Controlling the Vertical Positioning of a Heading or Footing
You can use several vertical positioning techniques to enhance the appearance and readability of a report:
- In a report generated in HTML, PDF, or other report formats, you can add one or more lines above or below heading or footing text using spot markers and free text lines. See Add Blank Lines to a Heading or Footing.
- In a PDF report you can control the space above or below a heading or footing line or the distance between the text and the surrounding grid lines in a heading or footing line using the TOPGAP and BOTTOMGAP attributes in a StyleSheet. See Controlling the Vertical Positioning of a Heading or Footing. For full information on TOPGAP and BOTTOMGAP, see Laying Out the Report Page.
- In a PDF report, you can position a page footing at the bottom of a page, rather than directly after the report data. See Controlling the Vertical Positioning of a Heading or Footing.
Add Blank Lines to a Heading or Footing
Use the following syntax options to add blank lines above or below, or within a heading or footing, where:
You can use these techniques separately or in combination.
Adding Blank Lines Above and Below a Report Heading
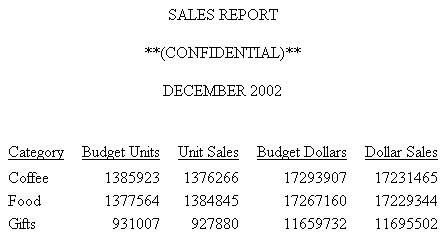
This request creates an HTML report with one blank line between each line of the page heading and two blank lines between the page heading and the actual report. The first blank line is added as an empty text line, the next blank lines are added with the skip-line spot marker.
TABLE FILE GGSALES SUM BUDUNITS UNITS BUDDOLLARS DOLLARS BY CATEGORY ON TABLE SUBHEAD "SALES REPORT" " " "**(CONFIDENTIAL)**</1" "December 2002 </2" ON TABLE SET PAGE-NUM OFF ON TABLE SET ONLINE-FMT HTML ON TABLE SET HTMLCSS ON ON TABLE SET STYLESHEET * TYPE=REPORT, GRID=OFF, TOPMARGIN=0, $ TYPE = TABHEADING, JUSTIFY = CENTER, $ ENDSTYLE END
The output is:
Control Vertical Spacing in a Heading or Footing
In a PDF report, you can use the TOPGAP and BOTTOMGAP attributes to control spacing above or below a heading or footing line or the distance between heading or footing text and the grid lines above and below them.
TYPE=headfoot, {TOPGAP|BOTTOMGAP}=gap, $
where:
In the absence of grids, the default value is 0.
In the presence of grids, the default value increases to provide space between the grid and the text.
Adding Blank Space to Separate Heading Text From Grid Lines in a PDF Report
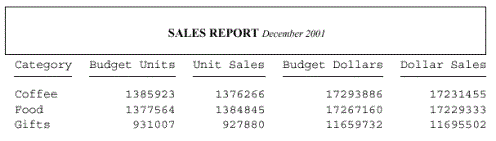
This request generates a PDF report with blank space added above and below the report heading to separate the text from the upper and lower grid lines. The space above is added by the TOPGAP attribute. The space below is added by the BOTTOMGAP attribute.
TABLE FILE GGSALES SUM BUDUNITS UNITS BUDDOLLARS DOLLARS BY CATEGORY ON TABLE SUBHEAD "SALES REPORT <+0>December 2001" ON TABLE SET PAGE-NUM OFF ON TABLE SET ONLINE-FMT PDF ON TABLE SET SQUEEZE ON ON TABLE SET STYLESHEET * TYPE = TABHEADING, GRID=ON, JUSTIFY=CENTER, TOPGAP=.25, BOTTOMGAP=.25, $ TYPE = TABHEADING, FONT='TIMES', SIZE=12, STYLE=BOLD, $ TYPE = TABHEADING, ITEM=2, SIZE=10, STYLE=ITALIC, $ ENDSTYLE END
The output is:
Adjusting Vertical Spacing Below a Sort Footing
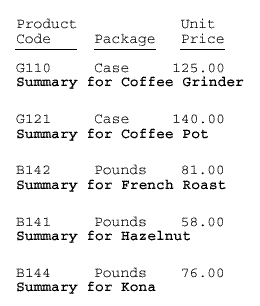
The request generates a PDF report in which the sort footings are bolded for emphasis and space is added below each footing to visually tie the footing text to the preceding data.
TABLE FILE GGPRODS PRINT PACKAGE_TYPE AND UNIT_PRICE WHERE UNIT_PRICE GT 50 BY PRODUCT_DESCRIPTION NOPRINT BY PRODUCT_ID ON PRODUCT_DESCRIPTION SUBFOOT "Summary for <PRODUCT_DESCRIPTION" ON TABLE SET PAGE-NUM OFF ON TABLE SET ONLINE-FMT PDF ON TABLE SET SQUEEZE ON ON TABLE SET STYLESHEET * TYPE=SUBFOOT, STYLE=BOLD, BOTTOMGAP=.25, $ ENDSTYLE END
The output is:
Position a Page Footing at the Bottom of a Page
You can position a page footing at the bottom of a page. By default, a page footing appears two lines below the report data.
FOOTING [BOTTOM] "content ... " ["content ... "] . . . ["content ... "]
where:
The text must start on a line by itself, following the FOOTING command.
Text can be combined with variables and spot markers.
For related information, see Limits for Headings and Footings.
Fields (real
data source fields, virtual fields created with the DEFINE command
in a Master File or report request, calculated values created with the
COMPUTE command in a request, system fields such as TABPAGENO).
You can qualify data source fields with certain prefix operators.
Dialogue Manager variables.
Images. You
can include images in a heading or footing.
For details, see Including an Element in a Heading or Footing.
<+0> divides a heading
or footing into items for formatting. For details, see Identifying a Report Component in an ibi WebFOCUS StyleSheet.
</n specifies
skipped lines. For details, see Controlling the Vertical Positioning of a Heading or Footing.
<-n to
position the next character on the line. For details, see Positioning Headings, Footings, or Items Within Them.
<0X continues
a heading or footing specification on the next line of the request.
For details, see Extending Heading and Footing Code to Multiple Lines in a Report Request.
Positioning a Page Footing at the Bottom of a Page
This request produces a PDF report in which the page footing appears at the bottom of the page, rather than in its default position, two lines below the report data.
TABLE FILE GGSALES PRINT UNITS DOLLARS BY CATEGORY BY STCD WHERE TOTAL DOLLARS GE 25000 FOOTING BOTTOM "PRELIMINARY SALES FIGURES" ON TABLE SET ONLINE-FMT PDF ON TABLE SET PAGE-NUM OFF END
The following output shows the end of the report, with the footing.
