Mapping Users
Mapping resources is an administrative task that will typically be performed before users start using the TIBCO BPM application.
Mapping resources can then be performed on an ongoing basis as resources are added or removed from the system, or if the organization model is revised (new positions, groups, etc.).
Mapping resources involves assigning resources to specific groups and/or positions in an organization model, which results in the resources receiving work items that are sent to the groups/positions to which the resources have been mapped. Resources can be mapped to:
- A
group, which represents a job type within the organization. It allows resources to be grouped by their job characteristics.
Groups can be hierarchical, i.e., you can have parent groups with sub groups. For example, you can have a CustomerServiceRepresentative group with subgroups of MotorInsuranceSpecialist, TravelInsuranceSpecialist, and HomeInsuranceSpecialist. Typically, sub-groups are specializations of the parent group. Groups can be nested several layers deep.
If a group has sub-groups, you can assign resources to either the parent group or the sub-group. Resources that belong to sub-groups receive work items that are offered to their parent groups, as well as to the sub-group to which they belong. Using the example above, resources in the MotorInsuranceSpecialist group will also receive work items offered to the CustomerServiceRepresentative group.
- A
position, which represents a set of responsibilities for a job within an organization unit. It allows resources to be grouped by job responsibility.
Positions are subordinate to an organization unit in the organization model. An organization unit can have many positions. For example, you can have a TravelInsurance organization unit with positions of OfficeManagerTravel and TravelInsuranceCSR. Positions cannot be nested, although organization units can.
Resources can be mapped to positions, but not organization units.
Resources that belong to a position receive work items offered to the position, as well as work items offered to the organization unit that is the immediate parent of the position.
Before a resource can be mapped to group or position, the resource must be created. This is accomplished with the createResource operation. Creating the resource assigns a GUID to that resource.
After being created, a resource can log into an ActiveMatrix BPM application, even if the resource has not been mapped to a group or position yet; the resource would not have access to any work items, however, as work items are only sent to resources mapped to groups or positions.
Also note that you will see references to whether or not a resource exists; a resource exists if it has been created with the createResource operation.
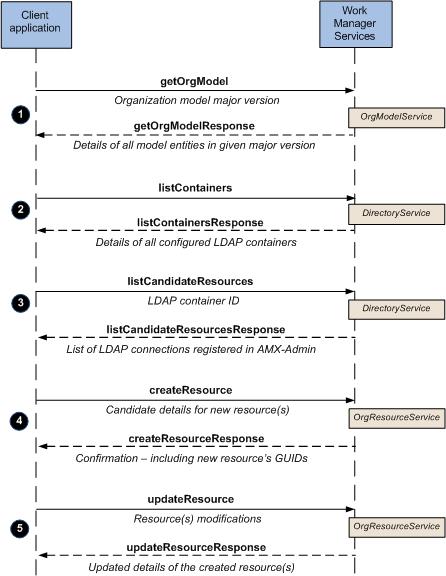
The following diagram shows an example of how calls to the Directory Services APIs can be used to map users.
The following step-by-step descriptions correspond to the numbered steps in the illustration above. Note that the descriptions are from a web service operation point of view, and provide an example of performing the operations using the web service API (SOAP). (For an equivalent example using the Service Connector API (Java), see Mapping a Resource — Service Connector API Example (Java).)