Runs a Jupyter notebook stored in your current workspace from a workflow in
Team Studio.

Information at a Glance
| Category
|
Tools
|
| Data source type
|
DB
|
| Sends output to other operators
|
Yes
|
| Data processing tool
|
Python
|
Note: The Python Execute (DB) operator is for database data only. For Hadoop data, use the
Python Execute (HD) operator.
Notebook setup: For a notebook to be usable with the Python Execute operator, it must have the automatically generated tag
Ready For Python Execute visible in your workspace. This attribute is set if the following conditions are met.
- At least one input or output is specified in the notebook with argument
use_input_substitution = True or
use_output_substitution = True.
- Notebook input(s) argument
execution_label are distinct and exclusively one of the following strings:
1,
2 or
3.
- For example, your Notebook code might look something like this:
df_account=cc.read_input_table(table_name='account', schema_name='demo', database_name='miner_demo',use_input_substitution=True, execution_label="1")
- Inputs/output defined with
use_input_substitution = True must all be DB inputs (in this case, the notebook is usable with the Python Execute (DB) operator).
Input
From zero to three inputs to use as substitute inputs for the notebook selected, depending on the number of inputs for substitution the notebook configuration allows.
You can substitute up to three inputs, or use the inputs defined in the notebook if you prefer not to specify substitutions. To run Python Execute, each substituted input must contain a superset of columns in the corresponding notebook input with compatible data types. One data set can be output, or zero outputs if this is a terminal operator in your workflow.
Depending on the notebook configuration for input and output, the operator can be a source operator (if no inputs are selected for substitution in the notebook), or a terminal operator (if no output is specified in the notebook). If a single output is specified, the operator transmits this output to subsequent operators.
- Bad or Missing Values
- Missing values are not removed if present in the input(s). They should be handled directly in the notebook or in preceding steps of the workflow.
Restrictions
If the notebook selected has no tabular output defined with argument
use_output_substitution = True, the Python Execute operator does not transmit any data to subsequent operators and is considered a terminal operator. Although following operators cannot run, the user can still draw a connection with subsequent operators.
The Python Execute (DB) operator can be used only in a flow connected to a single database data source.
If the notebook selected is set up to transmit an output that contains variables with datetime format, the Python Execute operator transmits those as string variables to the next operator (the user can then convert those to the correct format in a Variables operator).
Configuration
| Parameter
|
Description
|
| Notes
|
Any notes or helpful information about this operator's parameter settings. When you enter content in the
Notes field, a yellow asterisk is displayed on the operator..
|
| Notebook
|
Select the Python notebook to run in your current workspace. To appear in this list, notebooks must be set up for use with Python Execute.
Note: Clicking
Open Notebook Selected opens the notebook in a new browser tab.
|
| Substitute Input 1
|
Optional. Select the connected input to use as a substitute for notebook input with argument
execution_label = 1.
If the notebook contains such input and you do not select a substitute in your workflow, it runs with the input defined in the notebook.
|
| Substitute Input 2
|
Optional. Select the connected input to use as a substitute for notebook input with the argument
execution_label = 2.
If the notebook contains such input and you do not select a substitute in your workflow, it runs with the input defined in the notebook.
|
| Substitute Input 3
|
Optional. Select the connected input to use as a substitute for notebook input with the argument
execution_label = 3.
If the notebook contains such input and you do not select a substitute in your workflow, it runs with the input defined in the notebook.
|
| Data Source (DB)
|
Select the data source in which to store the output from notebook execution (if defined).
If inputs are connected to the Python Execute operator,
Data Source (DB) must match the data source of your inputs.
|
| Output Schema
|
The schema for the output table or view.
|
| Output Table
|
The table path and name where the results are output. By default, this is a unique table name based on your user ID, workflow ID, and operator.
|
| Drop If Exists
|
Specifies whether to overwrite an existing table.
- Yes - If a table with the name exists, it is dropped before storing the results.
- No - If a table with the name exists, the results window shows an error message.
|
Output
- Visual Output
- The operator result panel displays one or two tabs, depending on whether it is terminal.
-
-
Output (only available if the operator is not terminal):
-
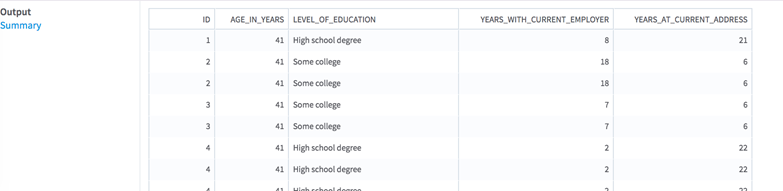
-
Summary of the parameters selected and notebook execution results:
-
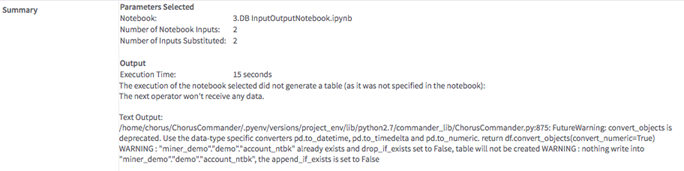
- Data Output
- If the notebook contains an output with argument
use_output_substitution = True, the operator transmits a tabular data set to subsequent operators. If no output is defined in the notebook, this operator is terminal.
Copyright © 2021. Cloud Software Group, Inc. All Rights Reserved.



