Configure Apache Module for RVRD Setup through a Firewall (DMZ)
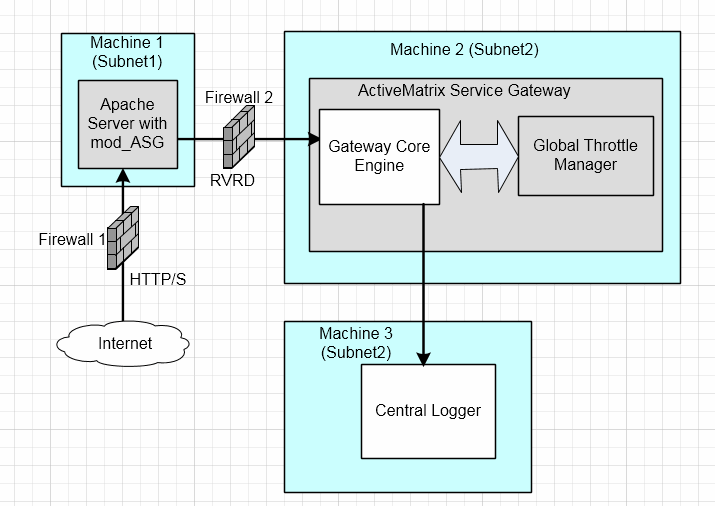
Deployment overview of Apache module in the DMZ setup and other gateway components in a secure network.
By default, the Core Engine uses the TIBCO Rendezvous daemon (rvd) to communicate with the Apache module. The Apache module receives client requests directly from the Internet and performs SSL validation. By placing a firewall between the DMZ (De-Militarized Zone) and the rest of the system, you can protect the system against the threat of malicious communications and provide stronger security.
When the services are exposed to an unsecured network (such as the Internet) it is usual to define different security zones with restricted connections allowed between them. Requests from the outside world are terminated behind a firewall in a de-militarized zone (DMZ). Applications running in the DMZ are not allowed to initiate connections into the more secured zones. In some cases, defense-in-depth is applied and multiple DMZs are used.
TIBCO Rendezvous routing daemon can be configured to forward the Rendezvous messages from the DMZ network through the firewall to the internal network where the TIBCO API Exchange Gateway components are deployed.
This section explains the deployment topology illustrating the deployment of Apache HTTP Server separately in the DMZ and all other gateway components in a secure network. See Figure 5, Apache HTTP Server in DMZ and Other Components in Secure Network.
Rendezvous transport can be configured so that all connections between the Core Engine (asg_core) and the Apache HTTP server are instantiated from the internal secure zone into the DMZ (that is, the server running asg_core).
In this layout only, the authentication is carried out in the DMZ and the minimal possible gateway configuration must be available in the DMZ.