Adding New Services
|
In this section: |
This section describes how to add new services in TIBCO DQ.
Service Requirements
|
In this section: |
To add a new service in TIBCO DQ, the new service must comply with the following TIBCO DQ service specifications.
Request Method
The service must support HTTP POST.
Authentication Method
The service may require basic authentication (user ID and password), but no other security mechanism is supported.
Service Inputs
- The input to the service must be a single block of CSV text.
- The input data must not include a column header.
- Input values must be provided in the order specified in the service definition provided to TIBCO DQ. For more information, see Service Definition JSON.
- When creating the service definition, input column names should be prefaced with in_.
For example, an email cleanse service should have an input variable called in_email.
Service Outputs
- Output column names that represent cleansed input values should be prefaced by out_.
Example: An email cleanse service should have an output variable called out_email.
- In addition, the output should contain one column named tag_value and another called tag_category.
- Tag value can be empty. Tag values should represent a list of issues or reportable facts identified in the input data. If
a tag value is generated it should be a string consisting of letters, underscores or digits.
Example: An email cleanse service can generate thee following types of tag values:
- EMPTY_OR_WHITESPACES. Input value is an empty string or contains white spaces.
- COULD_NOT_VERIFY. Value does not represent a valid email address.
- DISPOSABLE_TEMPORARY_COMPLAINER. The email address provided is a disposable mailbox.
- Tag category can be empty. Tag category should be used to categorize the final outcome of the data quality analysis that must
be either of these four values:
- MISSING. Indicates the input data is empty or missing.
- VALID. Indicates the input data is valid and has the same value as the output data.
- CLEANSED. Indicates that the input value was cleansed and a standardized, augmented, or enriched output value was generated.
- INVALID. Indicates the input value is invalid and the issues identified cannot be fixed.
- Tag value can be empty. Tag values should represent a list of issues or reportable facts identified in the input data. If
a tag value is generated it should be a string consisting of letters, underscores or digits.
- All input values should be included in the output and records should be emitted in the same order in which they were provided in the input data set.
- The output should be a CSV block with the first line being a header.
Service Parameters
Services may optionally specify a set of parameters. Parameters represent name-value pairs that can be included as request variables on the service URL.
Example: The cleanse_email service specifies its URL as http://server.com/cleanse_email and a possible parameter as default_email, which allows a rule author to set up a default email that replaces invalid email addresses in the output. Execution of the rule would result in the following URL:
http://server.com/cleanse_email?default_email=service@myco.com
Service Registration
|
In this section: |
This section describes service registration requirements.
Service Definition JSON
Create a definition for the service in JSON format (an example is provided below). All fields except credentials and parameters are required.
|
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
name |
Name of the service, has to be unique in the “custom” workspace |
|
workspace |
always set to “custom” |
|
description |
A brief description of the service |
|
createdBy |
User name of the account that is registering this service |
|
location |
Service location URL |
|
sendFullDataSet |
Set this to “true” if the service expects the entire data set as input as opposed to one row at a time. |
|
supportsJson |
Set this to “true” if the service can interpret the request body in JSON format and generate a response in JSON format. |
|
inputColumns |
An array of paired values that have:
|
|
outputColumns |
An array of paired values that have:
|
|
parameters |
An array of values that have:
|
|
credentials |
A pair of values that have:
|
The following is an example JSON document for a new service called cleanse_vin:
{
"name": "cleanse_vin",
"workspace": "custom",
"createdBy": "john_smith",
"description": "Cleanse vehicle identification number",
"location": "http://service.mysite.com/cleanse_vin",
"sendFullDataSet": false,
"supportsJson": true
"inputColumns": [
{
"name": "in_vin",
"description": "value to be cleansed or verified"
}
],
"outputColumns": [
{
"name": "out_vin",
"description": "input value when tag_category is VALID, cleansed value when tag_category is CLEANSED, default value when tag_category is MISSING or INVALID"
},
{
"name": "tag_value",
"description": "Tag value that provides explanation for malformed, unexpected or missing data"
},
{
"name": "tag_category",
"description": "Tag category that categorizes tags as Missing Data, Cleansed Data or Invalid Data"
}
],
"tags": [
{
"name": "EMPTY_OR_WHITESPACES",
"description": "Input value is an empty string or contains all whitespaces"
},
{
"name": "INVALID_VIN",
"description": "Value does not represent a valid email address"
},
{
"name": "VALID_VIN",
"description": "Input value is Valid"
},
{
"name": "NORMALIZED_VIN",
"description": "Input value was reformatted or cleansed"
}
],
"parameters": [
{
"name": "default_vin",
"description": "Default value when tag_category is MISSING or INVALID"
}
]
}Service Test Endpoint
To test a new service against the TIBCO DQ service requirements, POST the service definition JSON (described above) to the following endpoint:
https://{{host}}:9803/api/v1/service/testThe service will return a set of validation messages. If the message set is empty, then the service was successfully tested.
Service Registration Endpoint
To register a new service, POST the service definition JSON (described above) to the following endpoint:
https://{{host}}:9803/api/v1/service The response will contain the ID of the new service.
If a new service is successfully registered, it will be available for rule authors to create new TIBCO DQ rules using the new service. For more information, see Managing Rules.
Authoring Services Using TIBCO Omni-Gen Data Quality Server
|
In this section: |
Developers familiar with TIBCO Omni-Gen Data Quality Server (DQS) can create new projects and add them to their Data Quality server. Set the online file for the project to be of type Generic Http with a CSV input format and include parameters as shown below. Set all input columns to be of type string and prefix them with in_.
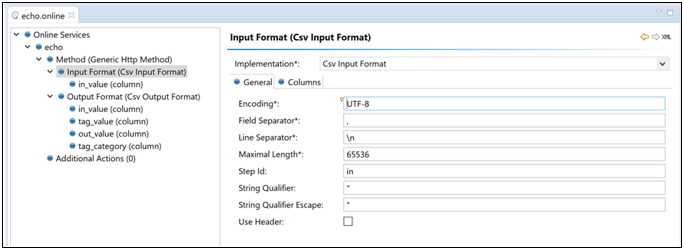
Set the output format to be of type CSV with parameters, as shown in the following image.
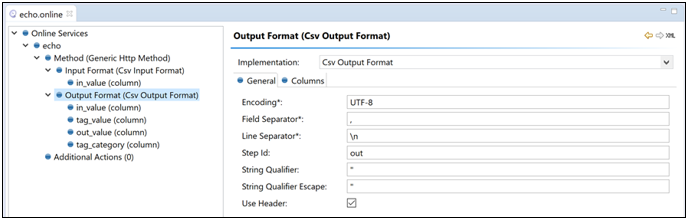
Note: The service must meet the service requirements as mentioned in Service Requirements.
Project Structure and Deployment
Create the service with a directory structure, as shown below:
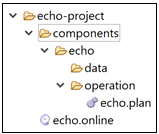
Copy the service to the running tdq-dqs container by executing the following command from the root of the project folder:

Follow the instructions in Service Registration to register the new DQS service. Inspect the DQS log for more information on any service-related errors.