Building a Regression Model in Spotfire
After you have determined which of the four Spotfire predictive models best suits your data and your desired analysis, use the predictive modeling options available to you from the Tools menu. This example task creates a regression model using sample data.
About this task
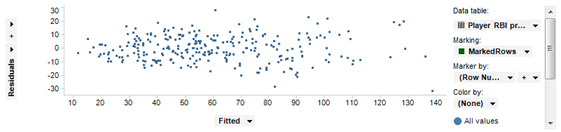
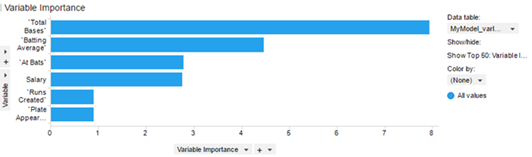
For demonstration purposes, use the Baseball Player Statistics data example, available from the Spotfire Library, in Demo/Analysis Files/Baseball. Open the example DXP. (Optionally, use your own suitable data set. )
Before you begin
Procedure
What to do next
You can create an evaluation model, you can predict from the model, or you can export the model to share with others. See the Spotfire help for more information.
Parent topic: Predictive Modeling
Related tasks
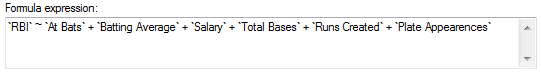
 ), which you can use to
edit the model, to create an evaluation model, to predict from the model, or to
duplicate the model to manipulate.
), which you can use to
edit the model, to create an evaluation model, to predict from the model, or to
duplicate the model to manipulate.