Data functions are calculations done by another engine than the internal Spotfire data engine. Data functions are often based on R scripts running under TIBCO Enterprise Runtime for R (TERR), but they can also be based on open-source R, Python scripts, SAS scripts, MATLAB scripts or S-PLUS.
To use TERR, you can use it either from the engine provided in your Spotfire installation, or from the TERR service, installed on a node available to your TIBCO Spotfire Server.
To use Python, you can use either a local installation of Python or the TIBCO Spotfire Service for Python, installed on a node available to your TIBCO Spotfire Server. You must be running a 64-bit version of Spotfire. Spotfire Analyst includes a python.exe but you can also switch to use another installation under Tools > Options > Data functions. Read more about how to work with Python in the document Python Data Functions in TIBCO Spotfire®.
To use open-source R, you can access it either from an installation of Spotfire Statistics Services Local Adapter using a locally-installed R engine, or from an engine that you have installed that is running under TIBCO Spotfire Statistics Services.
To use SAS, MATLAB or S-PLUS, you must access these engines via Spotfire Statistics Services. The SAS or MATLAB engines can only be accessed if you have a working installation of the selected software available.
Concerning R:
For more information on using R with Spotfire Statistics Services Local Adapter, see the README file included with the Statistics Services Local Adapter. (Other third-party calculation tools can be added using the TIBCO Spotfire API.)
For information on using R with Spotfire Statistics Services, see the TIBCO Spotfire Statistics Services Installation and Administration Guide.
Open-source R is available under separate open source software license terms and is not part of TIBCO Spotfire. As such, open-source R is not within the scope of your license for TIBCO Spotfire. Open-source R is not supported, maintained, or warranted in any way by TIBCO Software Inc. Download and use of open-source R is solely at your own discretion and subject to the free open source license terms applicable to open-source R.
See http://spotfi.re/sr for information about the TIBCO Spotfire Statistics Services system requirements.
Getting started
First, define a data function and save it to the library
using the Register Data Functions dialog. Second, apply the data function
to your analysis. For example, you can use a data function as a transformation
step when you add or replace data tables. You can also use it as a separate
tool, by opening a suitable data function using the Files
and data ![]() flyout or
using Insert in the Data
Function Properties dialog.
flyout or
using Insert in the Data
Function Properties dialog.
You can define an open-source R or S-PLUS data function either from an existing function in the corresponding TIBCO Spotfire Statistics Services package repository, or by writing a script directly in the Register Data Functions dialog, and then running using the appropriate engine (for R functions that would be either the TERR engine or the open-source R engine). Other types of data functions are always based on scripts.
You can specify input and output parameters when you run a data function.
To ensure a rapid response and a good user experience, avoid sending very large data sets from Spotfire to a statistical engine, or invoking complex, long-running calculations.
Tip: You can develop open-source R or TERR scripts in RStudio, a full-featured, open-source integrated development environment for working with R code. RStudio is provided independently of TIBCO Software Inc. You can configure RStudio to use the TERR engine, and to display its language reference. Also, you can access the TERR language reference at https://docs.tibco.com/products/tibco-enterprise-runtime-for-r.
Example 1:
A simple conversion of the values in a column from degrees Celsius to degrees Fahrenheit. Although this is easy to accomplish using the Add calculated column tool, it serves as an example simple enough to show input and output parameter handling in more detail.
To create and run an R script data function in a TERR Engine:
Assume that the data table in TIBCO Spotfire contains a column with temperatures expressed in degrees Celsius.
First, on the menu bar, select Tools > Register data functions.
For Type, specify R script - TIBCO Enterprise Runtime for R from the drop-down list.
Define the script to perform the conversion on the Script tab:
# Define the convertTemperature function:
convertTemperature <- function(x)
{
x*(9/5) + 32
}
# Run the function to produce the output:
out <- convertTemperature(x);
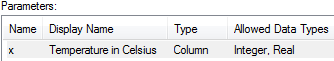
Define the input parameter
x as a column with the allowed
data types Integer and Real.
Tip: You can select the parameter in the Script tab and use the pop-up menu option Input Parameter to reach the Input Parameter dialog directly.
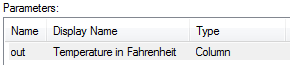
Define the output parameter
out as a column.
Tip: You can select the parameter in the Script tab and use the pop-up menu option Output Parameter to reach the Output Parameter dialog directly.
Note that the output display name will not be propagated to the output column name. The column name is always the output specified by the R script.
Save the data function to the library, as Temperature converter.
To run the calculation and
to connect the input and output parameters to your current data in
TIBCO Spotfire, on the authoring bar, click Files
and data ![]() and locate
the data function of interest by searching for a suitable keyword
or by browsing the different categories.
and locate
the data function of interest by searching for a suitable keyword
or by browsing the different categories.
Comment: To locate all data functions in the library, enter type:datafunction in the search field. To be able to add data functions that require a data table input, you must first have some data loaded in the analysis.
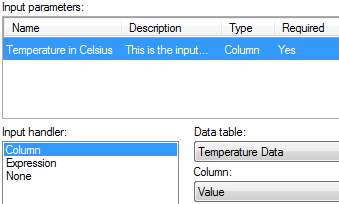
In the Data Function – Select
Input dialog, specify that the input parameter x
should be a column and select the data table and column to convert.
Click OK.
In the summary view, select how to add the new data; as a new data table or as a new column in an existing data table, and click OK when you are done.
The data function calculation is performed and a new column is added as specified. You can change the parameter settings or refresh the calculation later by selecting Data > Data functions properties.
Example 2:
If the function to use is a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) calculation, the input would be a number of numerical data columns retrieved from the current data in TIBCO Spotfire and, optionally, a parameter specifying the percent variation to be preserved by the principal components. The output would include three new data tables (scores, loadings and eigenvalue/explained variance table) and a scalar indicating the number of principal components generated.