Macro (SVB) Programs Example - Customizing Workbooks
Some examples of how to move individual graphs or spreadsheets into a workbook are presented in Accessing Multiple Modules in a Single Program and Opening and Saving Spreadsheets, Graphs. The Workbook object contains a number of properties and methods to edit and customize the appearance and layout of items. Here is an example:
' This program creates a new Workbook; a new ' Folder is then created in the Workbook, and ' named; then a new empty Spreadsheet is ' placed in the Folder, and named. Sub Main ' declare the Variables: a Workbook, a Workbook ' item to which we will assign a new Spreadsheet, ' and a Workbook item, to which we will assign a ' new FolderDim NewWBook As Workbook Dim NewItem As WorkbookItem Dim NewFolder As WorkbookItem ' Create the new WorkbookSet NewWBook=Workbooks.New ' Make it visibleNewWBook.Visible=True ' Create a new SpreadsheetSet NewSSheet=Spreadsheets.New ' Create a new folder, inside the new WorkbookSet NewFolder=NewWBook.InsertFolder(NewWBook.Root,scWorkbookFirstChild) ' Assign a name to the new folderNewFolder.Name="New Workbook Folder" ' Insert the new Spreadsheet into the Workbook, inside ' the new FolderSet NewItem=NewWBook.InsertObject(NewSSheet, NewFolder, ) ' Name the new Workbook item (Spreadsheet)NewItem.Name="This is a new Spreadsheet in the Folder" End Sub
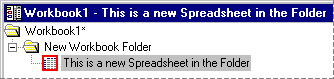
After running this program, the tree structure for the newly created workbook will look like this:
Again, the workbook can be customized by applying the methods and setting the properties associated with this object. The Object Browser will provide a complete listing of these methods and properties.
Copyright © 2021. Cloud Software Group, Inc. All Rights Reserved.