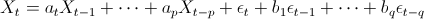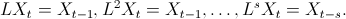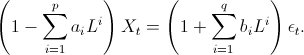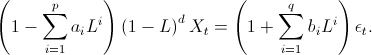ARIMA Time Series (HD)
Applies the ARIMA algorithm to an input time series data set and generates step forecasts for simulation or predictive modeling needs.
Information at a Glance
- Users must specify a column by which to order the time series data.
- The time series column should be evenly spaced, or else the resulting output is inconsistent.
- Users can specify a column to group the time series data by, and the operator applies the algorithm separately to the time series filtered by group.
Example use case applications of this operator include predicting future retail sales, modeling the evolution of financial market prices, forecasting weather trends, and predicting IT server loads.
- Algorithm
-
The ARIMA (AutoRegressive, Integrated, Moving Average) class of time series model is a generalization of the ARMA (AutoRegressive, Moving Average) models.
To understand an ARIMA model, it is necessary to first understand the ARMA model.
An ARMA model of order (p,q) for a time series
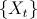 can be written as
can be written as
where p is the order of the autoregressive component, q is the order of the moving average, and the
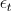 are the error (white noise) terms.
are the error (white noise) terms.
To understand the ARIMA model with integrated part, it is helpful to use the lag operator.
This lag, or backstep, operator L acts on a term in a time series by taking it back one time step:
Then the above ARMA(p,q) model can be written as
We can then introduce an integrated part of order d using a unit root of order d:
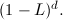
Thus, the full ARIMA(p,d,q) model is given by:
Input
- Bad or Missing Values
- If a row contains a null value in at least one of the Time Series, Column to Order By, or Grouping Column, the row is removed from the data set. The number of null values removed can be listed in the Summary section of the output (depending on the chosen option for Write Rows Removed Due to Null Data To File).
Configuration
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Notes | Any notes or helpful information about this operator's parameter settings. When you enter content in the Notes field, a yellow asterisk is displayed on the operator. |
| Column To Order By |
Define the column by which to order the time series data. Ordering is required to ensure the time series is correctly processed in sequence.
Supported data types: Int, Long, DateTime. |
| Time Series |
Define the column that contains the time series data.
Supported data types: Int, Long, Float, Double. |
| Grouping Column | (Optional) Define the column to use to split the time series data into groups or categories. This is useful when the input data set contains data sampled at the same time, but for multiple groups.
All data types are supported. |
| Include Intercept |
Specify whether the ARIMA model should be fitted with an intercept.
Default value: true. |
| Auto-regressive (p) |
Define the AR order, that is, the degree to which the time series data is to be lagged and regressed on itself.
Range: [0, Int.Max] although it is recommended to keep p < 5. |
| Integrated (d) |
Define the degree of differencing, that is, the number of times the time series data is replaced with the difference between the value of a time step and that of the previous step. This parameter is used to account for time series data that is non-stationary in nature.
Range:[0, Int.Max] although it is recommended to keep d < 5. |
| Moving Average (q) |
Define the MA order, that is, the degree by which the regression error of a time step is a linear combination of errors from previous time steps.
Range:[0, Int.Max] although it is recommended to keep q < 5. |
| Steps Ahead | Define the number of time steps to forecast using the fitted ARIMA model. |
| Write Rows Removed Due to Null Data To File | Rows with null values in at least one of the independent columns or the dependent column are removed from the analysis. This parameter allows you to specify that the data with null values are written to a file.
The file is written to: @default_tempdir/tsds_out/@user_name/@flow_name/@operator_name_uuid/bad_data
|
| Storage Format | Select the format in which to store the results. The storage format is determined by your type of operator.
Typical formats are Avro, CSV, TSV, or Parquet. |
| Compression | Select the type of compression for the output.
Available Avro compression options. |
| Output Directory | The location to store the output files. |
| Output Name | The name to contain the results. |
| Overwrite Output | Specifies whether to delete existing data at that path. |
| Advanced Spark Settings Automatic Optimization |
|
Outputs
- Visual Output
-
The output consists of three tabbed sections: Steps Ahead, Model, and Summary.
- The Steps Ahead tab tabulates ARIMA forecasts for the given input data set and configuration.
- The Model tab tabulates, for each model, the fitted parameters for the AR, MA, and intercept terms, along with other metrics describing the trained time series model.
- The Summary tab displays the parameters selected, a report on null data removal, and the steps ahead and model metrics data set locations in HDFS.
- Data Output
- The Steps Ahead output can be consumed by any operator that processes tabular data sets.