Decision Tree - MADlib
Team Studio supports the MADlib Decision Tree model implementation.
Information at a Glance
For more information about working with decision trees, see Classification Modeling with Decision Tree.
Algorithm
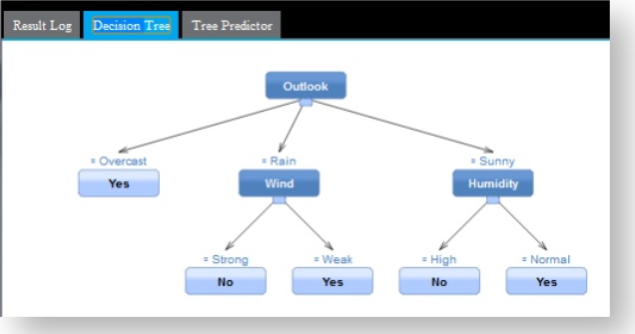
The Decision Tree (MADlib) Operator supports the C4.5 deterministic method for constructing the decision tree structure, allowing users to choose information gain, Gini coefficient, or gain ratio as the split criteria. The MADlib implementation also supports decision tree pruning and missing value handling.
Note that the MADlib Decision Tree is considered an 'Early Stage Development' algorithm.
More information including general principles can be found in the official MADlib documentation.
Configuration
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Notes | Any notes or helpful information about this operator's parameter settings. When you enter content in the Notes field, a yellow asterisk is displayed on the operator. |
| MADlib Schema Name | The schema where MADlib is installed in the database. MADlib must be installed in the same database as the input data set. If a madlib schema exists in the database, this parameter defaults to madlib. |
| Split Criterion | The criterion used to determine the split of the data at each node of the tree. The Split Criterion can be the Information Gain, Gini Coefficient, or Information Gain Ratio. |
| Model Output Schema Name | The name of the schema where the output is stored. |
| Model Output Table Name | The name of the table that is created to store the Regression model. The model output table stores:
id | tree_location | feature | probability | ebp_coeff | maxclass | scv | live | sample_size | parent_id | lmc_nid | lmc_fval | is_continuous | split_value | tid | dp_ids See the official MADlib decision tree documentation for more info. |
| Drop If Exists | |
| Validation Table Name | The table name for a validation data set to score the learned decision tree model against. A ratio of correctly classified items in the validation set is given.
Default value: null (or no validation table). |
| Continuous Features | The user can select the continuous
Independent Variable data columns for the decision tree training.
At least one Continuous Features column or one Categorical Features column must be specified. Click Column Names to open the dialog box for selecting the available columns from the input data set for analysis. |
| Categorical Features | The user can select the categorical
Independent Variable data columns to include for the decision tree training.
At least one Continuous Features column or one Categorical Features column must be specified. |
| Class Column | Required. The data column to be the Dependent Variable. This is the quantity to model or predict. |
| Confidence Level | Specifies the confidence % boundary to use for the pessimistic error algorithm of pruning.
Confidence Level controls the pruning phase of the Decision Tree algorithm.
Default value: 25, representing a 25% probability of there being an error in the leaf node classification set. |
| Handle Missing Values | Specifies how to handle missing values in the data set.
Default value: ignore |
| Maximum Tree Depth | Sets the "depth" of the tree or the maximum number of decision nodes it can branch out to beneath the root node. A tree stops growing any deeper if either a node becomes empty (that is, there are no more examples to split in the current node) or the depth of the tree exceeds this
Maximal Tree Depth limit.
Maximal Tree Depth is used during the tree-growth phase. Values must be greater than 0. Default value: 10 |
| Node Prune Threshold | The minimum percentage of the number of records required in a child node. This threshold applies only to the non-root nodes. |
| Node Split Threshold | Minimum percentage of the number of records required in a node for a further split to be possible. |
| Verbosity | A Boolean value that indicates whether to log all output of the training results. Default: false. |
Additional Notes
- Output Details
-
Connect this operator to the following succeeding operators.
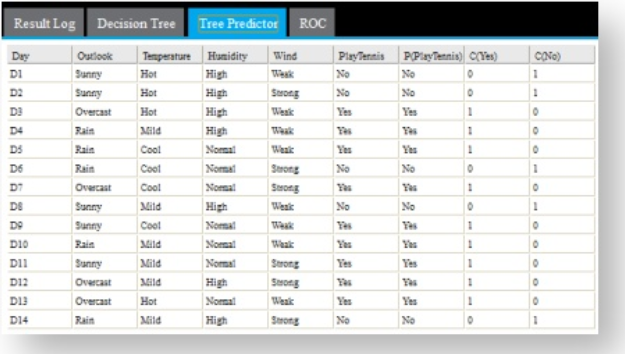
Decision trees need succeeding operators to effectively analyze their effectiveness. A Predictor operator provides the prediction value for each data row, compared against the actual data set training value and the associated confidence level.
Adding additional scoring operators, such as a ROC graph, is also helpful in immediately assessing how predictive the Decision Tree model is. For the ROC graph, any AUC value over .80 is typically considered a "good" model. A value of 0.5 just means the model is no better than a "dumb" model that can guess the right answer half the time.
The output from the Predictor operator appears as follows: