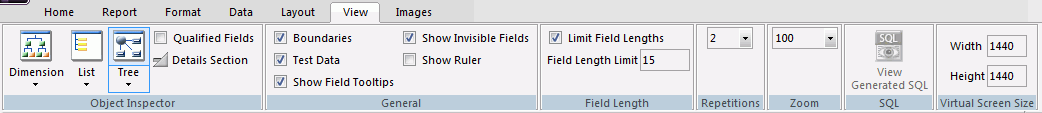
Building a Report Using the Report Tab
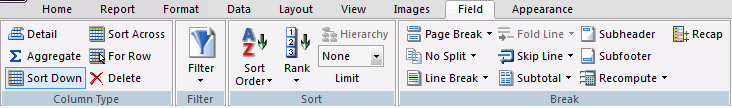
You use the Report tab to modify report properties, change the style of rows and columns on your report, or create filters. The Report tab contains the following groups: Filter, Report, Traffic Lights, Style, and Links. The Report tab is located at the top of the trademark and rebranding WebFOCUS App Studio interface and is available only when you are creating or working with a report. The Report tab is shown in the following image.
Defining a Filter Field Using the Filter Group
|
In this section: |
You use the Filter group to define filter fields when creating a report. The Filter group is shown in the following image.

The commands are:
- Filter
-
Filters fields using Where, If, Where Total, and Limits screening options. You can access the Expression Builder by selecting Where, If, or Where Total from the Filter drop-down menu.
Using the Expression Builder, you can create expressions quickly by selecting fields, relations, operators, and values from lists. You can base selection criteria on a specified value, a variable value, or a field value. For more information, see Creating Expressions Using the Expression Builder.
If you select Limits, the Retrieval Limits dialog box opens, where you can set the record limit and read limit values. This enables you to set how much data is displayed or previewed.
Creating Expressions Using the Expression Builder
|
How to: |
|
Reference: |
The Expression Builder enables you to create expressions quickly by selecting fields, relations, operators, and values from lists. You can base selection criteria on a specified value, a variable value, or a field value.
You can access the Expression Builder by clicking Where, If, or Where Total from the Filter drop-down menu. The Expression Builder dialog box displays.
The Expression Builder is divided into four sections. The Data section is located in the upper-left of the Expression Builder. The Criteria section is located to the lower-left of the Expression Builder. The Expression Grid is located to the upper-right of the Expression Builder. The Advanced section is located in the lower-right of the Expression Builder.
The Data section displays a list of all fields in the data source. Double-click or drag the field into the Expression Grid to build an expression using the options provided. You can also drag fields to the Criteria section and the Advanced section, once it is enabled.
The Criteria section displays which expression you are working on, as well as which expressions, of the same type, you have already created. If you double-click a field and it is added to the Expression Grid, the field will be shown in the Criteria section. Alternatively, you can drag a field into the Criteria section to begin working on a new expression. Dragging more than one field into the Criteria section allows you to create multiple of whatever type of statement you selected (Where, If, or Where Total). For example, if you clicked Where to open the Expression Builder, dragging more than one field into the Criteria section will create multiple Where expressions. Selecting an expression in the Criteria section will show you the details of that expression in the Expression Grid and/or the Advanced section.
Note: The type of expression you are creating is shown next to the Criteria section.
The Advanced section is where, instead of creating an expression using the Expression Grid, you are creating the expression using syntax. The Advanced check box is only available to be selected once a field is in the Criteria or Expression Grid. Once the Advanced check box is selected, the Advanced section, the Function button, and the Variable button are available for use.
The Expression Grid is where you build an expression using the drop-down options available. You can add more fields to the Expression Grid to make a more complex expression by using OR and AND.
Note: If you close the Expression Builder dialog box using the close icon (X), you are prompted to save changes, if changes were made.
Reference: Expression Builder Dialog Box
The Expression Builder dialog box has the following sections:
- Data section
-
Displays a list of all of the fields in the data source. Double-click or drag a field to add it to the Expression Grid.
If the selected field has a title attribute defined in the Master File, the title will be used in the prompt text for the variable. If the selected field does not have a title attribute, the name of the field will be used in the prompt text for the variable.
- Expression Grid
-
Create an expression by using the drop-down menus in correlation with a field.
You can delete expressions from the Expression Grid using the Delete key or right-click Delete option when either the And/Or or Column to filter columns are selected. If you use the Delete key or right-click Delete option on any other column, it will only delete that column option. You can only delete entire expressions, using the Expression Grid, when there are multiple expressions present. If you want to delete a single expression, you must do it from the Criteria section.
- And/Or
-
Displays the keyword used in the expression listed in the Expression list box. You must select more than one field for the expression to activate this option.
- Parentheses
-
Allows you to add one, two, or three parentheses before and after an expression.
- Column to filter
-
The field you clicked or dragged from the Data section. This field can be changed after being added by clicking the drop-down list and selecting a different field.
- Logical Relation
-
Displays a list of possible relations between the selected data source field and the value, parameter, or other field that WebFOCUS will compare it to. Select a relation to activate the Compare Type column.
The following relations are available from the drop-down list:
- equals
- does not equal
- is greater than
- is greater than or equal to
- is less than
- is less than or equal to
- is
- is not
- contains
- does not contain
- matches the pattern
- does not match the pattern
- is like
- is not like
- is missing
- is not missing
- includes
- excludes
- is from
- is not from
- is in literal list
- is not in literal list
- is in external file of literals
- is not in external file of literals
- none
Note: The is and is not relations are only available for an IF statement. The matches the pattern, does not match the pattern, is like, is not like, is in literal list, is not in literal list, is in external file of literals, and is not in external file of literals relations are only available for a WHERE statement.
- Compare Type
-
Indicates the nature of the comparison you wish to make to the field selected in the field section.
The following is a list of the available Compare Types and a brief description of what each is:
- Value is a set value the user creates, using the Multiple or Single Value Builder, in the Compare Value section.
- Field is a selected field the user specifies, using the Multiple or Single Value Builder, from the Compare Value section.
- Parameter (Editor) is a parameter created by the user, using the Variable Editor, in the Compare Value section.
- Parameter (Optional) is a parameter option that allows a user to create a parameter that does not require a value at run time.
- Parameter (Dynamic) is a parameter option that allows a user to multiselect values using a button. This option automatically generates the required syntax so that the Variable Editor does not need to be invoked.
- Parameter (Static) is a parameter option that presents a value list to select from. This option automatically generates the required syntax so that the Variable Editor does not need to be invoked.
- Parameter (Simple) is a parameter option that prompts the user to enter a value. This option automatically generates the required syntax so that the Variable Editor does not need to be invoked.
- Function is a function created by the user, from the Compare Value section, using the Function Arguments dialog box.
- Import Values is a list of values, created by the user, using
the Multiple or Single Value Builder, in the Compare Value section.
Note: The external file should be a text file with new line delimiters.
- Other allows you to enter your own expression.
Note: After choosing Other and double-clicking on Compare Value to enter a value, you will be prompted with the following warning message. You can choose to not show this message again by selecting the option at the bottom of the warning window.
If using a literal value, it must be enclosed in single quotes. Please use "Compare Type" "Value" instead for quotes to be added automatically.
- Compare Value
-
Specifies the literal value, parameter, or other field to which the selected field is compared.
The choices available here are dependent on the selection you make in the Compare Type column.
- Criteria
-
The Criteria section shows the different expressions you created. Selecting an expression in the Criteria section will show you details of the expression in the Expression Grid and/or the Advanced section.
- Advanced check box
-
This option can only be checked if there is an expression in the Criteria or Expression Grid section. This option will enable you to use the Advanced section, the Function button, and the Variable button.
- Advanced section
-
In this section, you can type an expression using syntax, instead of using the Expression Grid.
- Function
-
Only available when Advanced is checked. Opens the Function Arguments dialog box to assist in the creation of an expression that is being made with the Advanced section.
- Variable
-
Only available when Advanced is checked. Opens the Variable Editor dialog box to assist in the creation of an expression that is being made with the Advanced section.
- Delete
-
Deletes an expression.
- Up
-
Moves an expression up one.
- Down
-
Moves an expression down one.
Procedure: How to Display Records Based on Specified Values
In the Expression Builder dialog box:
- Select a field name from the Data section.
The field is added to the Expression Grid.
- Select a relation from the Logical Relation column.
- In the Compare Type column, select Value.
- Double-click the Compare Value column. The Multiple Value Builder dialog box opens.
- Click the Select a field button and select a value from the list.
- Double-click the value to add the value to the list.
Note: Repeat this process to add other values to the list.
- Click OK.
The values are shown in the Compare Value column.
Procedure: How to Display Records Based on a Variable Value
In the Expression Builder dialog box:
- Select a field name from the Data section.
The field is added to the Expression Grid.
- Select a relation from the Logical Relation column.
- In the Compare Type column, select Parameter (Dynamic).
This creates a Single Select parameter. If you want to create a Multiselect parameter, double-click the Compare Value column to open the Variable Editor and change the Variable Type to Multiselect.
Procedure: How to Display Records Based on Field Values
In the Expression Builder dialog box:
- Select a field name from the Data section.
- Select a relation from the Logical Relation column.
- In the Compare Type column, select Field.
- Double-click the Compare Value column to open the Single Value Builder dialog box.
- Double-click a field from the Data Source section to move it to the Value List.
- Click OK to close the Single Value
Builder dialog box.
The field is added to the Compare Value column.
Procedure: How to Display Records Based on Imported Values From an External File
In the Expression Builder dialog box:
- Select a field name from the field list.
The field is added to the Expression Grid.
- Select a relation from the Logical Relation column.
- Select Import Values from the Compare Type list options.
- Double-click the Compare Value column.
The Multiple Value Builder opens.
Note: A Single or Multiple Value Builder dialog box opens, based on your Logical Relation selection. In the Multiple Value Builder dialog box, you may select more than one value. In the Single Value Builder dialog box, only one value may be selected.
- Click the Select File button to import values from an external file.
- Select a text file from your local machine and click Open.
Note: The external file should be a text file with new line delimiters.
The imported values are loaded into the Data Source area of the Multiple Value Builder dialog box.
- Double-click an imported value to add it to the Values List.
- Click OK to close the Multiple
Value Builder dialog box and return to the Expression Builder.
The imported values are added to the Compare Value area.
Procedure: How to Select Multiple Values and Fields
In the Expression Builder dialog box, you can select multiple values or fields to be used for record selection criteria by selecting options in the And/Or column. The And/Or column is only available if you have more than one Column to filter.
- Select more than one field name from the Fields
window and drag them to the Expression Grid.
Note: For every Column to filter after the topmost one, And is already selected for you.
- Click the down arrow in the And/Or column. Select one
of the following:
- And
-
To start a new expression that will be combined with the previous expression by the keyword AND.
- Or
-
To start a new expression that will be combined with the previous expression by the keyword OR.
- Select remaining criteria from the other columns in the Expression Builder to complete the expression.
- Click OK.
When the keyword And is used, WebFOCUS only selects data that meet both conditions. When the keyword Or is used, WebFOCUS selects data that meet either condition.
Reference: Using the Variable Editor Dialog Box
You can use the Variable Editor dialog box to specify attributes for parameter filters, such as the name, prompt, type, and list of values.
To access the Variable Editor dialog box from the Expression Builder, point to Parameter in the Compare Type column and click Editor, right click the compare value for a parameter filter and click Edit, or select the Advanced check box and then click Variable.
The Variable Editor dialog box includes the following options:
- Name. The name of the parameter.
- Prompt. A description for the parameter that appears above it in an Autoprompt form.
- Variable Type. Determines the number of values that can be selected and how they will be handled. The parameter can accept a single value, multiple discrete values, or a range of values.
- Validate Input. When selected, uses .VALIDATE. syntax. The parameter will not pass any values that do not match its format.
- Accept List. Specifies whether the values available for selection are specified explicitly as a static list, retrieved from the data source
as a dynamic list, or retrieved from an ACCEPT list in a data source.
If you select Static list, you can add new values by clicking the New button and clicking Add New Item to type them in, or you can double-click field names or values from the Data Context area.
If you select Dynamic list, you can select a data source and then select a field from that source containing the return and display values for the parameter.
If you select Accept list from file, you can select a data source and a field in that data source from which to accept values. Fields that include an ACCEPT list in the Master File are listed in red. Values in the ACCEPT list will be available for use in the parameter. If there is no ACCEPT list for the selected field, only All Values will be available for selection.
Using Filters in the Autoprompt Page
|
In this section: |
Filters that you define in the Report canvas appear at run time in the autoprompt page. The autoprompt page appears before the report is run and allows users to select the filter values that they want to see in the report.
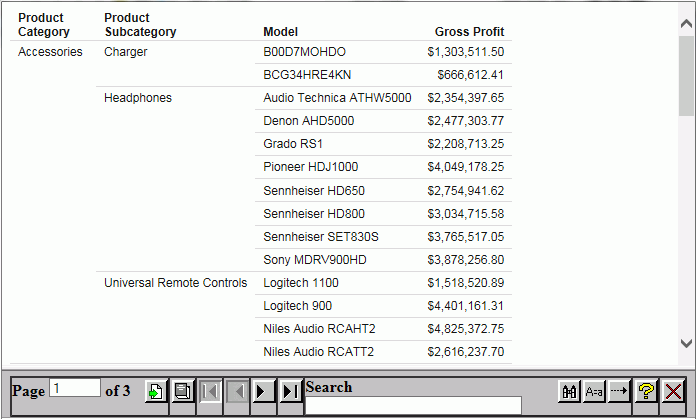
In the example shown in the following image, there is one filter for Product Category, appearing in the Filter Values area. Using the drop-down arrow in the Product Category field, select the product category that you want to see. Accessories is the selected value in the following image.
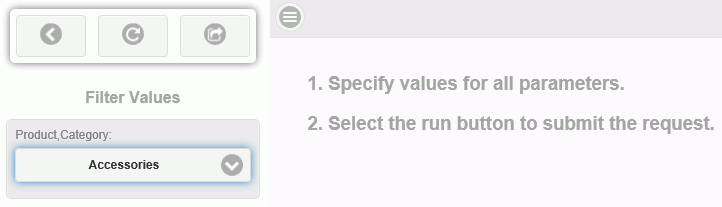
If there were multiple filters, the user would see multiple fields in the Filter Values area.
Using the autoprompt page button bar, you can click:
- Run with filter values. (Rightmost button) To run the report with the values displayed in the filter fields.
- Reset filter values. (Center button) To remove the selected values and display the default values. The default value for a filter is the first valid value, listed alphabetically.
- Close filter panel. (Leftmost button) To hide the autoprompt filter panel.
Additionally, you can toggle the hamburger control on the top of the report to reveal or hide the filter panel.
Chaining Input Controls in the Autoprompt Page
|
How to: |
Chaining lets you link two or more input controls when they call the same dimension hierarchy. For example, if you had chained input controls for State and City, the available list of cities would automatically be limited to those in the specified state. This saves users from scrolling through a list of invalid options when specifying a parameter value.
The Report canvas in WebFOCUS App Studio allows for cascading or chaining input controls in the autoprompt page. Chaining is also available in the HTML canvas. For more information, see Chaining in the HTML Canvas.
Procedure: How to Chain Input Controls in the Autoprompt Page
When you create a report with a dynamic WHERE filter, an input control prompt displays at run time asking the user to select a value. When you have multiple WHERE filters that reference the same dimension hierarchy, the input controls can be chained together, as detailed in the following procedure.
- Open the Report canvas and create a report that has two or more columns showing fields from the same dimension. Position the columns in
the same order in which they appear in the dimension hierarchy.
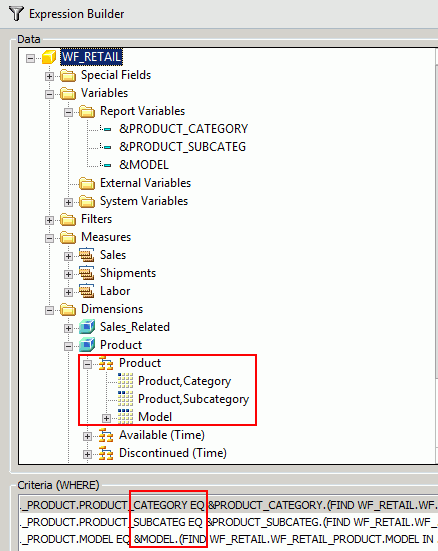
In the example below, we use the Category, Subcategory, and Model fields from the Product dimension of the WF_RETAIL database.
- On the Report tab, click the down arrow under the Filter command and select Where.
The Expression Builder dialog box is opened.
- In the Data area, expand the dimension that you used in your columns. Select the first field (which appears in the first
column) and drag it down to the Criteria (WHERE) window below.
The Column to filter field in the main area of the Expression Builder is automatically populated with the field you selected. In the example below, we selected Category. Complete the main area as follows:
- In the Logical Relation field, select equals.
- In the Compare Type field, select Parameter. From the sub menu, select Dynamic.
The first WHERE filter is complete.
- Repeat Step 3 for the next field, in order, that you want to include in the chain.
In the example below, a second filter for Subcategory and a third filter for Model are created.
Note: To support chaining, the WHERE filters must be created individually, as detailed above, in the correct order. A single WHERE filter that references multiple fields will not support chaining.
The following image shows three WHERE filters that will support chaining for the Product dimension.
- Click OK to close the Expression Builder. Click the Run button on the Quick Access toolbar.
The Autoprompt Filter Values window is displayed.
- Select values for all filters and click the autoprompt Run button.
A report like the following sample is displayed.
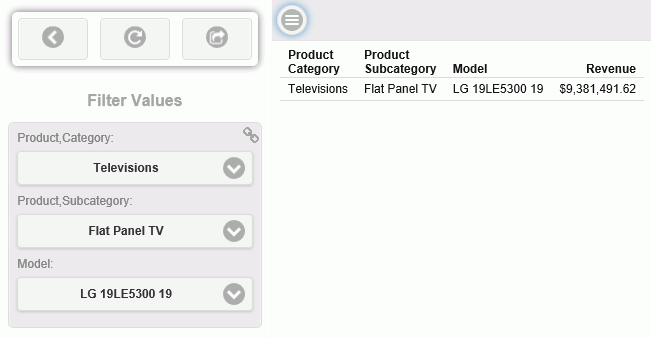
Note the chain icon in the upper right corner of the Filter Values box. This indicates that the input controls are chained.
Using a Calendar Control in the Autoprompt Page
|
How to: |
The Report canvas in WebFOCUS App Studio allows for calendar input controls in the autoprompt page, when you filter on full date fields. The calendar control appears as shown in the following image.
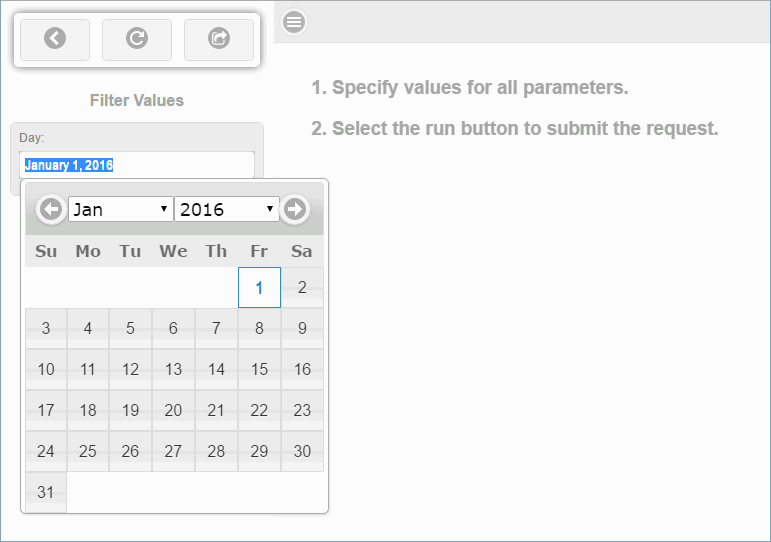
The default date will display in the calendar control in the language that the user used at sign in. The following image shows the filter pane with the default value in French and the calendar control with the month expanded to show the month values are French.
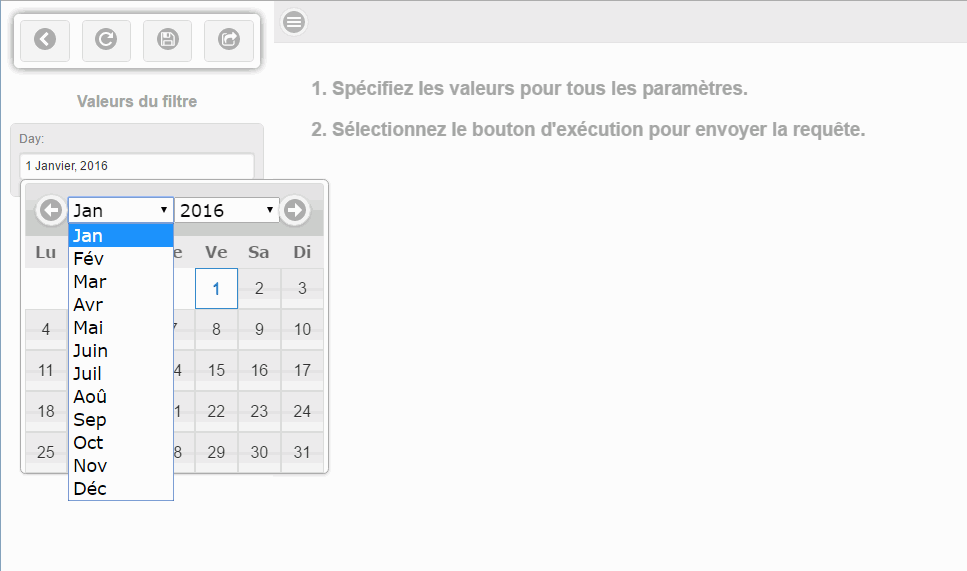
Calendar input controls are also available in the HTML canvas. For more information, see How to Set Calendar Properties.
Procedure: How to Use a Calendar Control in the Autoprompt Page
- Open the Report canvas and create a report that you want to filter by time.
- On the Report tab, click the down arrow under the Filter command and select Where.
The Expression Builder dialog box is opened.
- In the Data area, expand a dimension that includes a full date field. For example, in the WF_RETAIL database, the Sales_Related
dimension includes Transaction (Time). In this hierarchy, Sale,Day has an attribute Sale,Date that you can use to filter
with a calendar control.
Drag the selected field down to the Criteria (WHERE) window.
The Column to filter field in the main area of the Expression Builder is automatically populated with the field you selected.
- In the Logical Relation field, select equals.
- In the Compare Type field, select Parameter. From the sub menu, select Simple.
The WHERE filter is complete. The calendar is enabled by the (|FORMAT=YYMD) syntax which is automatically inserted in this, and all other expressions.
Note: To support the calendar control, the WHERE filter must be created individually, as detailed above. A single WHERE filter that references multiple fields will not support the calendar control.
- Click OK to close the Expression Builder. Click the Run button on the Quick Access toolbar.
The Autoprompt Filter Values window is displayed with the calendar control.
Customizing a Report Using the Report Group
|
In this section: |
|
How to: |
You use the options on the Report tab, in the Report group, to customize your reports. For example, you can add a header and footer to your report and include column and row totals. You can also sort the data on your report. The Report group is shown in the following image.
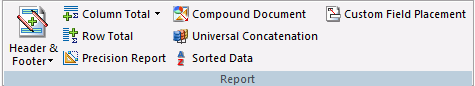
The commands are:
- Header & Footer
-
Adds a header, footer, or both to your report. You can define a Report Header, Page Header, Page Footer, or Report Footer. For more information, see Adding a Header and Footer.
- Column Total
-
Displays a menu of options for column totals:
- No Totals. To show no column totals or to remove existing column totals.
- Column Totals. To display totals below each numeric column.
- Subtotal. To create a subtotal on the table level. In effect, this creates column totals.
- Summarize. To create a summary on the table level. A summary performs calculations any again on total aggregated field values instead of simply summing calculated values, which is useful for reports that contain COMPUTE fields.
- Recompute. To create a recompute on the table level. A recompute performs calculations any again on total aggregated field values instead of simply summing calculated values, which is useful for reports that contain COMPUTE fields. When applied to the entire table, Recompute and Summarize behave the same.
For more information, see Adding Totals to a Report.
- Row Total
-
Displays totals to the right of each numeric row.
Row and Column Titles
The default title for columns and rows appears in the reporting canvas as {TOTAL}. At run time, this is automatically translated into the language that you have selected for WebFOCUS App Studio. For example, if you have selected Italian, the title appears as TOTALE. For more information on setting a language, see General Tab.
To specify a different title:
- Right-click the total and select Title (for
row) or Column Title (for columns) from the
shortcut menu.
The Title dialog opens.
- Clear the Default Title check box and type the desired title in the Enter Title field.
- Click OK.
At run time, the title appears as entered. Manual titles are not translated into the language that you have selected for WebFOCUS App Studio.
- Right-click the total and select Title (for
row) or Column Title (for columns) from the
shortcut menu.
-
For more information, see Adding Totals to a Report.
- Precision Report
-
Converts your report to a precision report. For more information, see Accessing the Precision Reports Canvas.
- Compound Document
-
Converts your report to a Compound document. The original report remains unchanged while a copy of that report is placed on the Document canvas.
- Universal Concatenation
-
Retrieves data from unlike data sources in a single request. Opens the Universal Concatenation dialog box, where you can add the additional data sources to concatenate. For more information, see How to Concatenate Data Sources.
- Sorted Data
-
Assumes that the data is already sorted in the database. If the data you are accessing is already in the correct sort order, you can prevent WebFOCUS from resorting it. This feature provides a fast method of retrieving data if it is already stored in the order required for display, and no further sorting is required.
- Custom Field Placement
-
Allows sort fields to be moved from their default location.
Adding a Header and Footer
|
How to: |
The Header & Footer option in the Report group enables you to add a header or footer to your report, as well as to the page. The following options are available from the Header & Footer drop-down list:
- Report Header
- Page Header
- Page Footer
- Report Footer
When you select one of the header or footer options, a text box displays in the appropriate location on the Report canvas. Type your text or right-click inside the Header or Footer text box to select one of the following options in the shortcut menu:
Footing Bottom. Available only in the Page Footer and Report Footer options, it adds a blank line to the bottom of the page or report, as specified.
Page Break. Available only in the Report Header and Report Footer options, it adds a page break either before or after the report, as specified.
Insert Date. Enables you to select the date format.
Insert Spotmarker. Enables you to refine the positioning of a header or footer.
Alignment Grid. Inserts grid lines so you can align text with one or more columns in the report.
Procedure: How to Add Headers and Footers to a Report
The following steps provide details on adding headers and footers to a report.
- On the Home tab, in the Content group, click Report,
or in the Environments Tree panel, right-click the desired folder,
point to New, and click Report.The Report Wizard opens.
- Click Create Report.
- On the Report tab, in the Report group, click Header
& Footer. The following options are available from
the Header & Footer drop-down list:
- Report Header
- Page Header
- Page Footer
- Report Footer
- Select the type of header or footer you would like to
add.A text box is added to the report where you can add the desired text.
Note: You may add ad many of the header and footer types as you like to your report or page.
- Use the Style group on the Report tab to change the font
or placement of each header or footer in relation to the report.
For more information on the Style group, see Applying
a Theme and Style to a Report Using the Style Group.
The following image shows the Report canvas with content added to all four header options.
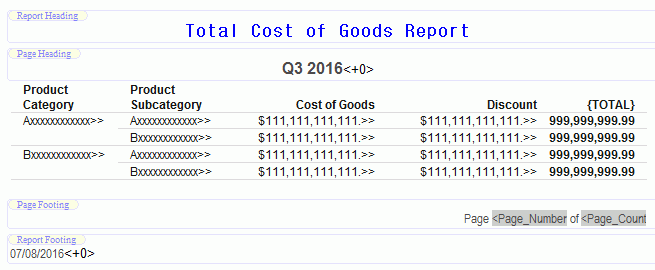
Adding Totals to a Report
|
How to: |
To help interpret detailed information in a report, you can summarize the information using column and row totals, grand totals, and subtotals. You can use these summary lines in a report to clarify or highlight information. You can produce totals for columns or rows of numbers in a report.
- Column Total. Inserts a grand total row at the bottom
of the report to sum numeric data in each column.
On the Report tab, in the Report group, click Column Total. Click the down arrow next to Column Total to launch a menu with the No Totals, Column Totals, and Summarize (for calculated values in your row or column totals) options.
For more information, see How to Create a Report with a Column Total and How to Create a Report with a Column Total on Selected Fields.
- Row Total. Inserts a new column containing the sum of
all numbers in each row.
On the Report tab, in the Report group, click Row Total.
For more information, see How to Create a Report with a Row Total.
You can use column totals and row totals in matrix reports (created by using a BY sort field and an ACROSS sort field in your report request), rename column and row total titles, and include calculated values in your column or row totals. You can also create row totals using ACROSS-TOTAL.
Procedure: How to Create a Report with a Column Total
- On the Home tab, in the Content group, click Report,
or in the Environments Tree panel, right-click the desired folder,
point to New, and click Report.
The Report Wizard opens.
- Click Create Report.
- Navigate to where you want to create the new procedure
and select a data source. For example, select wf_retail.mas.
The Report canvas opens.
- Add the following fields to your report in the order
shown. You can double-click the fields in the Object Inspector,
or drag them to the Report canvas.
- Product Category
- Product Subcategory
- Revenue
- Gross Profit.
- On the Home tab, in the Report group, click Column
Total and select Column Totals from
the drop-down menu.
A grand total row is added at the bottom of the report that sums numeric data in each column.
Procedure: How to Create a Report With a Column Total on Selected Fields
- On the Home tab, in the Content group, click Report,
or in the Environments Tree panel, right-click the desired folder,
point to New, and click Report.
The Report Wizard opens.
- Click Create Report.
- Navigate to where you want to create the new procedure
and select a data source. For example, select wf_retail.mas.
The Report canvas opens.
- Add the following fields to your report in the order
shown. You can double-click the fields in the Object inspector,
or drag them to the Report canvas.
- Product Category
- Product Subcategory
- Revenue
- Gross Profit
- On the Report tab, in the Report group, click Column Total,
and select Column Totals Summarize
, or Recompute from the drop-down menu.
A grand total row is added at the bottom of the report that sums numeric data in each column.
- To add column totals to only specific columns in the
report, right-click the Column Total row
and select Options.
The General dialog box opens.
- Select the columns for which you want a column total and click OK.
Procedure: How to Create a Report with a Row Total
- On the Home tab, in the Content group, click Report,
or in the Environments Tree panel, right-click the desired folder,
point to New, and click Rept.
The Rept Wizard opens.
- Click the Create Rept button.
- Navigate to where you want to create the new procedure
and select a data source. F example, select wf_retail.mas.
The Rept canvas opens.
- Add fields to your report. You can double-click the fields
in the Object inspector, or drag them to the Report canvas. For
example, add the fields listed below to your report in the following
order.
- Product Category
- Product Subcategory
- Cost of Goods
- Discount
- On the Report tab, in the Report group, click Row Total.
A grand total column that sums numeric data in each row is added at the far right of the report.

Procedure: How to Concatenate Data Sources
Universal concatenation specifies how to combine data from sources with dissimilar Master Files.
- Create the main request.
This contains all the formatting for the resulting report and names the first file to be concatenated. It also contains all printing and sorting information. The fields printed and the sort fields must exist as real or DEFINE fields in each file.
- On the Report tab, in the Report group, click Universal Concatenation.
The Universal Concatenation dialog box opens.
- Click the Add Source button to
add additional data sources.
The Open File dialog box appears.
- Select a Master File and click OK.
If there are temporary HOLD files associated with the procedure, HOLD files are available from the Open dialog box.
The selected data source is added, showing the Report Field Resolutions and Filters. Additionally, the Define Tool is activated.
Note: If the field names for the selected data source are not the same names and formats as the fields being printed and sorted in the main request, the Universal Concatenation dialog box indicates that you need to define these fields with status icons.
- Create or modify a field for the universal concatenation
with the Define Tool.
- Click the Define button from
the Universal Concatenation toolbar.
or
- Double-click the field name from the Additional Data Sources list.
The Define Tool opens.
Note: The Define Tool opens automatically if the Create all needed fields for a data source when launching the Define tool option is selected. This creates the missing defines for the data source. A message appears before the Define Tool opens, stating which DEFINEs will be created and require expressions, followed by a list of the created DEFINE fields. This option is off by default.
- Create the DEFINE expression using the selected universally concatenated Master File, generating the required DEFINEs for the data source to have the same field names and formats as the fields used in the main request.
- Click OK to close the Define Tool.
The DEFINE expression is written in the procedure ahead of the TABLE request.
- Click the Define button from
the Universal Concatenation toolbar.
- Create selection criteria for the universal concatenation
with a filter.
You may create a filter through a WHERE clause.
- Select the Where/If button to open the Expression Builder.
- To modify or view the filter, double-click the filter expression from the Additional Data Source list to open the Expression Builder.
- Click OK to close the Universal Concatenation dialog box and add the MORE command to the procedure.
Setting Conditional Styling Using the Traffic Lights Group
You use the Traffic Lights group to set styling conditions. The Traffic Lights group is shown in the following image.
- Traffic Lights
-
Sets the current condition for styling and hyperlinks. Options include:
- None. Displays a preview of the report with no visible conditional styling. This is the default.
- Forecast. Lets you apply conditional styling to the predictive analytics shown in a forecast column. For more information, see Overview of Forecasting.
- Add/Edit Conditions. Opens the Condition List dialog box. From this dialog box, you can define new conditions, and then apply styling to them.
The styling you add to a condition appears as a preview in the Report canvas when you select the condition in the Traffic Lights drop-down list box.
For a sample procedure, see How to Use the Traffic Lighting Feature to Set Conditional Styling.
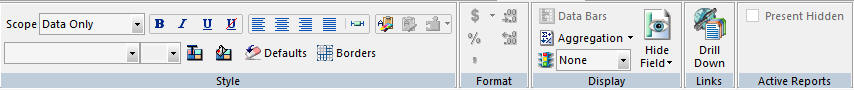
Applying a Theme and Style to a Report Using the Style Group
You use the tools in the Style group to apply stylistic changes to a report, including data, title, and all other components of the report. The Style group is shown in the following image.
This section details the Style group of the Reports tab, which you can use to apply report-level styles. The Style group also appears on the Appearance tab (excluding the Theme commands) which you use to apply field-level styles. For more information, see Styling Data, Titles, and Text Using the Style Group.
The commands are:
- Change Theme
-
Changes the theme of the report from a list of available style sheets.
- Manage Theme
-
References or embeds an external StyleSheet or applies no styling to your report. The WebFOCUS StyleSheet is applied by default. When you click this button, the StyleSheet Selection dialog box opens.
- Save Theme
-
Saves your current theme options.
- Scope
-
Indicates the scope to which your changes will apply. For example, if you choose Report, your style changes will be applied to the whole report. If you choose Footing, your changes will be applied to the footer only. You can use the Scope function to apply styling to different areas of your report. The Scope options available from the Report tab are:
- Report
- Title
- Data
- Report Header
- Report Footer
- Page Header
- Page Footer
- Subhead
- Subfoot
- Subtotal
- Subtotal Tag
- Across Title
- Across Data
- Column Totals
- Column Totals Tag
- Report Totals (Report)
- Report Totals (Title)
- Report Totals (Data)
- Recap
- Cell
- Page Color
- (Selected Item)
Note: The (Selected Item) scope is only available when you select a text or field item. The type of item selected will come before (Selected Item). For example, if you have text selected in the Page Footer, the Scope would display Page Footer (Selected Item).
- Bold
-
Applies bold font formatting to the highlighted text or text within a selected object.
- Italic
-
Applies italic font formatting to the highlighted text or text within a selected object.
- Underline
-
Underlines the highlighted text or text within a selected object.
- No Underline
-
Does not display underlines, even for drilldowns.
- Left
-
Aligns the highlighted text or text within a selected object to the left.
- Center
-
Aligns the highlighted text or text within a selected object to the center.
- Right
-
Aligns the highlighted text or text within a selected object to the right.
- Default
-
Aligns the highlighted text or text within a selected object to the default alignment option. This aligns numbers to the right and text to the left.
- Report Width
-
Sets report width options.
- Copy Style
-
Copies the current style settings, enabling the Paste Style button.
- Paste Style
-
Pastes the copied style settings.
- Font Name
-
Changes the font of the highlighted text or text within a selected object. Fonts are listed in alphabetical order.
- Font Size
-
Changes the font size of the highlighted text or text within a selected object. Font sizes range from 8 to 72 (whole numbers only).
- Color
-
Changes the font color of the highlighted text or text within a selected object. Applies the color change to the selected Scope. Opens the Color dialog box, where you can select the font color.
- Background Color
-
Changes the background color of the highlighted text or text within a selected object. Applies the color change to the selected Scope. Opens the Color dialog box, where you can select the background color.
- Defaults
-
Resets the style settings of the highlighted text or text within a selected object to the default (original) style.
- Borders/Grid
-
Turns on or disables borders and grid lines. You can apply borders and gridlines to HTML, Excel, and PDF reports. For all other report types, this option is disabled.
- User Style
-
Enables you to set User Format Style Blocks, if available.
Referencing or Embedding a Style Sheet Using the StyleSheet Selection Dialog Box
|
How to: |
|
Reference: |
The StyleSheet Selection dialog box enables you to reference or embed an external style sheet, use the default WebFOCUS StyleSheet, or apply no styling to your report. You may also save and include multiple style sheets. The StyleSheet Selection dialog box is accessible from the Style group on the Report canvas ribbon.
The StyleSheet Selection dialog box provides the following capabilities:
- Include a StyleSheet.
- Apply an external cascading style sheet (CSS).
- Embed a StyleSheet.
- Apply the default WebFOCUS StyleSheet.
- Save the modified style sheet as a new style sheet file (.sty).
To open the StyleSheet Selection dialog box, on the Report tab, in the Style Group, click Manage Theme.
Note: The StyleSheet Selection dialog box opens to the Include StyleSheet File section, since every procedure has existing embedded styling, by default. You may click Change Options and choose to embed or reference an external StyleSheet, use the WebFOCUS default StyleSheet, or turn off all report styling, as described in the following procedures.
Procedure: How to Include a StyleSheet in a Report
Since every procedure has existing styling, the Include StyleSheet File section opens, by default.
When a StyleSheet is included, part of the styling is embedded in the report. You may include StyleSheets up to an INCLUDE depth of three in your report, with the last selected StyleSheet having precedence.
- On the Report tab, in the Style group, click Manage
Theme.
The StyleSheet Selection dialog box opens.
- Click the Add new item button.
The Open File dialog box opens.
- Select a StyleSheet file and click OK.
- Optionally, you may select to include additional StyleSheets,
up to an INCLUDE depth of three in your report.
Note: The last selected StyleSheet has precedence in the report. You may use the arrows to reorder the arrangement of StyleSheets.
The following syntax will be added to the procedure for the included StyleSheets.
ON TABLE SET STYLE * INCLUDE = citrus, $ INCLUDE = teal, $ INCLUDE = olive, $ . . . - Click Finish to close the StyleSheet Selection dialog box.
- Optionally, you may apply styling options from the Report canvas and save the StyleSheet code using the Save Theme command, in the Style group, on the Report tab.
Procedure: How to Apply an External Cascading Style Sheet (CSS)
In addition to applying StyleSheets to your report, you may apply an external cascading style sheet to your report. An external cascading style sheet (CSS) is an extension to HTML that enables you to specify formatting for an HTML document. To link the CSS to the report, use the External Cascading Style Sheet URL field in the StyleSheet Selection dialog box.
Note: An external cascading style sheet is only applicable when using the HTML report output format.
- On the Report tab, in the Style group, click Manage
Theme.
The Stylesheet Selection dialog box opens.
- Type a name of the customized StyleSheet (.css) in the External
Cascading StyleSheet URL input field.
Note: The external CSS (cascading style sheet) file should be saved in an alias on the web server.
- Optionally, you may include StyleSheets to be added to
the report.
Note: A CSS file is separate from a StyleSheet file and can exist on its own.
- Click Finish to close the StyleSheet Selection dialog box.
Procedure: How to Embed a StyleSheet in a Report
Embedding a StyleSheet stores your style information within the report, from which you can read an existing file as a starting point, start with an empty style, or leave the current StyleSheet contents without any modifications.
- On the Report tab, in the Style group, click Manage
Theme.
The StyleSheet Selection dialog box opens.
- Click Change Options to change the StyleSheet Selection dialog box options. The StyleSheet Selection dialog box displays.
- Accept the default, Normal Embedded Styling, and click Next.
- To read an existing file as a starting point:
- Select Initialize with the contents
of a pre-existing file.
Note: Preserve referenced StyleSheets so any “INCLUDE=name” will not be deleted is selected, by default. When a StyleSheet is included, a reference of the StyleSheet is added to the report syntax as INCLUDE=name. This reference is added to the existing style information already in the TABLE request.
- Click Next.
The StyleSheet File Selection dialog box appears.
- Select a Predefined Template file to use as your starting
point and click OK.
The selected StyleSheet file is shown as the origin embedded StyleSheet file. Optionally, you may include additional StyleSheets or add an External cascading style sheet (CSS).
- Click Finish to close the StyleSheet Selection dialog box.
The selected StyleSheet code is imported into the procedure and overwrites any existing styling in the report.
- Select Initialize with the contents
of a pre-existing file.
- To start with an empty style:
- Click Change Options to change the StyleSheet Selection dialog box options.
- Keep Normal Embedded Styling selected and click Next.
- Select Start fresh with an empty StyleSheet.
Note: Preserve referenced StyleSheets so any “INCLUDE=name” will not be deleted is selected, by default. When a StyleSheet is included, a reference of the StyleSheet is added to the report syntax as INCLUDE=name. This reference is added to the existing style information already in the TABLE request.
- Click Next.
The Include StyleSheet File section opens indicating that the origin of the embedded StyleSheet file is unknown.
Tip: You may select StyleSheet files to embed to your currently empty style.
- Click Finish to close the StyleSheet Selection dialog box.
- Click OK to close the StyleSheet Selection dialog box.
Starting with an empty style clears any styling from the report and initializes a procedure with the WebFOCUS default style code (basic styling that is used when styling is not specified).
- To leave Report canvas generated styling untouched:
- Click Change Options to change the StyleSheet Selection dialog box options.
- Keep Normal Embedded Styling selected and click Next.
- Select Leave current StyleSheet contents
without modification.
Note: Preserve referenced StyleSheets so any “INCLUDE=name” will not be deleted is selected, by default. When a StyleSheet is included, a reference of the StyleSheet is added to the report syntax as INCLUDE=name. This reference is added to the existing style information already in the TABLE request.
- Click Next.
The Include StyleSheet File section opens indicating that the origin of the embedded StyleSheet file is unknown.
Tip: You may include StyleSheets to be added to the report.
- Click Finish to close the StyleSheet Selection dialog box.
- Optionally, you may apply styling options from the Report canvas and save the StyleSheet code.
Procedure: How to Apply the Default WebFOCUS StyleSheet
The WebFOCUS Default Styling section applies the default StyleSheet to your report, with no styling visible in the procedure.
Note: The default WebFOCUS StyleSheet disables any styling options in the report. No further styling options of any kind can be applied to the report.
- On the Report tab, in the Style group, click Manage
Theme.
The StyleSheet Selection dialog box opens.
- Click Change Options to change the StyleSheet Selection dialog box options.
- Select WebFOCUS Default Styling and
click Finish.
Tip: To remove the default WebFOCUS StyleSheet and enable styling, click the Style File Selection button to open the StyleSheet Selection dialog box and select the Normal Embedded Styling option.
Procedure: How to Reset the Default Report Canvas Styling
To reset the default the Report canvas styling in the StyleSheet Selection dialog box:
- On the Report tab, in the Style group, select Manage
Theme.
The StyleSheet Selection dialog box opens.
- Highlight the added StyleSheet files (.sty) listed in the Include StyleSheet File section and click Delete selected items (Del).
Procedure: How to Save a StyleSheet
After including StyleSheets and applying styling options from the Report canvas, you may save the StyleSheet as a new StyleSheet file (.sty).
- On the Report tab, in the Style group, click Save Theme.
The Save As dialog box opens.
- Type a name for the StyleSheet in the File name input
field and click OK.
The .sty file is saved in the working directory. You may browse to select a different location.
Tip: The saved StyleSheet can be included in other reports from the StyleSheet File Selection dialog box.
Reference: Usage Notes for the StyleSheet Selection Dialog Box
The following apply when using the StyleSheet Selection dialog box in the Report canvas:
- Applying StyleSheets through the StyleSheet Selection dialog box follows the same rules of WebFOCUS StyleSheet inheritance. For details, see WebFOCUS StyleSheet Attribute Inheritance in the Creating Reports With WebFOCUS Language manual.
- When including or referencing a StyleSheet that is not in the
current application, the StyleSheet gets copied to the working directory.
If the StyleSheet already exists in the current application, it does not get overwritten.
To refresh an existing StyleSheet, you must copy the new StyleSheet to the working directory or remove the StyleSheet from the procedure, delete it from the working directory, and then add it back to the procedure.
- The default location for StyleSheets that are Included or referenced in WebFOCUS App Studio is drive:\AppStudionn\ibi_html\javaassist\intl\locale\combine_templates, which contains a set of sample StyleSheets. You can also search other WebFOCUS locations for available StyleSheets.
- When a StyleSheet is used in the procedure and the StyleSheet
Selection dialog box is opened, it opens in the Include StyleSheet
File section, enabling you to change the included StyleSheet. You
may also change the StyleSheet options. This occurs even when the Defaults option
(located in the Style group on the Report canvas ribbon in WebFOCUS App Studio)
is clicked.
Note: If you go back and select to embed or reference a StyleSheet, or use the WebFOCUS default option, the StyleSheet that was in the report will get overwritten.
- If the report does not have any styling, the StyleSheet Selection
dialog box opens to the Change Options section. The report code
contains the command:
ON TABLE SET STYLE OFF
Assigning a Color Value Using the Color Dialog Box
|
How to: |
The Color dialog box lets you choose a color by selecting it from the color palette or entering a hexadecimal value.
Procedure: How to Access the Color Dialog Box
- On the Report tab, in the Style group,
click Color or Background Color.
The Color dialog box displays.
- Click Default to restore the formatting back to its original state.
- Click Custom to access custom coloring.
- Click OK to close the Color dialog box.
Adding Borders to a Report Using the Borders Dialog Box
|
How to: |
You use the Borders dialog box to add borders to your report.
Procedure: How to Add Borders to an HTML, Excel, or PDF Report
You can add borders to an entire report, a column, or another object area, such as a heading or footing.
Note: You must remove grids from the report, column, or object area before you can apply borders.
You can set borders to a report globally, so that they will apply to all objects you subsequently add to the report.
Note: Ensure that HTML, Excel, or PDF is selected as the report output format on the Format tab.
To set global borders:
- On the Report tab, in the Style group, click Borders/Grid and
then click Borders, or right-click the Report canvas area and click Borders.
The Borders dialog box opens.
Note: By default, the Make all borders the same option is selected.
- To specify border settings for the top, bottom, left,
and right borders, click the Make all borders the same check
box to disable that option. Make your border selections:
- Select the following options from the Width drop-down
list:
- OFF to turn borders off. (This is the default.)
- LIGHT to apply thin border lines.
- MEDIUM to apply medium border lines.
- HEAVY to apply thick border lines.
- From the Style drop-down list, select a line style.
- From the Color drop-down list, select a color.
After you select your border width, style, and color selections, you can see them in the Border Preview window in the Borders dialog box.
Note: You can restore the original default borders by clicking the Default button.
- Select the following options from the Width drop-down
list:
- Click OK.
To apply a border to a column:
- Select the column to which you want to apply a border.
- On the Appearance tab, in the Style group, select an option
from the Scope drop-down command. The options are:
- Data and Title applies grids to the column title and data.
- Data Only applies grids to the column data.
- Title Only applies grids to the column title.
- On the Appearance tab, in the Style group, click Borders.
The Borders dialog box opens.
- To specify border settings for the top, bottom, left, and right borders, select the Make all borders the same check box to turn off that option.
- Make your border selections:
- Click the down arrow in
the Width drop-down list box and select:
- OFF to turn borders off. (This is the default.)
- LIGHT to apply thin border lines.
- MEDIUM to apply medium border lines.
- HEAVY to apply thick border lines.
- From the Style drop-down list, select a line style.
- From the Color drop-down list, select a color.
After you select your border width, style, and color selections, you can see them in the Border Preview window in the Borders dialog box.
Note: If the OFF option is selected in the Width drop-down list, no borders will be shown.
- Click the down arrow in
the Width drop-down list box and select:
- Click OK.
To apply a border to cells in a header, footer, subheader, or subfooter:
You can divide a header or footer into cells, which you can align to columns in the report. In PDF, PowerPoint PPTX, and DHTML formats, you can add borders to all header, footer, subheader, or subfooter cells at once.
- On the Format tab, in the Output Types group, click PDF to set the output format to PDF, click PowerPoint and then click PowerPoint PPTX to set the output format to PowerPoint PPTX, or click Output Format, point to Styled report formats, and click DHTML Web Document (DHTML) to set the output format to DHTML.
- Optionally, set output format options in the Output Format Options dialog box.
- Add fields to the report.
- On the Report tab, in the Report group, click Header & Footer and click Report Header, Page Header, Page Footer, or Report Footer, or select a field and, in the Field tab, in the Break group, click Subheader or Subfooter.
- Right-click the header, footer, subheader, or subfooter and click Alignment Grid.
The Insert Alignment Grid dialog box opens.
- Select Align with Data to make the cells in the header, footer, subheader, or subfooter line up with the cells in the report.
- Use the Number of lines option to set the number of rows in the header or footer grid.
- Use the Default justification or Decimal alignment options to specify how text is aligned in each cell.
- On the Report tab, in the Style group, select the header, footer, subheader, or subfooter object that you added a grid to from the Scope menu.
- On the Report tab, in the Style group, click Borders/Grid and then click Borders.
The Borders dialog box opens.
- Select the Border all cells in the grid check box to add the same borders to every cell in the header, footer, subheader, or subfooter grid.
- Make your border selections:
- Click the down arrow in
the Width drop-down list box and select:
- OFF to turn borders off. (This is the default.)
- LIGHT to apply thin border lines.
- MEDIUM to apply medium border lines.
- HEAVY to apply thick border lines.
- From the Style drop-down list, select a line style.
- From the Color drop-down list, select a color.
After you select your border width, style, and color selections, you can see them in the Border Preview window in the Borders dialog box.
Note: If the OFF option is selected in the Width drop-down list, no borders will be shown.
- Click the down arrow in
the Width drop-down list box and select:
- Click OK.
- When you run the report, all of the cells in the header, footer, subheader, or subfooter use the specified borders.
To apply a border to another object area:
- On the Report tab, in the Style group, select
an option from the Scope drop-down command. The options are:
- Report
- Title
- Data
- Report Header
- Report Footer
- Page Header
- Page Footer
- Subhead
- Subfoot
- Subtotal
- Subtotal Tag
- Across Title
- Across Data
- Column Totals
- Column Totals Tag
- Report Totals (Report)
- Report Totals (Title)
- Report Totals (Data)
- Recap
- Cell
- Page Color
- (Selected Item)
- On the Report tab, in the Style group, click Borders/Grid and
then click Borders.
The Borders dialog box opens.
- To specify border settings for the top, bottom, left, and right borders, select the Make all borders the same check box to turn off that option.
- Make your border selections:
- Select the following options
from the Width drop-down list:
OFF to turn borders off. (This is the default.)
LIGHT to apply thin border lines.
MEDIUM to apply medium border lines.
HEAVY to apply thick border lines.
- From the Style drop-down list, select a line style.
- From the Color drop-down list, select a color.
After you select your border width, style, and color selections, you can see them in the Border Preview window in the Borders dialog box.
Note: If the OFF option is selected in the Width drop-down list, no borders will be shown.
- Select the following options
from the Width drop-down list:
- Click OK.
Specifying a Width Limit for a Value Using the Width Options Dialog Box
|
How to: |
The Width Options dialog box allows you to set how values will be handled if they extend the report cell. You can also enter a value to specify a limit for how large or small a value can be before these options take effect.
Procedure: How to Set Width Options for a Report
- On the Report tab, in the Style group,
click Report Width.
The Width Options dialog box displays.
- From the <not set> drop-down
dialog box, select one of the following options:
- Minimum
- Maximum
- Truncate
- Wrap
- Wrap Off
- Indicate a value (in inches) by which to limit the width
of the report.
Note: This only applies to Truncate and Wrap.
- Click OK.
Specifying Styling for User Selected Output Formats Using the User Format Menu
|
How to: |
If the output format for a report is set to user selection, the User Format menu becomes available. You can specify different styling for each available format by expanding the User Format menu, pointing to Create new empty styling block or Copy active styling to, and selecting an output format, as shown in the following image.
Once an output format is selected, styling changes that you make are applied only when that format is selected at run-time. Styling for the General output selection is applied to all output formats for which styling is not explicitly applied.
Selecting a format from the Create new empty style block submenu clears all styling for that for the selected format, including the StyleSheet. You can then style the report for the selected format.
If you point to Copy active styling to and then click an output format, you can copy the styling defined for another output format or for general output. Click the User Format menu, point to Activate style block, and select an output format to make additional changes specific to the selected format.
If you have multiple output format styles defined, you can point to Copy styling from and select an output format to apply the styling from that format to the active output format.
To reset the styling changes made for the active output format, open the User Format menu and click Clear current style block. To remove the specified styling for an output format entirely and instead use the styling specified for the General output type, click Delete current style block.
Procedure: How to Specify Styling for User Selected Output Formats
- Create a report in App Studio.
- On the Format tab, in the Output Types group, click Output Format, point to Styled report formats, and click User.
The User Format Selection dialog box opens.
- Clear the check boxes for any output formats that you do not want to be available at run time. Optionally, click the double-arrows in the Options column to specify output format options for each available format, and change the text that displays in the user selection prompt at run time by changing the text in the Enter text for the WFFMT prompt text box.
- Click OK.
On the Report tab, in the Style group, the User Format menu becomes available. It is initially set to General, allowing you to style the report for any output formats that do not have their own styling explicitly specified.
- Optionally, use the commands in the Style group to style the report for general output.
- Configure separate styling for an available output type using one of the following methods.
- In the User Format menu, point to Create new empty style block and click an output format. The selected output format now uses its own style settings, and currently has not styling characteristics defined. The StyleSheet has also been removed for the selected output format. The selected output format is now active for editing.
- In the User Format menu, point to Copy active styling to and click an output format. The selected output format now uses its own style settings, copied from the styling for the active
output format.
Note: Styling characteristics are copied to the selected output format, but that output format is not active for editing. To activate the selected output format, click the User Format menu, point to Activate style block, and select the output format that you want to edit.
- Optionally, use the commands in the Style group to style the report for the active output format.
- Repeat steps 6 and 7 for any other output formats that you want to have their own unique styling.
- Run the report.
When you run the report with an output format for which you have defined unique styling, that styling is applied. When you run the report with an output format that you did not style separately, the styling characteristics defined for general output are used.
Creating Drill-Down Hyperlinks Using the Drill Down Command
|
In this section: |
|
How to: |
You can use the Drill Down command in the Links group to create hyperlinks in your report. These hyperlinks allow you to see more detail in the ad-hoc reports that are automatically created when you click a link. The Drill Down command is shown in the following image.

The Drill Down command appears in both the Report and the Appearance tabs. The resulting hyperlinks differ, depending on the tab you invoke the command from.
- The Report tab Drill Down command creates hyperlinks in every field in the report.
- The Appearance tab Drill Down command creates hyperlinks only in the fields of the specified column.
Procedure: How to Create Drill-Down Hyperlinks
- On the Report tab (for links in every field) or Appearance tab (for links in a column only),
in the Links group, select Drill Down.
The Drill Down dialog box displays.
- Click the Add new item button
on the Drill Down dialog box toolbar.
The Drill Down fields are enabled.
- In the Drill Down dialog box:
- The Drill Menu Items field is automatically populated with a default drill-down name. You may rename it as needed, or delete the name if you are using only one drill down.
- Select one of the following Drill Down Types from
the drop-down menu:
- Execute Procedure
- Execute Guided Procedure
- URL
- URL from field
- JavaScript
- Refresh BI Portal
Note: The Refresh BI Portal drill-down type will be displayed only when you are working with a report that was created in the Content development area.
- Double-click in the Source field.
- If you selected the Execute Procedure
Drill Down Type, the Open File dialog box opens.
Select the procedure to drill to and click OK.
- If you selected the Execute Guided Procedure Drill Down Type, the Guided DrillDown dialog box opens. For more information, see How to Create a Guided Drill Down Procedure.
- If you selected the URL Drill Down Type, type a fully qualified URL to drill to.
- If you selected the URL from field Drill Down Type, select a source field from the drop-down menu which contains the URL to drill to.
- If you selected the JavaScript Drill Down Type, enter the function to drill to. In the Parameters field (Step 4 below), type the arguments for the function.
- If you selected the Refresh BI Portal Drill Down Type, select Current page only or All pages in portal to refresh when the drill down is triggered.
- If you selected the Execute Procedure
Drill Down Type, the Open File dialog box opens.
- Select a Target Frame from the drop-down menu:
- _blank opens the target procedure in a new window.
- _self opens the target procedure in the same window as the source. This is the default. In addition, it is the only option available if you selected the Refresh BI Portal drill down type.
- _parent opens the target procedure in the same frame as the anchor.
- _top opens the target procedure in the current window.
- Double-click in the Parameters field.
The Parameters dialog box opens.
- Click the Add new item button
on the Parameters dialog box toolbar.
The Parameter fields are enabled.
- In the Parameters dialog box:
- The Parameter Name field may appear, depending on the Drill Down Type you selected. Select a name from the drop-down menu or, if no drop-down menu appears, type a parameter name.
- Select a parameter type from the drop-down list box:
- Field allows you to select a specific field from the Parameter Value drop-down menu.
- Constant Value allows you to specify a constant value for the parameter in the Parameter Value field.
- Variable allows you to specify a variable for the parameter in the Parameter Value field.
- Click OK.
The Parameters dialog box closes and you return to the Drill Down dialog box.
- Click OK.
The Drill Down dialog box closes.
Procedure: How to Create Guided Drill Down Hyperlinks
- On the Report tab (for links in every field) or Appearance tab (for links in a column only), select Drill Down.
The Drill Down dialog box opens.
- Click the Add new item button
on the Drill Down dialog box toolbar.
The Drill Down fields are enabled. The Drill Menu Items field is automatically populated with a default drill-down name. You may rename it as needed, or delete the name if you are using only one drill down.
- In the Drill Down type list, click Execute Guided Procedure.
- Double-click in the Source field.
The Guided DrillDown dialog box opens.
- Click Browse.
The Open File dialog box opens.
- Select the drill-down procedures that you want to use.
To select multiple procedures, hold down the Ctrl key and click the procedures.
- Click OK.
You are returned to the Guided DrillDown dialog box, with the selected procedures displayed in the procedures list box.
- Optionally, use the procedures list box toolbar to change the order of the procedures, undo or redo changes, or delete a procedure from the list.
- To add parameters for a procedure, select it in the procedures
list box, then click Add in the Parameters
list box.
The Drill Down Parameter dialog box opens.
- In the Drill Down Parameter dialog box, do the following:
- Type a parameter name in the Parameter name field.
- To specify a field as a parameter value, select Field and use the drop-down list to select a field from the highlighted procedure.
- To specify a constant value as a parameter value, select Constant value and type the value in the available field.
- To change the wording of the prompt that displays when users select a drill down procedure, type the new wording in the Prompt field.
- Click OK.
You are returned to the Guided DrillDown dialog box.
- Click OK.
You are returned to the Drill Down dialog box.
- In the Drill Down dialog box, select a Target Frame from
the drop-down menu. The available options are:
- _blank opens the target procedure in a new window.
- _self opens the target procedure in the same window as the source.
- _parent opens the target procedure in the same frame as the anchor.
- _top opens the target procedure in the current window.
- Click OK.
The Drill Down dialog box closes.
Creating a PDF Compound Report With Drill Through Links
A common technique in business reporting is to create two related reports:
- Summary Report. Contains condensed information for a category such as a business account, with summed data such as total balances and total sales.
- Detail Report. For specified fields in the associated summary report, a detail report contains all the component values that contributed to each summary field value.
Drill Through provides a way to easily relate the data in these two types of reports. For example, a user scanning a summary report account may see an unusual figure in one of the accounts, requiring examination of the specific data behind that figure.
Drill Through Compound Layout Reports use document syntax declarations to create the compound procedure and define which reports will be related through hyperlinks.
Reference: Drill Through and Drill Down Compared
Using Drill Down, you can construct a summary report in which clicking a hyperlink displays detail data. A Drill Down is implemented dynamically. Clicking a hyperlink causes a new report to run. The detail report typically displays only the detail data for a selected field on the summary report.
In contrast, Drill Through reports are static. Drill Through creates a PDF document that contains the summary report plus the detail report, with the detail report containing all the detail data for designated fields in the summary report. Clicking a Drill Through hyperlink navigates internally in the PDF file. No additional reports are run. You can save the PDF file to disk or distribute it using ReportCaster. When opened with Adobe Reader, it retains its full Drill Through functionality.
Drill Through provides flexibility in the appearance of reports and location of hyperlinks:
- Drill Through hyperlinks may appear in headings and subheadings, as well as, in rows of data.
- You can format the reports using a WebFOCUS StyleSheet.
- You can indicate a hyperlink by color, font, underlining, and so forth.
- You can mix conventional Drill Down hyperlinks freely in the same report with Drill Through hyperlinks.
- The PDF file created with Drill Through can consist of more than two reports.
Reference: Use With Other Features
You can use Drill Through with other WebFOCUS features:
- Compound reports that contain linked Drill Through reports may also contain unrelated reports, before or after the Drill Through reports. For example, you can add to the compound report package a PDF report that contains embedded graphs.
- You can add Drill Down and URL hyperlinks to a PDF report that contains Drill Through hyperlinks.
- Since Drill Through reports are standard PDF compound reports packaged into a single PDF file, you can distribute them using ReportCaster.
- Reports with DRILLTHROUGH syntax can be rendered in all other styled output formats: HTML, PostScript, XLSX, and so on. In these other formats, the DRILLTHROUGH syntax is ignored. It is useful, for example, to generate a PostScript version of a Drill Through report, which is formatted identically to the PDF version, but which you can send directly to a PostScript printer using ReportCaster or operating system commands.
- Drill Through automates the process of navigating quickly and easily from general to specific information in related reports packaged in a single PDF compound report. Drill Through syntax sets up hyperlinks that take you from an item in a summary report to a corresponding item in a detail report.
Procedure: How to Create a Drill Through in a PDF Compound Layout Report
To create a Drill Through in a PDF Compound Layout report:
- Create the summary report with a DRILLTHROUGH hyperlink.
- Create the detail report with sort values that match the hyperlink field values.
- Create the Compound Layout report with page layouts for each component report, and define a DRILLMAP attribute within the calling report to specify the targets of the drill through hyperlinks.
Procedure: How to Create a Drill Through in a PDF Compound Report
To create a Drill Through in a PDF Compound Report:
- Create the summary report.
- Create the detail report.
- Connect the reports with hyperlinks.
- Merge the summary and detail reports into a PDF compound report.
Reference: Usage Notes for Drill Through
- Individual component reports containing Drill Through designations can be run standalone. You will see a warning message in the Message Viewer indicating that outside of the compound report, the Drill Through will not be active.
- Only one Drill Through behavior can be specified per report.
- The field specified to contain a Drill Through behavior must also be present in the target report.
- The originating report containing the Drill Through link must be rendered (by the Reporting Server) prior to the target report. The order of reports must be handled by the user.
- Live Drill Through links are only generated for PDF output. Reports with DRILLTHROUGH syntax can be rendered in all other styled output formats: HTML, PostScript, XLXS, and so on. In these other formats, the DRILLTHROUGH syntax is ignored. It is useful, for example, to generate a PostScript version of a Drill Through report, which is formatted identically to the PDF version, but which you can send directly to a PostScript printer using ReportCaster or operating system commands.
- Drill Through is only supported for reports (TABLE).
Procedure: How to Create the Summary Report (Step 1)
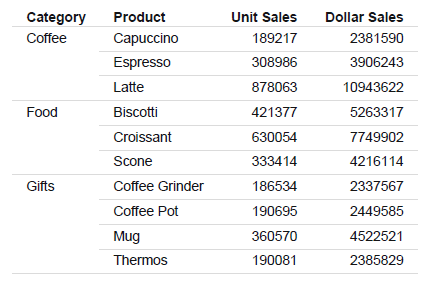
The following procedure generates a sample summary report.
- Create a report in the Report canvas using the GGSALES Master File.
- Add the following fields to your report in the following order. You can double-click the fields in the Object Inspector,
or drag them to the Report canvas.
- Category (By)
- Product (By)
- Units (Sum)
- Dollars (Sum)
- On the Format tab, in the Output Types group, click PDF.
The Output Format Options dialog box opens.
- Optionally, change the output format options, or click OK.
- Save and run the report.
The output is:
Procedure: How to Create the Detail Report (Step 2)
The following procedure generates a sample detail report.
- Create a report in the Report canvas using the GGSALES Master File.
- From the Procedure View, right-click Comment, point to New, and then click Set.
- From the Available Settings pane, select SQUEEZE, click Add, and set Current Value to On.
- Add the following fields to your report in the following order. You can double-click the fields in the Object Inspector,
or drag them to the Report canvas.
- Category (By)
- Product (By)
- Units (Sum)
- Budunits (Sum)
- Dollars (Sum)
- Right-click the Category field and set Invisible to On.
- Right-click the Product field and set Invisible to On.
- Select the Category field, and from the Field tab, in the Break group, set Page-Break to On.
- On the Report tab, in the Header & Footer group, select Page Header.
- Double-click the Page Heading field:
- Type Category:
- From the Object Inspector, double-click the Category field. This inserts the Category value in the heading of the report.
- Press Enter to add a blank line between the heading and the report.
- Right-click and from the Styling toolbar, select Center.
- Select the Product field, and from the Field tab, in the Break group, select Subheader.
- Double-click the Subheading field:
- Type **** Product:
- From the Object Inspector, double-click the Product field. This inserts the Product value in the subheading of the report.
- Select the Product field, and from the Field tab, in the Break group, select Subfooter.
- Double-click the Subfooting field:
- Press Enter to add a blank line between the report and the footer.
- Type <15 **** Return to Summary ****.
- Select the Product field, and from the Field tab, in the Break group, set Page-Break to On.
- Add the Region and City fields, as sort fields, to the report after the Product field.
- On the Format tab, in the Output Types group, click PDF.
The Output Format Options dialog box opens.
- Optionally, change the output format options, or click OK.
- Save and run the report.
The output is:
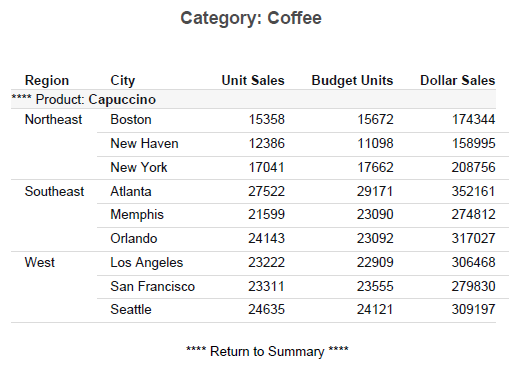
Procedure: How to Create the Summary Hyperlink Report (Step 3)
The following procedures describe how to use the Drill Through feature to create a compound report with a summary and detail report and navigate between them.
The example illustrates the following:
When you place a Drill Through hyperlink on a sort-break element, ensure the sort-break is at least at the level of the last sort field participating in the Drill Through. For example, in the second report, the Drill Through hyperlink is on the subfooting associated with PRODUCT rather than the heading (with a sort break) associated with CATEGORY.
Although the code can infer a value of PRODUCT for the CATEGORY heading (you can verify this by embedding the field <PRODUCT> in the heading), it is always the value of the first PRODUCT within that CATEGORY. Typically you want a Drill Through hyperlink for each value of PRODUCT within each CATEGORY.
You do not need to place the hyperlink on an embedded item. You can just as effectively place it on a text item. Any item in the subfooting is associated with the same values of CATEGORY and PRODUCT. Similarly, you can place a hyperlink on any field in a DATA line, and the values of the associated link fields will be identical. Conventional Drill Down hyperlinks also work this way.
The summary report:
- Places a hyperlink on the PRODUCT field on each DATA line.
- Specifies that the fields to link to the next report are CATEGORY and PRODUCT. Since the target fields in the detail report have identical names in the summary report, you can use the notation CATEGORY rather than CATEGORY=CATEGORY.
- Specifies the action DOWN, so that clicking a hyperlink brings you to the location in the next report that has the corresponding values of the two link fields.
- Uses the default appearance for the hyperlinks, which is blue, underlined text.
- Open the report you created in How to Create the Summary Report (Step 1).
- Select the Product field, and on the Appearance tab, in the Style group, select Data Only from the Scope drop-down menu.
- On the Appearance tab, in the Links
group, select Drill Down.
The Drill Down dialog box displays.
- Click the Add new item button on the
Drill Down dialog box toolbar.
The Drill Down fields are enabled.
- In the Drill Down dialog box:
- From the Drill Down Types drop-down menu, select Drill Through.
- From the Source drop-down menu, select Down.
- Double-click in the Parameters field.
The Parameters dialog box opens.
- Click the Add new item button on the Parameters dialog box toolbar.
The Parameter fields are enabled.
- In the Parameters dialog box:
- From the Parameter Value drop-down menu, select the Category field.
- Click the Add new item button on the Parameters dialog box toolbar.
- From the Parameter Value drop-down menu, select the Product field.
- Click OK.
The Parameters dialog box closes and you return to the Drill Down dialog box.
- Click OK.
The Drill Down dialog box closes.
- Save the report.
Procedure: How to Create the Detail Hyperlink Report
The detail report:
- Places a hyperlink in the subfooting associated with the link field PRODUCT. Since CATEGORY is a higher level BY field than PRODUCT, each PRODUCT subheading is also associated with a unique value of CATEGORY.
- Places a hyperlink on the first item of the second line of the subfooting, which is the text Return to Summary.
- Specifies action FIRST, so that clicking the hyperlink jumps to the line in the first (summary) report that contains the same values of the two link fields CATEGORY and PRODUCT.
- Open the report you created in How to Create the Detail Report (Step 2).
- Select the **** Return to Summary **** line in the Subfoot field.
- On the Report tab in the Links
group, select Drill Down.
The Drill Down dialog box displays.
- Click the Add new item button on the
Drill Down dialog box toolbar.
The Drill Down fields are enabled.
- In the Drill Down dialog box:
- From the Drill Down Types drop-down menu, select Drill Through.
- From the Source drop-down menu, select First.
- Double-click in the Parameters field.
The Parameters dialog box opens.
- Click the Add new item button on the Parameters dialog box toolbar.
The Parameter fields are enabled.
- In the Parameters dialog box:
- From the Parameter Value drop-down menu, select the Category field.
- Click the Add new item button on the Parameters dialog box toolbar.
- From the Parameter Value drop-down menu, select the Product field.
- Click OK.
The Parameters dialog box closes and you return to the Drill Down dialog box.
- Click OK
The Drill Down dialog box closes.
- Save the report.
Procedure: How to Create the Compound Layout Report (Step 4)
Perform this version of Step 4 if you are creating a Compound Layout report.
To create the Compound Layout report:
- Add a COMPOUND LAYOUT and SECTION declaration to the top of the procedure.
- Add PAGELAYOUT and COMPONENT declarations for the two reports. Add DRILLMAP attributes to the COMPONENT declarations.
- Add SET COMPONENT commands and the two reports.
- End the procedure with a COMPOUND END command.
- On the Home tab, in the Content group, click HTML/Document, or in the Environments Tree panel, right-click the desired folder, point to New, and click HTML/Document.
The HTML/Document Wizard opens.
- In the File Type area, select Document.
- Navigate to where you want to select a recent procedure.
Note: If you used the shortcut menu in the Environments Tree panel to create your document, a location is already selected.
- Click Next to set the Document Properties.
The Document Properties dialog box opens.
- From the Output Format list, choose PDF.
- Click Finish.
The Document canvas and Properties panel open.
- Insert a report component.
- Right-click the report and select Reference existing procedure.
- Select the summary procedure and click OK.
- Right-click the Document canvas and select Insert new page after.
- Insert a report component.
- Right-click the report and select Reference existing procedure.
- Select the detail procedure and click OK.
- Select the Summary report and in the Properties panel, select the Detail report for the Drill Through Destination parameter.
- Select the Detail report and in the Properties panel, select the Summary report for the Drill Through Destination parameter.
- Save and run the report.
Procedure: How to Run the Drill Through Report (Step 5)
When you run the drill down report, the first page of output has the summary report with the hyperlinks to the individual products in blue and underlined, as shown in the following image.
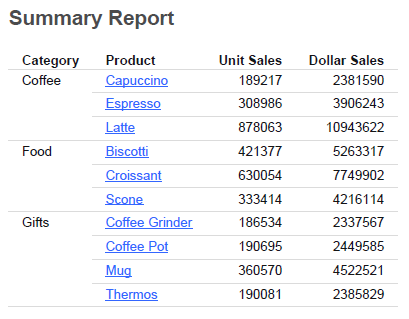
Click the Croissant hyperlink for the Food category. You jump to the detail information. In the detail report, the hyperlink back to the summary report is underlined, as shown in the following image.
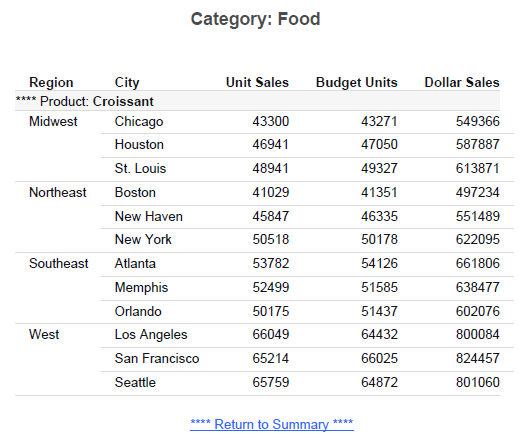
Click the Return to Summary hyperlink to return to the first page (summary report).
Reference: Guidelines on Links For FIRST
The following guidelines apply:
- The set of link fields used with FIRST must correspond to the set of link fields used with DOWN on the first report.
- The action of a FIRST hyperlink in the last report should return to the corresponding line in the first report. The chosen set of links must uniquely identify that line of the first report.
- The DOWN hyperlink on the line of the first report must uniquely identify that line of the first report to locate the matching line of the detail report. The set of links for the DOWN in the first report and the FIRST link in the last report are the same, since they both must uniquely identify a line in the first report.
Reference: Rules For Drill Through Hyperlinks
Reports linked with Drill Through must follow certain rules to ensure that the hyperlinks between them work correctly. The following are key concepts:
- Source report. The report from which you are linking. The source report contains hyperlinks to the target report.
- Target report. The report to which you are linking.
- Link field. One of a set of corresponding fields of the same data type that exist in both the source and target reports. Link fields locate the position in the target report to which a hyperlink in the source report jumps.
Source and target terminology refer to each pair of linked reports. For example, if there are three reports linked with Drill Through, the second report is generally the target report of the first report, and also the source report of the third report.
To process a report as a Drill Through, you must identify the link fields in the source report that relate to the target report:
- Choose meaningful link fields whose values match in the source and target reports. For example, if a field in the source report contains a part number and a field in the target report contains a Social Security number, the field values will not match and you cannot construct hyperlinks.
- Specify as many link fields as necessary to uniquely locate the position in the target report that corresponds to the link fields in the source report. For example, if the source report is sorted by STATE and CITY, specifying CITY alone as the link field will be problematic if different states contain a city with the same name.
- The link fields in the source and target reports must have the same internal (actual) format: the stopped data type and internal length must be identical. Formatting options, such as number of displayed digits and comma suppression, may differ. For example, an A20 field must link to another A20 field. However, an I6C field may link to an I8 field, since internally both are four-byte fields.
- The link fields must be sort fields or verb objects in both the source and target reports. You can include a NOPRINT (non-display) field, which is useful when constructing a report in which a field is in embedded in heading text.
- Designing Drill Through reports is very similar to designing Drill Down reports. Choosing the link fields for a Drill Through report is similar to choosing the parameter fields in a Drill Down report. Likewise, the syntax of a Drill Through closely parallels the syntax of a Drill Down.
- Since Drill Through reports are linked by corresponding values of link fields, the hyperlinks must appear on report elements associated with a particular value of a link field. However, hyperlinks do not have to appear on any link itself.
- Not all line types are appropriate for placement of a Drill Through hyperlink. For example, if a page break occurs on a BY field that is also a Drill Through link, each page heading is clearly associated with a value in that field. However, if a page break occurs because of page overflow, avoid placing a Drill Through link in a heading. Similarly, subheadings, subfootings, subtotals, and recaps are associated only with the values of particular BY fields.