Decision Tree Classification - CART
Uses the MADlib built-in function tree_train() to generate a decision tree that predicts the value of a categorical column based on several independent columns.
The generated tree is a binary tree, with each node representing either a branching condition or a predicted value. The output of the operator can be sent to a predictor or confusion matrix. MADlib 1.8 or higher must be installed on the database.
Important: This operator does not work with MADlib 1.7.1 or lower, due to a change in the way MADlib handles column names. If you have an older version of MADlib, consider using
Decision Tree - MADlib instead.
For more information about working with decision trees, see Classification Modeling with Decision Tree.
Input
The input table must have a single, categorical (string or integer) column to predict, and one or more independent columns to serve as input.
Configuration
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Notes | Any notes or helpful information about this operator's parameter settings. When you enter content in the Notes field, a yellow asterisk is displayed on the operator. |
| MADlib Schema | Name of schema where MADlib is installed. By default, this is madlib. |
| Model Output Schema | The name of the schema to use for MADlib-generated output tables. |
| Model Output Table | The name of the MADlib-generated output table. This table is generated by the tree trainer. An additional table with the same name and the suffix _summary also is generated. |
| Drop If Exists | |
| ID column | All source tables must have a numeric ID column to uniquely identify each row. |
| Dependent Variable | The name of the numeric column to predict. This must be a floating-point column. |
| Feature List | Click Select Columns to specify one or more columns to use as independent variables to predict the dependent variable. See Select Columns Dialog Box for more information. |
| Split Criterion | The algorithm to use for calculating branch nodes during tree generation. For categorical tables, this must be gini, entropy, or misclassification. The default is gini. |
| Maximum Tree Depth | The generated tree does not exceed this depth. If not specified, the default is 10. |
| Minimum Observations Before Splitting | If not specified, the default is 20. |
| Minimum Observations in Terminal Nodes | If not specified, the default is the minimum observations before splitting, divided by 3. |
| Number of Bins for Split Boundaries | If not specified, the default is 100. |
Outputs
- Visual Output
-
This operator produces the following tabs.
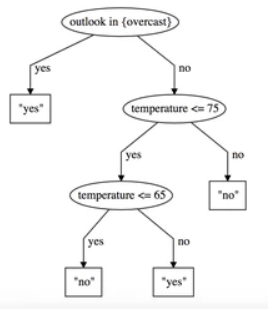
- Decision Tree Text - Contains a text representation of the generated decision tree. Each branch node contains a number of rows and a prediction. Branch nodes also contain a branching condition.
- Decision Tree Graph - Contains a tree graph. Branches reflect split conditions and associated predictions.
Related reference
Copyright © Cloud Software Group, Inc. All rights reserved.