Contents
- Overview
- Where is JMS Configuration Information Stored?
- Opening the JMS Configuration Editor
- Best Practices and Cautions
- Server/Destinations Tab
- Timestamp Formats Tab
- Minimum Server Configuration Requirements
- Configuring More Than One Server
- Using Legacy JMS and EMS Adapter Configurations
- Unsupported Features
- Editor Section: Servers and Destinations
- Editor Section: Server Overview
- Editor Section: Destination Options
- Editor Section: Connection Type, JNDI
- Editor Section: Connection Type, Direct
- Editor Section: Advanced JNDI Options
- Editor Section: Connection Options
- Editor Section: Destination Overview
- Editor Section: Consumer Options
- Editor Section: Producer Options
StreamBase Studio includes the JMS Configuration Editor, which provides a forms-based
method for editing the server connection and destination specifications for one or
more JMS or TIBCO EMS message servers. Starting with TIBCO StreamBase® release 7.5.4,
the JMS Configuration Editor supports the JMS or TIBCO EMS operators introduced in that release. In
particular, the JMS Configuration Editor now stores all JMS configuration information
in the current Studio project's server configuration file, and no longer in separate
.jmsconf files.
The JMS and TIBCO EMS Adapter is implemented as a suite of five operators for JMS and five for TIBCO EMS, as shown in the following table:
JMS and TIBCO EMS Operators
| JMS Adapter | TIBCO EMS Adapter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| JMS Consumer | EMS Consumer | Connects to a JMS or EMS destination on the target server and reads messages from it. |
| JMS Producer | EMS Producer | Connects to a JMS or EMS destination on the target server and sends messages to it. |
| JMS Connect | EMS Connect | Manually connects to or disconnects from the target JMS or EMS server. |
| JMS Ack | EMS Ack |
Acknowledges receipt of messages from the connected server (when using the
CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE or other explicit
acknowledgement mode).
|
| JMS Commit | EMS Commit | Either commits or rolls back transactions on a transacted JMS or EMS session. |
Each server connection specification is saved with a per-project unique connection name, and each JMS destination has a unique name per configured server. When using one of the JMS or TIBCO EMS operators, you specify a configured server and destination name, and the operator does the work of making and maintaining the connection to the specified server.
Starting with TIBCO StreamBase 7.5.4, the specifications for connecting to JMS and
TIBCO EMS message servers are stored in an <adapter-configuration> element in the current project's
primary server configuration file, usually named sbd.sbconf. As always, you are free to directly edit the XML of the
sbconf file. However, Studio provides the JMS Configuration Editor described on this
page as an easy-to-use forms-based method of editing JMS and TIBCO EMS
specifications.
Note
The JMS Configuration Editor does not have an explicit button, and it does not automatically save changes. Be sure to save changes with Ctrl+S before switching between views and tabs of the Editor.
In releases before 7.5.4, JMS and TIBCO EMS configuration was specified in separate
XML files with the .jmsconf extension that were
independent of the project's server configuration files. The current JMS
Configuration Editor can no longer be used to create new .jmsconf files or save in the .jmsconf format, but it can open such files and convert their
server and destination specifications into the new <adapter-configuration> format. See Using Legacy Configurations.
To open the JMS Configuration Editor for the current Studio project, use steps like the following:
-
Start with a JMS or EMS operator icon on the EventFlow canvas:
-
If you already have a JMS or EMS operator icon, select and double-click it to open its Properties view.
-
If the current canvas does not have a JMS or EMS operator, drag the Adapters, Java Operators icon from the Palette view to the canvas. Type
jmsoremsin the search field to narrow the list of results, and select any JMS or TIBCO EMS operator. Select and double-click the newly placed icon to open its Properties view.
-
-
Close any currently open JMS Configuration Editor. Close any other Editors of the current project's
sbd.sbconffile. -
Click the button in the Operator Properties tab of the Properties view. This opens the JMS Configuration Editor.
The default placement of the JMS Configuration Editor view is as a new tab in the same mid-central window where EventFlow canvases appear.
Because the JMS Configuration Editor edits the current project's sbd.sbconf file, it is possible for more than one editor to have
the same .sbconf file open at the same time, which can
lead to confusing and conflicting editing situations. For the utmost editing clarity,
follow the rules and best practices in this section when using the JMS Configuration
Editor:
-
Always close any other editor currently open on any
.sbconffile in the current project before clicking the Edit button to open a new JMS Configuration Editor session.This includes any text-based or XML editors open on the
sbd.sbconffile itself, or on any subordinate.sbconffile included into the top-level file. -
Do not mix JMS operators and TIBCO EMS operators in the same EventFlow module.
-
If you must have have connections to TIBCO EMS servers and to another JMS-compliant server in the same StreamBase application (for example, for a temporary migration application from a generic JMS server to a TIBCO EMS server), then:
-
Place operators for each connection type into separate EventFlow modules.
-
Configure one set of xMS server and destination connections at a time. Both sets can successfully co-exist in the same
sbd.sbconffile, but only one set can be edited at a time.
-
-
The JMS Configuration Editor takes on different characteristics, depending on whether it is opened from a JMS operator or from a TIBCO EMS operator. In particular, Editors opened from an EMS operator show an error dialog if you try to select a non-EMS provider from the JMS Provider drop-down list.
-
The JMS Configuration Editor retains the editing characteristics of the last-opened xMS configuration type, if you open a new Editor session while the last session is still open.
For example, consider the following sequence of events: 1. You open the Editor from a TIBCO EMS operator and leave that Editor session open. 2. You drag a JMS operator onto a canvas and click the Edit button in its Properties view. In this case, the newly opened Editor session behaves like an EMS editor, even though opened from a JMS operator. For example, it only allows you to select
TIBCO EMSfrom the JMS Provider drop-down list.To recover from this situation, close all open JMS Configuration Editor sessions and any other text or XML editor sessions on any of this project's
.sbconffiles. Then re-open the JMS Configuration Editor session from the xMS icon of choice. -
If you inadvertently violate these rules and try to open the JMS Configuration Editor from a JMS operator while an EMS operator editing session is already open (or vice versa), Studio does open the Editor session, but only shows server definitions that use the last-opened EMS (or JMS) type. A message across the top of the Editor view reminds you of the problem, like the following example:

Use the Server/Destinations tab to define connection configurations for JMS and TIBCO EMS servers, and to configure destinations for defined servers. This tab takes on a different look, depending on what it is currently editing:
-
The tab shows server configuration fields when a server's name is selected in the Servers and Destinations control on the upper left.
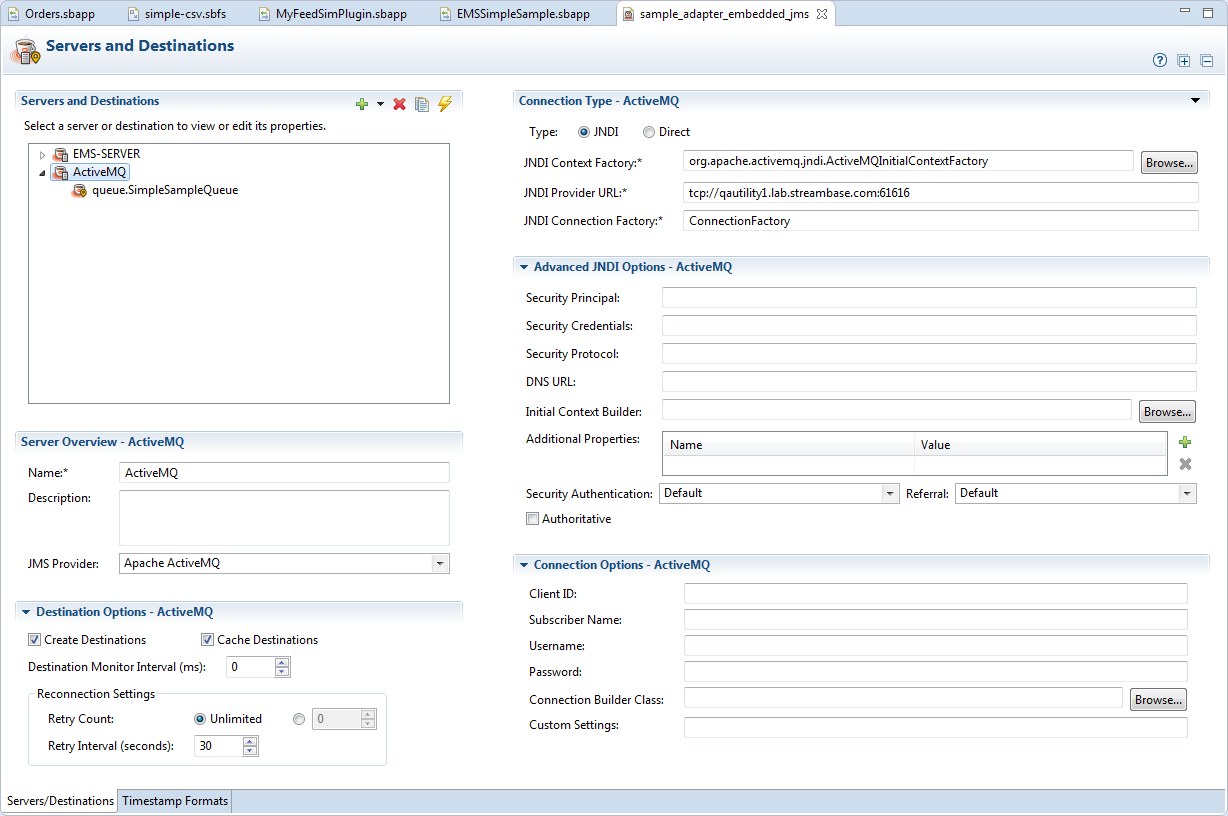
-
The tab shows destination configuration fields when a destination's name is selected.
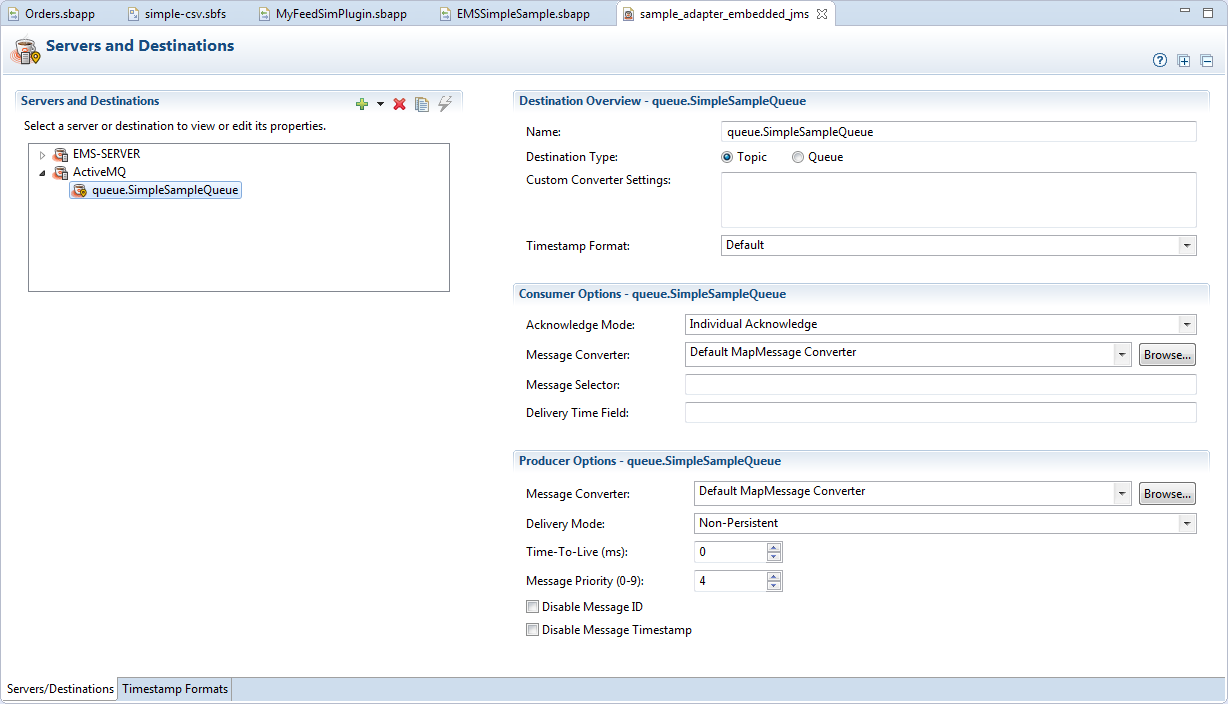
Moreover, the set of available server configuration fields adapts to whether you select Direct or JNDI as the server connection type in the Connection Type quadrant in the upper right.
If you open the JMS Configuration Editor in a project with no previous JMS or EMS
configuration in the current Studio project, then the Servers
and Destinations control is blank. Click the green plus sign (![]() ) to create
a new server definition; this creates a server with the default name
) to create
a new server definition; this creates a server with the default name Server, which has one destination with the default name Destination. Each defined server must have at least one defined
destination.
To rename a newly added server configuration, select the default name and enter a new name in the Name field of the Server Overview section. To rename the destination, select the default name and enter a new name in the Name field of the Destination Overview section.
See Minimum Configuration Requirements below for a discussion of the few server configuration settings you must specify to allow a successful connection.
The JMS Configuration Editor has two tabs selectable along its bottom edge. The primary Server/Destinations tab is described in other sections of this page.
The Timestamp Format tab has the single purpose of gathering timestamp format definitions for use in the Server/Destinations tab as part of the configuration of destinations.
A field, property, or header in a JMS or EMS message might represent a timestamp as a
string such as yyyy-MM-dd. Use this tab to specify the
format of that string, and provide a name for that format. Your named formats then
appear in the Timestamp Format drop-down list in the
Destination Overview section of each destination's
configuration.
Define your time formats using the format characters recognized by the java.text.SimpleDateFormat standard.

|
If you do not specify any custom timestamp format strings in this tab, the
Timestamp Format drop-down list in the destination
configuration section contains the single format “DefaultTimestampFormat”. This default format string is:
MM/dd/yyyy hh:mm:ss aa
The Server/Destinations tab allows for maximum flexibility in configuring JMS server and destination definitions, and allows for many special-case settings. At first glance, the number of fields in this tab can appear daunting. However, to make a successful connection to a JMS or TIBCO EMS message server requires only a few settings.
The particular minimum settings required depend on the JMS Provider you are using. The JMS Operators have native support for four JMS Providers:
-
TIBCO Enterprise Messaging Service™ (EMS)
-
Apache ActiveMQ
-
IBM WebSphere Application Server
-
Solace Systems
The required settings for these four JMS providers are shown in Configuration Settings Examples on the Authoring Guide's JMS Operators page.
See Connection Type Section, JNDI and Connection Type, Direct below for examples and explanations of the fields you must configure in the Connection Type section to allow a simple JMS or EMS connection to proceed.
For a successful connection, you also need the JAR files that implement JMS client
functionality for your JMS Provider, as listed in JAR File
Requirements. These JAR files must either be listed in the current Studio
project's Java Build
Path, or in the <java-vm> section of the
project's sbd.sbconf file, or both.
When the minimum configuration settings are in place, test your connection by selecting your server's name in the Servers and Destinations control, and clicking the Test Connection button. This results in a dialog that reports either the success or failure of the connection attempt.

|
Both the JMS Configuration Editor and the underlying <adapter-configurations> element in sbd.sbconf support the configuration of more than one JMS and/or
EMS servers, and you can easily mix configurations for different JMS Providers:
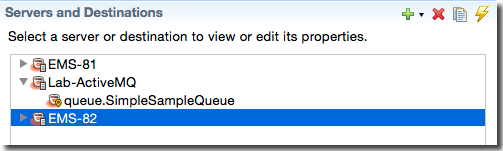
In the underlying XML, each server's configuration, along with all of its configured
destinations, is kept in a separate <jms-server>
child element:
<adapter-configurations>
<adapter-configuration name="jms">
<sb-jms-adapter-config
adapter-class="com.streambase.sb.adapter.jms2.JMSConsumer">
<jms-servers>
<jms-server name="EMS-81" provider-name="TIBCO EMS"
connection-factory-name="ConnectionFactory"
provider-context-factory="com.tibco.tibjms.naming...
...
<destinations>
<destination is-topic="false" name="queue.SimpleSampleQueue"/>
<destination is-topic="false" name="queue.TextMessageQueue2"/>
</destinations>
</jms-server>
<jms-server name="Lab-ActiveMQ" provider-name="Apache ActiveMQ"
connection-factory-class="org.apache.activemq...
...
<destinations>
<destination name="queue.SimpleSampleQueue"/>
</destinations>
</jms-server>
</jms-servers>
</sb-jms-adapter-config>
</adapter-configuration>
</adapter-configurations>
As illustrated in this XML excerpt, there is no conflict between JMS servers from different JMS Providers. However, you must configure each server's configuration one at a time, independent of each other, following the best practice rules in Best Practices and Cautions above.
The JMS and EMS Input Adapter and Output Adapter from StreamBase release 7.5.3 and earlier are still present but deprecated in release 7.5.4 and later. Your StreamBase applications that use these adapters still compile and run under current StreamBase Server releases.
If you must maintain an application that uses the older JMS or EMS Adapters, then
keep an installed copy of TIBCO StreamBase 7.5.3 or earlier. You can use the previous
version of the JMS Configuration Editor from the older release to continue
maintaining your .jmsconf files until you are ready to
upgrade.
However, as noted above, the JMS Configuration
Editor included with TIBCO StreamBase 7.5.4 and later does not save configurations in
the .jmsconf file format. TIBCO strongly recommends
upgrading your applications to take advantage of the features of the new JMS operator
suite in place of the Adapters provided in earlier releases.
You can easily migrate the server and destination configurations from an existing
project's .jmsconf file. To do so:
-
Add one of the new JMS or EMS operators to an EventFlow canvas. Double-click to select the newly added icon's Properties view.
-
In the Properties view's Operator Properties tab, click . This opens a file selection dialog.
-
Navigate to the project folder that contains your existing
.jmsconffile. Select the file and click . -
This opens the JMS Configuration Editor with the server name from the
.jmsconffile newly added to the list of servers, along with its configuration and all of its defined destinations. -
Press Ctrl+S to save the imported configuration back to the current project's
sbd.sbconffile.
The import always preserves the server name specified in the .jmsconf file. This means:
-
If the current project has a configured server with the same name, its configuration is overwritten by the import.
-
Every import of a configuration with the same server name overwrites the previous configuration for that server name. Thus, if you used the same server name in separate
.jmsconffiles for JMS Input and Output Adapters, and you import each.jmsconffile separately, the last-imported configuration is the one used.
The following features of the older JMS Configuration Editor from StreamBase release 7.5.3 and earlier have no corresponding feature in the Editor of release 7.5.4 and later:
| Unsupported Feature from 7.5.3 and Earlier | Workaround |
|---|---|
| The previous Editor's Field Maps tab for name maps, header maps, and property maps.* | Instead, consider receiving your JMS messages in their JMS-native forms, then placing a StreamBase Map operator downstream from the JMS or EMS Consumer icon, and mapping field and header names there. |
| The previous Editor's Source tab. |
Instead, close all instances of the JMS Configuration Editor, then open the
current project's sbd.sbconf file using
right-click, then → .
|
| The → → menu option. | This is no longer needed, because there is no longer a separate file type to hold JMS configurations. |
| The Import settings from TIBCO BusinessWorks feature of the → → menu option. |
Instead, you can use StreamBase release 7.5.3 or earlier to import the
BusinessWorks settings into a .jmsconf file,
then import that .jmsconf file using release
7.5.4 or later.
|
*However, the Timestamp Formats section of the old Field Maps tab is preserved in the Timestamp Formats tab of the new Editor.
Each server and each destination within it must have a unique name per Studio project folder. When you add a new server in the Servers and Destinations section of the Servers/Destinations view, provide a name for it in the Server Overview section.
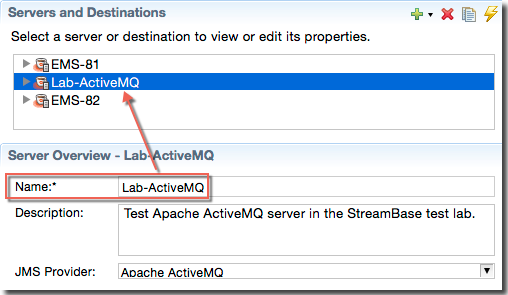
Use the tool bar at the upper right to add and remove servers and destinations, and to test server connections:
-
To add a server or a destination, click the green plus sign (
 ), or
use the down arrow to the right of the plus sign to select Add Server. This adds an empty server definition named Server
with one empty destination named Destination. To add only a new destination,
select a server name, then use the down arrow to select Add Destination.
), or
use the down arrow to the right of the plus sign to select Add Server. This adds an empty server definition named Server
with one empty destination named Destination. To add only a new destination,
select a server name, then use the down arrow to select Add Destination.
-
To remove a server or a destination, select it and click the red button (
 ). When you remove a
server, all of its destinations are also removed. You can press Ctrl+Z to undo a deletion.
). When you remove a
server, all of its destinations are also removed. You can press Ctrl+Z to undo a deletion.
-
To duplicate the configuration for a server or a destination, select it and click the white button (
 ). When you duplicate a server configuration, all its
configured destinations are also copied.
). When you duplicate a server configuration, all its
configured destinations are also copied.
-
To test a configured server's connection, select a server name, and click the yellow button (
 ). You
receive a report of connection success or a diagnostic if the connection does
not succeed.
). You
receive a report of connection success or a diagnostic if the connection does
not succeed.
Newly added servers must have a certain minimum set of configured fields for a test connection to that server to succeed. See Minimum Server Configuration Requirements.
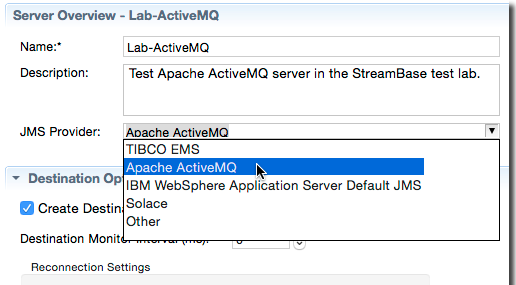
Use the Server Overview section to specify a name and optional description for the selected server.
If you opened the JMS Configuration Editor from a JMS operator, the JMS Provider drop-down list shows the four supported JMS Providers, plus Other. Select the appropriate JMS Provider or select Other if you intend to define your own JMS Provider configuration.
Use the Destination Options section for the selected server to specify certain defaults for all destinations configured for this server. The following image shows the default selections for this section.
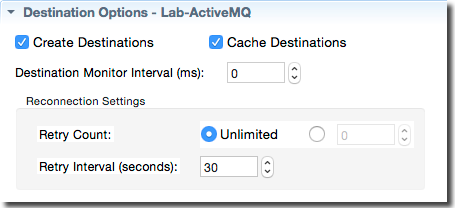
The following table describes the Destination Options settings of this section.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Create Destinations | Boolean. When selected (the default), this indicates that destinations are to be created when first used. When unselected, this means to look up destinations in JNDI. If supported by the JMS provider, destinations can be created even if they already exist. Creating destinations is faster than looking them up in JNDI. |
| Cache Destinations | Boolean. When selected (the default), this indicates that destinations are to be cached once created. Caching provides better performance. However, if you are creating thousands of destinations, caching them may increase your memory footprint. |
| Destination Monitor Interval | Integer in milliseconds. When non-zero, enables monitoring the health of JMS destinations on a given server at intervals you specify in milliseconds. The default setting is zero, which means destinations are not monitored. |
| Reconnection Settings | |
| Retry Count | Select either Unlimited or use the number control to specify the number of retries to attempt. By default, JMS adapters only try to connect to a JNDI or JMS server once before giving up. Use this control to specify zero or more than one retry attempts, or an unlimited number of attempts. |
| Retry Interval (seconds) | Integer in seconds. Set the value to specify the number of seconds between connection retry attempts. The default is 30 seconds. |
The minimum settings for a JNDI connection to TIBCO EMS and Apache ActiveMQ require only three settings for a JNDI type connection:
-
JNDI Context Factory: the fully qualified name of the class that implements the JNDI Context Factory API. For the four supported JMS Providers, this field is filled in for you when you select a provider name from the JMS Provider drop-down list in the Server Overview section. If you are configuring a different JMS Provider, obtain the name of this class from the provider vendor's documentation.
You must provide a connection factory class name to instantiate. It is assumed that this class implements a constructor taking one String parameter that represents the URL of the JMS broker, which you must also specify in the next field if it is not
localhost. -
JNDI Provider URL: The URI of the JMS server to connect to, whether running for development purposes on
localhostor on a host in your site's network. JNDI Provider URIs start with the name of the JMS protocol (which is proprietary for each JMS Provider), followed by the DNS name or IP address of the server of interest, followed by a colon and the port number on which the JMS service is running. -
JNDI Connection Factory: This is the default string
ConnectionFactoryor a string specific to your JMS Provider.
These minimum settings are made in the Connection Type section in the upper right quadrant of the Server/Destinations tab, when the JNDI connection type is selected.

|
Remember that a successful connection requires the JAR files that implement JMS
client functionality for your JMS Provider, as listed in JAR File
Requirements. These JAR files must either be listed in the current Studio
project's Java Build
Path, or in the <java-vm> section of the
project's sbd.sbconf file, or both.
You can test your configuration's connection to its specified server as described in Minimum Server Configuration Requirements.
To specify a connection to a JMS or TIBCO EMS server using the Direct connection type, you must specify two fields:
- Connection Factory Class
-
With two of the four supported JMS Provider names selected in the JMS Provider drop-down list in the Server Overview section, when you click the Direct button to specify that connection type, the name of the connection factory class is automatically filled in in this field. Those two Providers are TIBCO EMS and Apache ActiveMQ.
For IBM WebSphere AS Default JMS and Solace Systems, you must provide the fully qualified name of the direct connection class provided in the documentation for those Providers.
- Connection Provider URL
-
Enter the URL for the JMS server in the form
tcp://host:port.
Examples, first for a direct connection to TIBCO EMS:

|
For an Apache ActiveMQ direct connection:
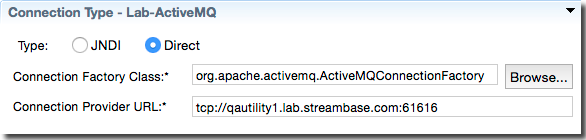
|
Of course, direct connections have the same JAR file requirements listed in the previous section, and can be tested with the Test Connection button described in Minimum Server Configuration Requirements.
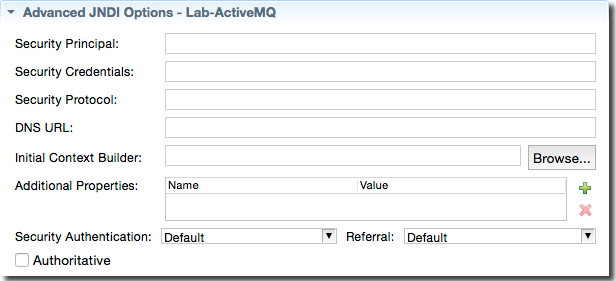
The are sometimes needed to establish the proper InitialContext for JNDI lookups. These fields have no default values. Contact your site's JMS Network Administrator for the correct values for your site.
|
The following table describes the fields of the Advanced JNDI Options section
| Option | JNDI Correspondence or other |
|---|---|
| Security Principal |
javax.naming.Context.SECURITY_PRINCIPAL
|
| Security Credentials |
javax.naming.Context.SECURITY_CREDENTIALS
|
| Security Protocol |
javax.naming.Context.SECURITY_PROTOCOL
|
| DNS URL |
javax.naming.Context.DNS_URL
|
| Initial Context Builder | Fully-qualified name of the Java class implementing com.streambase.sb.adapter.common.jms.common.JNDIInitialContextBuilder |
| Additional Properties |
Defines additional properties that may be required beyond those defined in
javax.naming.Context. These may be site-specific or JMS Provider specific
properties. Use the green plus button to add a row, whose initial values are
Name and Value.
Select the newly added row to edit these values as needed.
|
| Security Authentication |
javax.naming.Context.SECURITY_AUTHENTICATION
|
| Referral |
javax.naming.Context.REFERRAL
|
| Authoritative |
javax.naming.Context.AUTHORITATIVE
|
The values of the Connection Options section are optional unless your JMS Provider requires authentication information such as a user name and password.
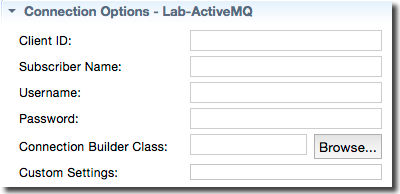
The following table describes the Connection Options properties, which are all string values.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Client ID |
Causes the operator to call javax.jms.Connection.setClientID() with the provided value.
|
| Subscriber Name | Causes a durable subscription to be made and used with the specified subscriber name. This setting is valid only when used in conjunction with destinations that are Topics. |
| Username | The username to use when connecting to the JMS server. |
| Password | The password to use when connecting to the JMS server. |
| Acknowledge Mode | The mode used to acknowledge JMS messages. Defaults to AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE. You can also select DUPS_OK_ACKNOWLEDGE, and for TIBCO EMS only, NO_ACKNOWLEDGE. |
| Connection Builder Class | The fully-qualified name of a class that implements the com.streambase.sb.adapter.common.jms.common. ConnectionBuilderInterface, responsible for creating and initializing JMS Connection objects. If this parameter is not specified, the operator's default implementation is used. |
| Custom Settings | An arbitrary string passed verbatim to the implementer of the CustomConnectionBuilder interface. |
A destination is a queue or a topic on a particular server.
Select a destination name in the Server and Destinations control, which puts the JMS Configuration Editor into its destination editing mode.
Use the Destination Overview section to specify a name for the selected destination, and its Destination Type, either Topic or Queue.

Use the Custom Converter Settings field to enter an
arbitrary string that is to be passed verbatim to the message converter specified in
the Consumer Options or Producer
Options section. Remember that the string you specify here will be stored in
an XML element in the sbd.sbconf file. You must
therefore escape characters that could be interpreted as part of the enclosing XML,
such as < and >.
Escape such characters with double quotes, or by substituting a character entity.
The Timestamp Format control is a drop-down list that
by default has a single entry, defaultTimestampFormat.
This default format string is defined internally as MM/dd/yyyy hh:mm:ss aa. To add your own timestamp
format entries to this drop-down list, use the Timestamp
Formats tab as described in Timestamp Formats Tab above.
The options in the Consumer Options section apply when the currently selected destination is used by a JMS Consumer or EMS Consumer operator.
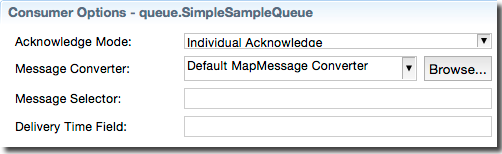
The following table describes the Consumer Options section of each destination's configuration.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Acknowledge Mode |
The mode used to acknowledge JMS messages for the selected destination.
Defaults to Individual Acknowledge. You can also
select Dups OK Acknowledge, Client Acknowledge, or Auto-Acknowledge.
|
| Message Converter |
Specifies how the currently selected destination translates messages into a
tuple. Four predefined message translation types are supported: Default MapMessage Converter (this control's default
selection), Default TextMessage Converter,
Default BytesMessage Converter, and Default Simple Message Converter . You can also select
Custom, in which case you must provide a class
that implements the FromJMSMessageConverter interface.
|
| Message Selector | The message selector expression (if any) to use for this destination. |
| Delivery Time Field | The field in the StreamBase tuple that will be marked with a message's delivery time. |
The options in the Producer Options section apply when the currently selected destination is used by a JMS Producer or EMS Producer operator.
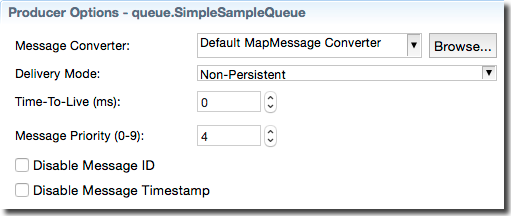
The following table describes the Producer Options section of each destination's configuration.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Message Converter |
Specifies how the currently selected destination translates tuples into JMS
messages. Four predefined message translation types are supported:
Default MapMessage Converter (this control's
default selection), Default TextMessage
Converter, Default BytesMessage
Converter, and Default Simple Message
Converter . You can also select Custom,
in which case you must provide a class that implements the
ToJMSMessageConverter interface.
|
| Delivery Mode |
Messages from JMS Producer operators can be delivered via either of two
delivery modes, Non-Persistent (default) or
Persistent. TIBCO EMS Producer operators have a
third mode available, Reliable Delivery.
|
| Time-To-Live (ms) | Specifies the number of milliseconds to wait after a message is published before destroying the message if it is not yet delivered. The default is zero. |
| Message Priority (0-9) | Specifies the urgency of a message, from 0 (lowest) to 9 (highest). The JMS Provider tries to deliver higher-priority messages before lower-priority ones, but this is not guaranteed. The default setting is 4. |
| Disable Message ID | A JMS provider may be able to reduce message overhead when given a hint that a client does not use message IDs. Select this check box if your application ignores IDs. |
| Disable Message Timestamp | A JMS provider may be able to reduce message overhead when given a hint that a client does not use timestamps. Select this check box if your application ignores timestamps. |
