Base and Overlay Calendars
There are two kinds of calendars: base and overlay.
These calendar types work together, as follows:
Base calendars
A base calendar defines the normal working hours. It defines which hours in a standard seven-day week are available as working hours, repeating every week throughout the year, but does not map these working hours to specific calendar dates.
Base calendars can also define exceptions to the normal defined working hours. These working-day exclusions do apply to specific dates. For example, a base calendar might define working hours as 08:00 to 17:00 on Mondays to Fridays; but public holidays are not working days, so the calendar might contain an exclusion for 01 January. Exclusions have a defined duration—an exclusion for a public holiday would last all day, while one for a company meeting might last a couple of hours—and may be defined as recurring after a specified interval, such as every week or every month.
A default base calendar, with the name SYSTEM, is provided. This calendar is used when no other calendars apply.
A base calendar specifies the time zone to which it applies.
Overlay calendars
An overlay calendar is applied at runtime on top of the base calendar. An overlay calendar contains only working-day exclusions. These are the same as the exclusions defined in base calendars, in that they apply to specific dates, have a defined duration, and may be defined as recurring.
Overlay calendars do not have a time zone defined, but take the time zone of the base calendar on top of which they are applied.
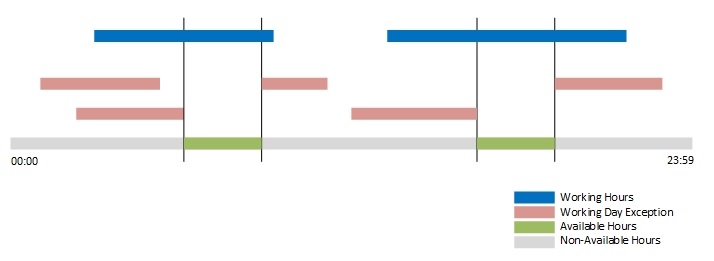
The following illustration shows the effect of combining base and overlay calendars. The working hours defined in the base calendar, and the working day exclusions defined (in this example) in both the base and the overlay calendars, are combined to determine the available working hours.