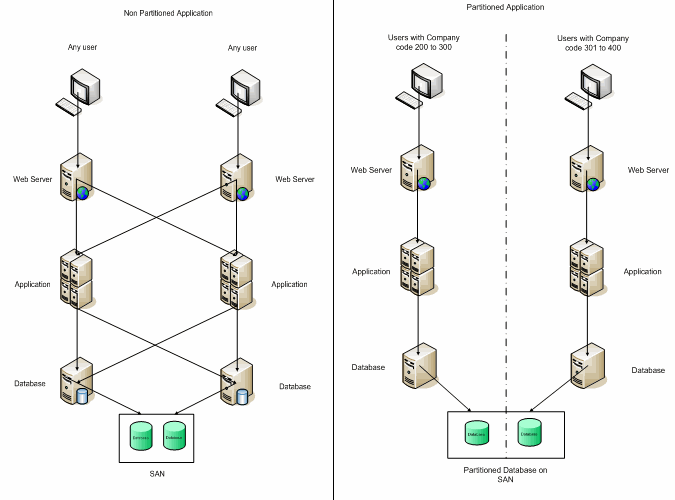
How Partitioning Works
While defining repository metadata, TIBCO MDM identifies one of the attributes as a partitioning key.
Only a single attribute (INTEGER type) can be set as a partitioning key. Based on the partitioning key, the application gets partitioned vertically across the user-specified key.
To take full advantage of partitioning, the application access to TIBCO MDM also needs to be partitioned. For example, if the company_code is used as a partitioning key, all users and JMS messages pertaining to that specific company_code should ideally access only one of the application partitions.
TIBCO MDM takes advantage of Oracle RAC architecture. The underlying data store is accessible to all vertical partitions, but higher performance can be achieved if each partition accesses disjoint sets of records. This allows Oracle RAC to optimally manage the data.
At the same time, as the underlying data store is shared, any access which crosses the partition boundary is allowed, though not as efficient. If a partition fails, failover to another partition can be configured.