Working with Context Parameters
You can retrieve a context parameter from a request or from a response, and set a context parameter in a request or a response.
Distributed File System Example
A distributed file system component manages files based on the host
address of the machine on which the file was created. The address is tracked in
a context parameter named httpHost:
The file system component is invoked by SOAP clients through a service with a SOAP binding and by a web application component.
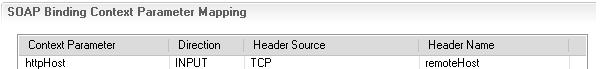
- If a request comes
through the SOAP binding, the context parameter is mapped to the TCP remote
host header by the SOAP binding:
- If the request
originates from the web application, the parameter value is retrieved from the
HTTP request and manually set by the servlet implementing the web application
component:
String host = req.getRemoteHost(); MutableRequestContext mutableRequestContext = componentContext.createMutableRequestContext(); mutableRequestContext.setParameter("httpHost", String.class, host); componentContext.setRequestContext(mutableRequestContext);
The file system component retrieves the value of
the context parameter as follows:
RequestContext requestContext = componentContext.getRequestContext();
String host requestContext.getParameter("httpHost", String.class);
Dynamic Binding Example
Application logic can depend on the value of the application and
service name. In particular, the application logic may be used to dynamically
determine the target of a reference invocation (also referred to as wire by
implementation) in a mediation flow. The following example illustrates how to
retrieve the application and service name in a Java component that invokes a
mediation component service, and set context parameters with that data:
String appName = componentContext.getApplicationName();
String svcname = componentContext.getRequestContext().getServiceName();
MutableRequestContext mutableRequestContext =
componentContext.createMutableRequestContext();
mutableRequestContext.setParameter("ServiceName", java.lang.String.class,
svcname);
mutableRequestContext.setParameter("ApplicationName",
java.lang.String.class, appName);
componentContext.setRequestContext(mutableRequestContext);
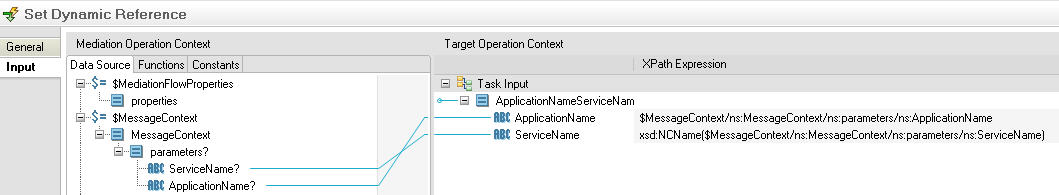
The context parameters are then mapped in the mediation flow's Set
Dynamic Reference task property sheet as follows:
Copyright © Cloud Software Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
