How Is the Data Stored in a Data Grid?
Unlike traditional RDBMS, a data grid is not stored in one place. An ActiveSpaces data grid leverages the storage capacity and computing power from multiple computers.
- Nodes
-
A node is an ActiveSpaces process running within a computer. The node holds a portion of the data forming the data grid both in memory and on disk. The smallest unit of data held by a node is a row. Other than storing data of a row, the node is also responsible for handling requests to read or update the row. As a result, the data spanning across a group of nodes collectively form a data grid.
Nodes can be run from a physical computer, a virtual machine, or a Docker container.
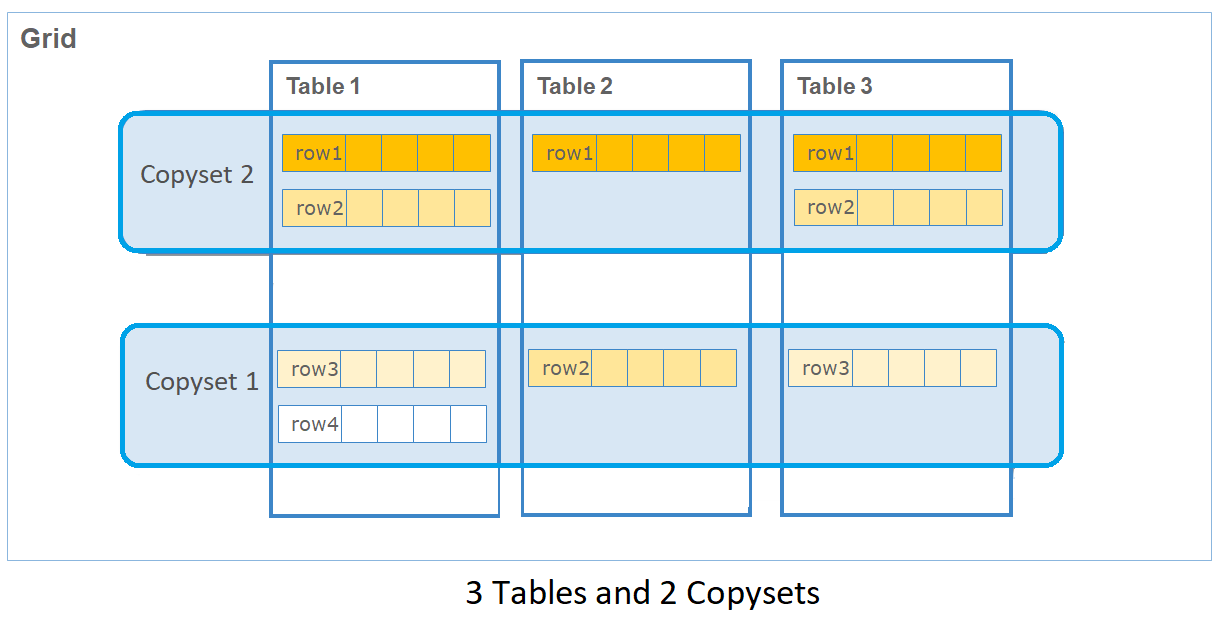
- Copysets
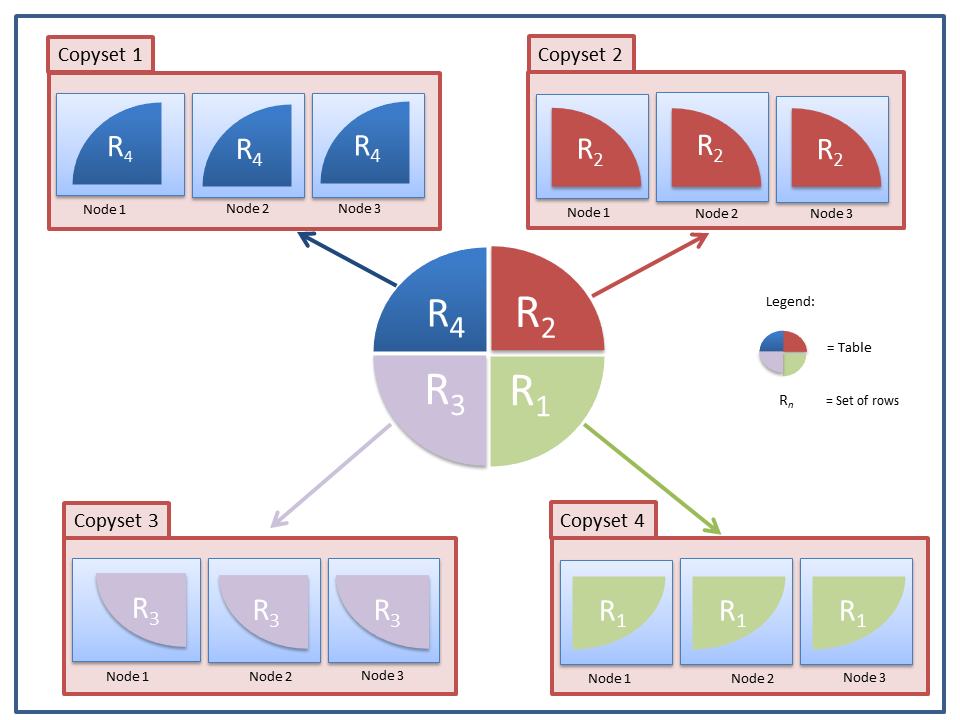
- Copysets are logical grouping of nodes such that a portion of the data is shared uniformly by all the nodes that form a copyset. This ensures fault tolerance. Every node in the copyset, also known as the replica, has an identical copy of the data. For example, assume that a row (R1) comprises employee name, employee ID, and department. There are nodes, N1, N2, and N3 in copyset1. N1, N2, and N3 store identical copies of R1. When you add new data or request for an update on a row in a copyset, the update is written to all the nodes in the copyset before acknowledging the success of the operation. Keeping the nodes of a copyset on different computers helps prevent data loss during system failures.
- Primary Node
- When a copyset has more than one node in a copyset, one of the nodes is the primary node, which stores data and provides read access. The other nodes in the copyset are secondary nodes that store backup copies of the data. The key role of the primary node is to interact with the proxy process. The primary node receives the client operation and replicates it to the other nodes in the copyset. The client operation is applied in parallel at the primary node and all secondary nodes. The primary node is responsible for sharing the result of the request with the proxy.
- Reasons for Using Multiple Nodes
-
There are several reasons for using multiple nodes:
- Nodes in different copysets are created with the goal of scaling horizontally. Thus, multiple copysets are created, each with a slice of the data.
- Nodes in the same copyset are created to provide multiple replicas for fault tolerance. These contain identical copies of the data.
- In a production environment, you might decide to use multiple nodes for a combination of reasons. For example, you might choose to have two replicas per copyset and multiple copysets (say three) to scale horizontally. In this example, your environment would have a total of six nodes.
To sum it up, the data is stored in copysets as described in the previous sections. The copysets put together form a data grid.