|
SQL Current Date and Time Functions |
Description |
|---|---|
CURRENT_DATE |
Returns the date in YYMD format. |
CURRENT_TIME[(precision)]
|
Returns the current time of the operating system in the form, HHMMSS. |
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
[(precision)]
|
Returns the current timestamp of the operating system (date and time) in the form, YYYYMMDDHHMMSS. |
CURRENT_TIMEZONE() |
Returns the current time zone. |
|
SQL Data Type Conversion Functions |
Description |
|---|---|
CAST(expression AS data_type[(length)]) |
Converts the value of its argument to a specified data type. Length is an optional integer that specifies the length of the target data type. |
CHAR(arg[,date_format]) |
Converts a number to a character string, or data value to a string in a specified format. |
DATE(arg)
|
Returns a date, time, or timestamp value that is computed from arg. |
DECIMAL(arg, [length [dec_places]]) |
Converts a number into a fixed-length decimal where dec-places is the number of decimal places in the result. |
DIGITS(arg)
|
Converts a numeric expression to a fixed length character string. Db2 only. |
DT_FORMAT(arg, date_format) |
Converts a date/timestamp expression to a character string. |
FLOAT(arg)
|
Converts arg to a floating point value. |
FOCDATE(arg, format) |
Converts an alphanumeric expression to a date. |
INT(arg)
|
Converts a number to an integer. Identical to INTEGER. |
OLDDATE(arg, format) |
Converts a date expression to an alphanumeric value. |
PHONETIC(string)
|
Returns the phonetic key of the string. |
SMALLINT(arg)
|
Converts a number to a small integer. |
TIME(arg)
|
Converts the argument to a time. |
TIMESTAMP(arg)
|
Converts the argument to a timestamp. |
VARGRAPHIC(arg)
|
Converts the argument to a vargraphic. |
|
SQL Date and Time Functions |
Description |
|---|---|
DAY(arg)
|
Returns a number that contains the day of the month from a date or timestamp. |
DAYS(arg)
|
Returns the number of days since December 31, 1900. |
DAY_OF_YEAR(arg)
|
Returns an integer from 1 to 366 that represents the day of the year for a date or date-time expression. |
DTDIFF(end_date, start_date, component) |
Returns the number of component boundaries between two dates. |
DTIME |
Returns the value of all of the time components up to and including the requested component. The remaining time components in the value are set to zero. |
DTRUNC(date_or_timestamp, date_period) |
Returns the date, which is the first day of the date period (YEAR, QUARTER, MONTH, DAY, etc.), encompassing the given date or timestamp. |
datetime + INTERVAL increment c omponent |
Returns a new date or date-time value by adding an interval to a date or date-time expression. |
EXTRACT(field FROM arg) |
Extracts a numeric value from a date or time value arg, where field is either a year, month, day, hour, minute, or second. |
HOUR(arg)
|
Returns the hour field from a time or timestamp value. |
MICROSECOND(arg)
|
Returns the number of microseconds from a time or timestamp value. |
MILLISECOND(arg)
|
Returns the number of milliseconds from a time or timestamp value. |
MINUTE(arg)
|
Returns the number of minutes from a time or timestamp value. |
MONTH(arg)
|
Returns the number of the month in which arg falls. |
QUARTER(arg)
|
Returns an integer value representing the quarter of the year for a date or date-time expression. |
SECOND(arg)
|
Returns the second field from a time or timestamp value. |
WEEKDAY(arg)
|
Returns an integer value between 1 and 7 representing the day of the week for a date or date-time expression. |
YEAR(arg)
|
Returns the year in which arg falls. |
|
SQL DBMS Pass-Through Function |
Description |
|---|---|
DB_EXPR(sql_expression )
|
Inserts the SQL expression as-is into the native SQL generated for an SQL language request. |
|
SQL Miscellaneous Functions |
Description |
|---|---|
COUNTBY(arg)
|
Produces a column whose values are incremented row-by-row by a specified amount. |
CURRENT_EDASQLVERSION() |
Retrieves the current SQL parser version. |
GREATEST(arg1,arg2[,...arn]) |
Finds the maximum value. |
HEX(arg)
|
Converts the input value to hexadecimal. Note: This
function is available only for Db2, Ingres, and Informix.
|
IF(test, val1, val2) |
Tests a condition and returns a value based on whether the condition is true or false. |
LEAST(arg1,arg2[,...arn]) |
Finds the minimum value. |
LENGTH(arg)
|
Returns the number of bytes of storage used by arg. |
USER() |
Returns the user ID running the query. |
|
SQL Numeric Functions |
Description |
|---|---|
ABS(arg)
|
Returns the absolute value of a number. |
CEIL(number)
|
Returns the smallest integer that is greater than or equal to the number. |
EXP(arg)
|
Returns e raised to the power of the argument. |
FLOOR(number)
|
Returns the largest integer that is less than or equal to the number. |
LOG(arg)
|
Returns the natural logarithm of the input value. |
MOD(dividend, divisor) |
Calculates the remainder from a division as an integer. |
POWER (arg1, arg2)
|
Returns the first number raised to the power of the second. |
RAND(seed)
|
Returns a stream of random numbers uniformly distributed between 0 and 1. |
SIGN(arg)
|
Returns a value (1 or -1) identifying the sign of the number. |
SQRT(arg)
|
Returns the square root of the input value. |
|
SQL Operators |
Description |
|---|---|
CASE test-expr WHEN value-expr-1 THEN result-expr-1 . . . WHEN value-expr-n THEN result-expr-n [ ELSE else-expr ] END |
Allows a value to be computed depending on the values of expressions. |
CASE WHEN cond-1 THEN result-expr-1 . . . WHEN cond-n THEN result-expr-n [ ELSE else-expr ] END |
Allows a value to be computed depending on the truth or falsity of conditions. |
COALESCE(arg1, arg2, [ ... argn ]) |
Can take two or more arguments. The first argument that is not NULL, is returned. If all arguments are NULL, NULL is returned. |
EXISTS(SELECT * FROM LOOKUP_MFD SQ [WHERE condition] )
|
Tests if subquery returns one or more rows. |
NULLIF(arg1, arg2) |
Returns NULL if its two arguments are equal. Otherwise, the first argument is returned. |
test_exp1 IN (exp1, exp2) |
Determines whether a specified value matches any value in a list. |
(SELECT lookup_result from LOOKUP_MFD [WHERE condition]) |
Used in a select list to return a column value. |
(SELECT * FROM LOOKUP_MFD SQ [WHERE condition] )
|
Returns result set based on subquery. |
(test_exp1, test_exp2) IN ( SELECT exp1, exp2 FROM mfd WHERE condition) |
Determines whether a specified value matches any value in a subquery. |
|
SQL Aggregation Functions |
Description |
|---|---|
ASQ(field)
|
Computes the average sum of squares of the field. |
AVG(field)
|
Computes the average of the field. |
AVG(DISTINCT field)
|
Computes the average of the distinct values of the field. |
COUNT(field)
|
Counts the number of occurrences of the field. |
COUNT(DISTINCT field)
|
Counts the number of distinct values in the field. |
MAX(field)
|
Computes the maximum value of the field. |
MEDIAN(field)
|
Computes the median of the field values. |
MIN(field)
|
Computes the minimum value of the field. |
MODE(field)
|
Computes the mode of the field values. |
SUM(field)
|
Computes the sum of the field values. |
SUM(DISTINCT field)
|
Computes the sum of the distinct values in the field. |
|
SQL Analytic Functions |
Description |
|---|---|
AVG(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part] ORDER BY ord [window]) |
Calculates the average over a group of lines determined by a partition and window. |
COUNT(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part] ORDER BY ord [window]) |
Calculates the count over a group of lines determined by a partition and window. |
DENSE_RANK(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part] ORDER BY ord]) |
Calculates the dense rank over a group of lines determined by a partition. |
FIRST_VALUE(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part] ORDER BY ord [window]) |
Calculates the first value of an ordered set of lines determined by a partition and window. |
LAG(exp, offset, default) OVER([PARTITION BY part] ORDER BY ord]) |
Retrieves values from a previous row over a group of lines determined by a partition. |
LAST_VALUE(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part] ORDER BY ord [window]) |
Calculates the last value of an ordered set of lines determined by a partition and window. |
LEAD(exp, offset, default) OVER([PARTITION BY part] ORDER BY ord]) |
Retrieves values from a future row over a group of lines determined by a partition. |
MAX(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part])
|
Calculates the maximum over a group of lines determined by a partition and window. |
MEDIAN(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part] ORDER BY ord [window]) |
Calculates the median of a group of lines determined by a partition. |
MIN(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part])
|
Calculates the minimum over a group of lines determined by a partition and window. |
MODE(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part] ORDER BY ord [window]) |
Calculates the mode of a group of lines determined by a partition. |
PERCENT_RANK(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part] ORDER BY ord]) |
Calculates the percent rank over a group of lines determined by a partition. |
RANK(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part] ORDER BY ord]) |
Calculates the rank over a group of lines determined by a partition. |
STDDEV_POP(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part])
|
Calculates the population standard deviation over a group of lines determined by a partition and window. |
STDDEV_SAMP(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part])
|
Calculates the sample standard deviation over a group of lines determined by a partition and window. |
SUM(exp) OVER([PARTITION BY part] ORDER BY ord [window]) |
Calculates the sum over a group of lines determined by a partition and window. |
|
SQL Statistical Functions |
Description |
|---|---|
CORRELATION(input_field1, input_field2) |
Calculates the correlation between two fields. |
STDDEV_POP(field)
|
Calculates population standard deviation for the field. |
STDDEV_SAMP(field)
|
Calculates sample standard deviation for the field. |
|
SQL Trigonometric Functions |
Description |
|---|---|
ACOS(number)
|
Calculates the angle in radians whose cosine is the specified value. |
ASIN(number)
|
Calculates the angle in radians whose sine is the specified value. |
ATAN(number)
|
Calculates the angle in radians whose tangent is the specified value. |
ATAN2(x,y) |
Calculates the angle in radians between the positive x-axis and the vector from the origin to the specified point. |
COS(angle)
|
Calculates the cosine of the angle given in radians. |
COT(angle)
|
Calculates the cotangent of the angle given in radians. |
DEGREES(angle)
|
Converts the angle given in radians to degrees. |
PI() |
Returns the number pi. |
RADIANS(angle)
|
Converts the angle given in degrees to radians. |
SIN(angle)
|
Calculates the sine of the angle given in radians. |
TAN(angle)
|
Calculates the tangent of the angle given in radians. |