Configuring Persistence
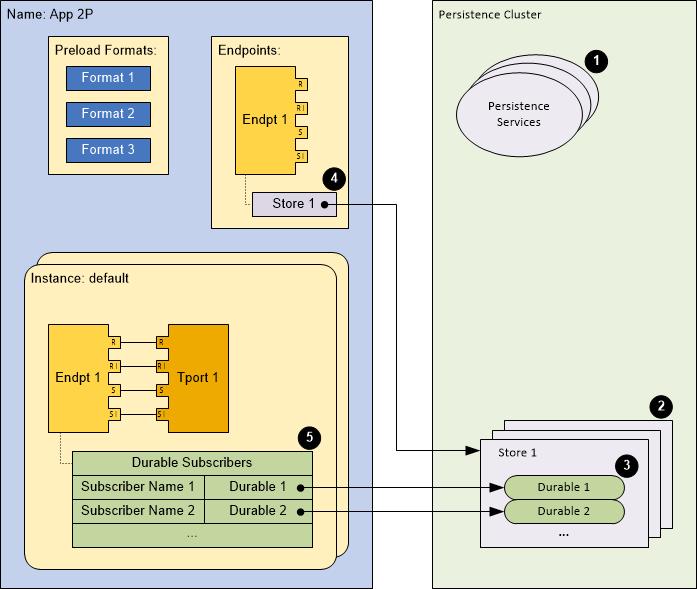
The realm definition schematic in the following diagram indicates five configuration tasks for persistence stores and durables. (Numbers in the diagram correspond to the task steps that follow.)
Prerequisites
Before starting this task, developers and administrators coordinate to determine the need for durables, and the parameters for those durables. See TIBCO FTL Durable Coordination Form.
Procedure
Related concepts
Copyright © Cloud Software Group, Inc. All rights reserved.