Filtering data
You can base the visualizations on the entire set of data, or you can base them on certain data values you have filtered to.
When you filter, certain data values in the data table are filtered
out, and only the filtered values, that is the remaining values, are included
in what is being visualized. All visualizations that are based on this data
table will immediately update to reflect only the filtered values. However, you
can anytime change what is filtered, or return to the full set of data.
Note: Not only
visualizations on the open page are affected; every visualization that is based
on this data table will be updated in your analysis.
The filtering is handled from the
Data in analysis flyout or the
Filters panel. If you think of your loaded data as
a table with rows and columns, each column gets a filter of its own in the
panel. If any column value is filtered out, every row that contains that value
will temporarily be taken away.
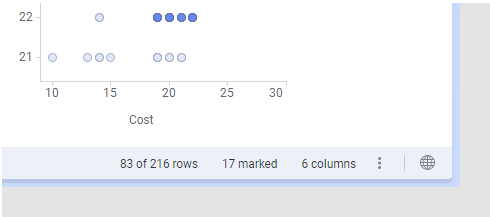
How many rows that remain after filtering, and the total number in the
data table, can be viewed at the bottom of a page. In this example, the entire
data table consists of 216 rows and 83 rows remain after filtering.
As data columns contain different types of data, their associated filters are of different types to make it easy to filter to the values you want to keep. You can however change the filter type that is suggested.

As data columns contain different types of data, their associated filters are of different types to make it easy to filter to the values you want to keep. You can however change the filter type that is suggested.
How to filter data is described in Filtering data using the Data in analysis flyout and Filtering data using the Filters panel.
- Filtering data using the Data in analysis flyout
In your analysis, you can filter to data in which you are particularly interested and filter out the rest. The filtering can be handled from the Data in analysis flyout. - Filtering data using the Filters panel
In your analysis, you can filter to data in which you are particularly interested and filter out the rest. The filtering can be handled from the Filters panel. - Filter types
A number of filter types are available for filtering the loaded data to certain values in which you are particularly interested. Each filter type has its own characteristics, allowing you to select the most suitable way to filter your data. - Changing filter type
Data columns are by default associated with filters. The filters are of different types depending on the type of data. You can change the filter type though. - Creating a filter transformation
Filtering out data using filters, or deleting marked rows, might sometimes not be permanent enough to remove unwanted data from your analysis, because reloading the data or resetting the filters might bring the undesired data back. If you want to make sure that values gets permanently removed, you can instead add a filter transformation. - Filtering schemes
One of the main strengths of Spotfire is the ability it gives you to filter your data, that is, to control which data should be visible and used in calculations. This means that you can easily show or hide data for specific categories, change the time range to look at, step through a sequence of values one at a time, and so on. Filtering usually affects all pages and visualizations, but you can also define different filtering schemes to be used by different pages or visualizations. - Filtering in related data tables
When you have multiple data tables that are related to each other in your analysis, and the data tables do not include exactly the same rows, you might want to handle filtering in the related data tables in different ways, depending on whether you are interested in the filtered rows or the filtered out rows.