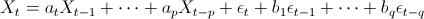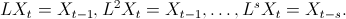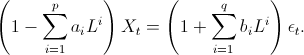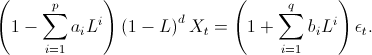ARIMA Time Series (DB)
Applies the ARIMA algorithm to an input time series data set and generates step forecasts for simulation or predictive modeling needs.
Information at a Glance
- Users must specify a column by which to order the time series data.
- The time series column should be evenly spaced, or else the resulting output is inconsistent.
- Users can specify a column to group the time series data by, and the operator applies the algorithm separately to the time series filtered by group.
Example use case applications of this operator include predicting future retail sales, modeling the evolution of financial market prices, forecasting weather trends, and predicting IT server loads.
- Algorithm
-
The ARIMA (AutoRegressive, Integrated, Moving Average) class of time series model is a generalization of the ARMA (AutoRegressive, Moving Average) models.
To understand an ARIMA model, it is necessary to first understand the ARMA model.
An ARMA model of order (p,q) for a time series
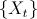 can be written as
can be written as
where p is the order of the autoregressive component, q is the order of the moving average, and the
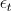 are the error (white noise) terms.
are the error (white noise) terms.
To understand the ARIMA model with integrated part, it is helpful to use the lag operator.
This lag, or backstep, operator L acts on a term in a time series by taking it back one time step:
Then the above ARMA(p,q) model can be written as
We can then introduce an integrated part of order d using a unit root of order d:
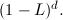
Thus, the full ARIMA(p,d,q) model is given by:
Input
A tabular data set from the preceding operator that contains a column of time series data and a column by which to order the time series data.
- Bad or Missing Values
- If a row contains a null value in at least one of the Time Series, Column to Order By, or Grouping Column, the row is removed from the data set. The number of null values removed can be listed in the Summary section of the output (depending on the chosen option for Write Rows Removed Due to Null Data To File).
Configuration
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Notes | Any notes or helpful information about this operator's parameter settings. When you enter content in the Notes field, a yellow asterisk is displayed on the operator. |
| MADlib Schema | The schema where MADlib is installed in the database. MADlib must be installed in the same database as the input data set. If a "madlib" schema exists in the database, this parameter defaults to madlib. |
| Time Stamp | Choose the column that contains the timestamp data for the ARIMA model. This can be a numeric or datetime type. |
| Time Series | Choose the column to use as the time series. This can be a numeric column with the datatype double. If needed, a preceding Variable operator can be used to convert other numeric types to double. |
| Grouping Columns | Choose a list of column names used to group the input data set into discrete groups, training one ARIMA model per group. It is similar to the SQL GROUP BY clause. When this value is null, no grouping is used and a single result model is generated. |
| Include Mean | The mean value of the data series is added in the ARIMA model if this variable is True. Default value: true. |
| Steps Ahead | Choose the number of steps ahead the ARIMA time series runs. Default value: 20. |
| Autoregressive | The AR parameter ϕ(B). Default value: 1. |
| Integrated | The integrated parameter. Default value: 1. |
| Moving Average | The MA parameter θ(B). Default value: 1. |
| Max Iterations | The maximum number of iterations to run learning algorithm. Default value: 100. |
| Optimizer tau | Computes the initial step size for gradient algorithm. Default value: 0.001. |
| Optimizer e1 | The algorithm-specific threshold for convergence. Default value: 1e-15. |
| Optimizer e2 | The algorithm-specific threshold for convergence. Default value: 1e-15. |
| Optimizer e3 | The algorithm-specific threshold for convergence. Default value: 1e-15. |
| Optimizer Hessian Delta | The delta parameter to compute a numerical approximation of the Hessian matrix. Default value: 1e-6. |
| Output Schema | The schema for the output table or view. |
| Output Table | The table path and name where the results are output. By default, this is a unique table name based on your user ID, workflow ID, and operator. |
| Storage Parameters | Advanced database settings for the operator output. Available only for
TABLE output.
See Storage Parameters Dialog Box for more information. |
| Drop If Exists | Specifies whether to overwrite an existing table. |
Output
- Visual Output
-
The output consists of four tabbed sections: Steps Ahead, Model, Summary, and Residual.
- The
Steps Ahead tab tabulates ARIMA forecasts for the given input data set and configuration.
- The Model tab tabulates, for each model, the fitted parameters for the AR, MA, and intercept terms, along with other metrics describing the trained time series model.
- The Summary tab displays the parameters selected, a report on null data removal, and the steps ahead and model metrics data set locations in HDFS.
- The Residual tab shows the tabular data used to train the model.
- The
Steps Ahead tab tabulates ARIMA forecasts for the given input data set and configuration.
- Data Output
- The
Steps Ahead output can be consumed by any operator that processes tabular data sets.
- Example