Specialization and Scalability - Logical Node Distribution
Logical nodes can also be distributed to different physical nodes, to provide specialization and horizontal scalability capabilities according to the enterprise’s needs.
Note: A distributed configuration requires homogenous software configuration. Each member of the cluster must use the same TIBCO ActiveMatrix BPM logical node type.
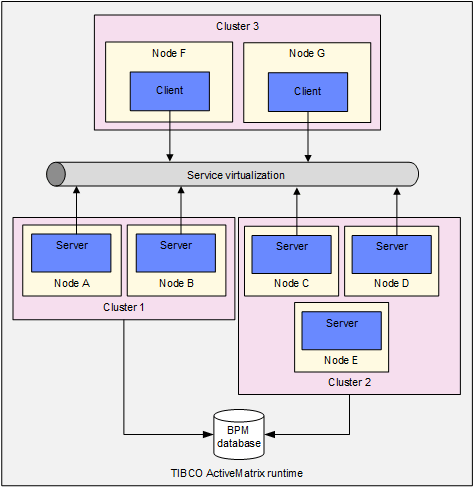
The figure shows an example of a distributed configuration. (For simplicity, host instances are not shown in this figure - each Node is assumed to be running on its own host instance.)
In this example, TIBCO ActiveMatrix BPM is distributed between three sets of clustered machines, Clusters 1, 2 and 3.
- Cluster 1 runs two logical nodes of type Server.
- Cluster 2 runs three logical nodes of type Server.
- Cluster 3 runs two logical nodes of type Client.
Note that:
- The capacity of each part of the system - client or server - can be scaled up or down as requirements change, simply by adding or removing further logical nodes to the relevant cluster (subject of course to the underlying capabilities of the cluster itself).
- Although this example hosts the nodes on individual clusters, it would also be valid to host single or all parts of the system on non-clustered machines.
- Users do not need to be aware of the topology of TIBCO ActiveMatrix BPM when deploying applications. An application is simply deployed to the TIBCO ActiveMatrix BPM runtime, which automatically deploys the relevant parts of the application to all the logical nodes where it is required.
Copyright © Cloud Software Group, Inc. All rights reserved.