T-Test - Paired Samples
Computes a test of statistical significance for two measures of the same data points. This is the same as computing a single sample t-test against the difference between the two columns and a known mean of zero.
Information at a Glance
| Category | Model Validation |
| Data source type | HD |
| Sends output to other operators | Yes |
| Data processing tool | Spark |
The paired samples t-test is used to test whether two responses measured on the same statistical unit are significantly different. Mathematically, it is the same as running a single sample t-test on the delta of the two samples for each row against an assumed mean of 0.0.
For information about Student's t-distribution, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Student%27s_t-distribution
Algorithm
The means and variances for all of the test statistics are computed using Spark's MultivariateStatisticalSummary object, but the t-tests themselves are computed from Java's commons-math library.
Configuration
Output
- Visual Output
- See
Paired Samples T-Test Use Case for example data on a puppy training program that illustrates use of the paired samples t-test. In this case, we see that on average, puppies are not statistically better at the skills test after the training program, since none of the p-values are close to zero.
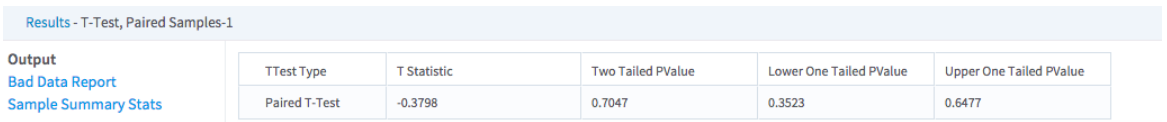
- Data Output
-
- T Statistic - A value computed based on the average and variance. The higher the magnitude of the t-statistic, the higher the difference between the means.
- Two Tailed PValue - The sum of the area under the Students t-distribution above the absolute value of the t-statistic and below the inverse of the t-statistic. A higher value indicates a greater absolute difference in the sample compared. We usually reject the null hypothesis if p < 0.05.
- Lower One Tailed PValue - The area under the Student's t-distribution between negative infinity and the t statistic. A lower p-value indicates that sample a is less than sample b. We usually reject the null hypothesis if p < 0.05.
- Upper One Tailed PValue - The area under the Student's t-distribution between positive infinity and the t statistic. A lower p-value indicates that sample a is greater than sample b. We usually reject the null hypothesis if p < 0.05.

